Abstract
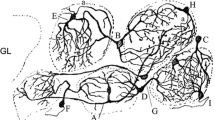
The glomeruli of the olfactory bulb of mammals are the primary coding elements of olfactory information. The excitation pattern produced by individual glomeruli in response to olfactory stimulation is stable and specific to certain odors. First of all, this is due to the structure of the neural circuits of the olfactory bulb. Nevertheless, there is reason to believe that auxiliary cells of the nervous system—astrocytes—play a role in the organization of the primary processing of the olfactory signal. It is known that astrocytes not only have a direct effect on synaptic activity and plasticity, but coordinate the joint work of neuronal circuits and the vascular component, forming so-called “neuro-glio-vascular ensembles” as well. In this study, we carried out a morphological study of peripheral processes and gap junctions of astrocytes in order to study the structure of neuro-glio-vascular ensembles at the level of organization of the olfactory bulb glomeruli neuropil. The study showed that the main part of the astrocytic processes inside the glomeruli is located in the area of dendro-dendritic connections of the interneurons and projection neurons of the olfactory bulb, while in the zone of the primary switching of the olfactory signal, the astrocytic processes are practically absent. We also found a pronounced imbalance in the expression of the main astroglial connexins between the different functional poles of the neuro-glio-vascular ensembles of the olfactory bulb and the presence of heterotypic contacts formed by Cx30. The functional significance of the observed features of connexins expression in the olfactory bulb has yet to be studied.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bailey, M.S. and Shipley, M.T., Astrocyte subtypes in the rat olfactory bulb: morphological heterogeneity and differential laminar distribution, J. Comp. Neurol., 1993, vol. 328, p. 501.
Banker, G.A., Trophic interactions between astroglial cells and hippocampal neurons in culture, Science, 1980, vol. 209, p. 809.
Blinder, P., Tsai, P.S., Kaufhold, J.P., Knutsen, P.M., Suhl, H., and Kleinfeld, D., The cortical angiome: an interconnected vascular network with noncolumnar patterns of blood flow, Nat. Neurosci., 2013, vol. 16, p. 889.
Eilam, R., Aharoni, R., Arnon, R., and Malach, R., Astrocyte morphology is confined by cortical functional boundaries in mammals ranging from mice to human, Elife, 2016, vol. 5. e15915.
Griemsmann, S., Höft, S.P., Bedner, P., Zhang, J., Von Staden, E., Beinhauer, A., Degen, J., Dublin, P., Cope, D.W., Richter, N., Crunelli, V., Jabs, R., Willecke, K., Theis, M., et al., Characterization of panglial gap junction networks in the thalamus, neocortex, and hippocampus reveals a unique population of glial cells, Cerebral Cortex, 2015, vol. 25, p. 3420.
Guerra-Gomes, S., Sousa, N., Pinto, L., and Oliveira, J.F., Functional roles of astrocyte calcium elevations: from synapses to behavior, Front. Cell Neurosci., 2017, vol. 11, p. 427.
Houades, V., Koulakoff, A., Ezan, P., Seif, I., and Giaume, C., Gap junction-mediated astrocytic networks in the mouse barrel cortex, J. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 28, p. 5207.
Kamasawa, N., Sik, A., Morita, M., Yasumura, T., Davidson, K.G.V., Nagy, J.I., and Rash, J.E., Connexin-47 and connexin-32 in gap junctions of oligodendrocyte somata, myelin sheaths, paranodal loops and schmidt-lanterman incisures: implications for ionic homeostasis and potassium siphoning, Neuroscience, 2005, vol. 136, p. 65.
Kasowski, H.J., Kim, H., and Greer, C.A., Compartmental organization of the olfactory bulb glomerulus, J. Comp. Neurol., 1999, vol. 407, p. 261.
Kirichenko, E.Y., Logvinov, A.K., Filippova, S.Y., Povilaytite, P.E., and Kirichenko, Y.G., Gap junctions in the composition of neurogliovascular ensembles in rat cortical barrel columns, Cell Tissue Biol., 2018, vol. 12, no. 6, p. 477.
Leithe, E., Mesnil, M., and Aasen, T., The connexin 43 C‑terminus: a tail of many tales, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2018, vol. 1860, p. 48.
Linster, C. and Cleland, T.A., Glomerular microcircuits in the olfactory bulb, Neural. Netw., 2009, vol. 22, p. 1169.
Mansour, H., McColm, J.R., Cole, L., Weible, M., 2nd, Korlimbinis, A., and Chan-Ling T., Connexin 30 expression and frequency of connexin heterogeneity in astrocyte gap junction plaques increase with age in the rat retina, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, p. e57038.
Nagayama, S., Homma, R., and Imamura, F., Neuronal organization of olfactory bulb circuits, Front. Neural. Circuits, 2014, vol. 8, p. 98.
Nagy, J.I., Patel, D., Ochalski, P.A.Y., and Stelmack, G.L., Connexin30 in rodent, cat and human brain: selective expression in gray matter astrocytes, co-localization with connexin 43 at gap junction and late developmental appearance, Neuroscience, 1999, vol. 88, p. 447.
Nielsen, M.S., Axelsen, L.N., Sorgen, P.L., Verma, V., Delmar, M., and Holstein-Rathlou N.H., Gap junctions, Compr. Physiol., 2012, vol. 2, p. 1981.
Orthmann-Murphy, J.L., Freidin, M., Fischer, E., Scherer, S.S., and Abrams, C.K., Two distinct heterotypic channels mediate gap junction coupling between astrocyte and oligodendrocyte connexins, J. Neurosci., 2007, vol. 27, p. 13949.
Pannasch, U., Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength by controlling astroglial synapse invasion, Nat. Neurosci., 2014, vol. 17, p. 549.
Pérez-Alvarez, A. and Araque, A., Astrocyte-neuron interaction at tripartite synapses, Curr. Drug Targets, 2013, vol. 14, p. 1220.
Rash, J.E., Yasumura, T., Davidson, K.G.V., Furman, C.S., Dudek, F.E., and Nagy, J.I., Identification of cells expressing Cx43, Cx30, Cx26, Cx32 and Cx36 in gap junctions of rat brain and spinal cord, Cell Comm. Adhes., 2001, vol. 8, p. 315.
Ressler, K.J., Sullivan, S.L., and Buck, L.B., Information coding in the olfactory system: evidence for a stereotyped and highly organized epitope map in the olfactory bulb, Cell, 1994, vol. 79, p. 1245.
Roux, L., Benchenane, K., Rothstein, J.D., Bonvento, G., and Giaume, C., Plasticity of astroglial networks in olfactory glomeruli, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2011, vol. 108, p. 18442.
Savtchouk, I. and Volterra, A., Gliotransmission: beyond black-and-white, J. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 38, p. 14.
Wachowiak, M., Denk, W., and Friedrich, R.W., Functional organization of sensory input to the olfactory bulb glomerulus analyzed by two-photon calcium imaging, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2004, vol. 101, p. 9097.
Zeinieh, M.P., Talhouk, R.S., El-Sabban, M.E., and Mikati, M.A., Differential expression of hippocampal connexins after acute hypoxia in the developing brain, Brain Dev., 2010, vol. 32, p. 810.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 19-015-00325.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. Animal keeping and experimental studies were carried out in accordance with the protocol approved by the Bioethics Commission of Southern Federal University on April 18, 2012.
Additional information
Abbreviations: OB—olfactory bulb, NGVE—euro-glio-vascular ensemble, GJ—gap junction; GFAP—glial fibrillar acidic protein.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirichenko, E.Y., Logvinov, A.K., Filippova, S.Y. et al. Structural Features of Neuro-Glio-Vascular Ensembles in the Glomeruli of the Rat Olfactory Bulb. Cell Tiss. Biol. 14, 372–379 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X20050053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X20050053