Abstract
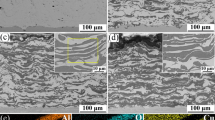
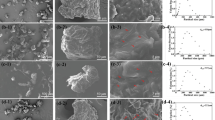
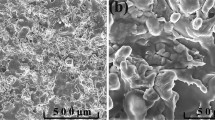
Aluminium-polymethyl methacrylate-copper (Al-PMMA-Cu) composite coatings were developed using cored wire arc spraying. The bacteria Bacillus sp. was used to evaluate the antifouling performances of the coatings. The microstructures and antifouling mechanisms of the coatings were investigated and discussed. The results show that the composite coatings presented improved antifouling performances, and two antifouling mechanisms were explored. On the one hand, the Cu nano-particles were released to seawater due to corrosion of the Al components, converted to cupric ions, and killed the bacteria. Meanwhile, oxidation of Al was accelerated due to Cu-Al galvanic reaction, and the needle-like corrosion products were formed, which pierced the cell membranes and killed the bacteria. The effects of the PMMA on the electrochemical properties of the coatings were also evaluated. The results show that the sealing function of the PMMA components enhanced the corrosion resistance of the Al-PMMA-Cu coatings. This investigation shed light on one-step construction of antifouling and anticorrosion layers for marine applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Yebra, S. Kiil, and K. Dam-Johansen, Antifouling Technology—Past, Present and Future Steps Towards Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings, Prog. Org. Coat., 2004, 50(2), p 75-104
I. Banerjee, R.C. Pangule, and R.S. Kane, Antifouling Coatings: Recent Developments in the Design of Surfaces That Prevent Fouling by Proteins, Bacteria, and Marine Organisms, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(6), p 690-718
O. Sarikaya, S. Anik, S. Aslanlar, S.C. Okumus, and E. Celik, Al-Si/B4C Composite Coatings on Al-Si Substrate by Plasma Spray Technique, Mater. Des., 2007, 28(9), p 2443-2449
F. Ahnia and B. Demri, Evaluation of Aluminum Coatings in Simulated Marine Environment, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2013, 220, p 232-236
X. Wang, H. Zhao, S. Wu, X. Suo, X. Wei, and H. Li, Aluminum-Polyethylene Composite Coatings with Self-sealing Induced Anti-corrosion Performances, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, 282, p 116642
Y. Liu, X. Suo, Z. Wang, Y. Gong, X. Wang, and H. Li, Developing Polyimide-Copper Antifouling Coatings with Capsule Structures for Sustainable Release of Copper, Mater. Des., 2017, 130, p 285-293
Z. Jia, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Gong, P. Jin, X. Suo, and H. Li, Flame Spray Fabrication of Polyethylene-Cu Composite Coatings with Enwrapped Structures: A New Route for Constructing Antifouling Layers, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 309, p 872-879
X. He, X. Suo, X. Bai, C. Yuan, and H. Li, Functionalizing Aluminum Substrata by Quaternary Ammonium for Antifouling Performances, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 440, p 300-307
S. Sharma, Y.A. Jaimes-Lizcano, R.B. McLay, P.C. Cirino, and J.C. Conrad, Subnanometric Roughness Affects the Deposition and Mobile Adhesion of Escherichia coli on Silanized Glass Surfaces, Langmuir, 2016, 32(21), p 5422-5433
S. Hou, H. Gu, C. Smith, and D. Ren, Microtopographic Patterns Affect Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation on Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Surfaces, Langmuir, 2011, 27(6), p 2686-2691
A. Sakamoto, Y. Terui, C. Horie, T. Fukui, T. Masuzawa, S. Sugawara, K. Shigeta, T. Shigeta, K. Igarashi, and K. Kashiwagi, Antibacterial Effects of Protruding and Recessed Shark Skin Micropatterned Surfaces of Polyacrylate Plate with A Shallow Groove, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2014, 361(1), p 10-16
X. Li, G.S. Cheung, G.S. Watson, J.A. Watson, S. Lin, L. Schwarzkopf, and D.W. Green, The Nanotipped Hairs of Gecko Skin and Biotemplated Replicas Impair and/or Kill Pathogenic Bacteria with High Efficiency, Nanoscale, 2016, 8(45), p 18860-18869
D.P. Linklater, N.H.K. Duy, C.M. Bhadra, S. Juodkazis, and E.P. Ivanova, Influence of Nanoscale Topology on Bactericidal Efficiency of Black Silicon Surfaces, Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(24), p 245301
ASTM D1141-98(2003), Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2003.
J.D. Buck and R.C. Cleverdon, The Spread Plate as A Method for The Enumeration of Marine Bacteria, Limnol. Oceanogr., 1960, 5(1), p 78-80
A. Abedini, A. Pourmousa, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Effect of Substrate Temperature on the Properties of Coatings and Splats Deposited by Wire Arc Spraying, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 201(6), p 3350-3358
N. George, M. Mahon, and A. McDonald, Bactericidal Performance of Flame-Sprayed Nanostructured Titania-Copper Composite Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(5), p 1042-1053
K. Bohinc, G. Drazic, R. Fink, M. Oder, M. Jevsnik, D. Nipic, K. Godic-Torkar, and P. Raspor, Available Surface Dictates Microbial Adhesion Capacity, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes., 2014, 50, p 265-272
G. Kear, B.D. Barker, and F.C. Walsh, Electrochemical Corrosion of Unalloyed Copper in Chloride Media—A Critical Review, Corros. Sci., 2004, 46(1), p 109-135
T. Ge, W. Zhao, Y. He, X. Wu, Y. Wu, Y. Wu, and X. Ci, Contrasting the Electrochemical Behaviors of Graphene Film with Hexagonal Boron Nitride Film Before and After Modification with Stearic Acid on Cu in 3.5 wt% NaCl Solution, Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop., 2019, 7(4), p 045008
C. Cervantes and F. Gutierrez-Corona, Copper Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria and Fungi, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 1994, 14(2), p 121-137
P.C. Liu, J.H. Hsieh, C. Li, Y.K. Chang, and C.C. Yang, Dissolution of Cu Nanoparticles and Antibacterial Behaviors of TaN-Cu Nanocomposite Thin Films, Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(17), p 4956-4960
D.W. Green, K.K.H. Lee, J.A. Watson, H.Y. Kim, K.S. Yoon, E.J. Kim, J.M. Lee, G.S. Watson, and H.S. Jung, High Quality Bioreplication of Intricate Nanostructures from A Fragile Gecko Skin Surface with Bactericidal Properties, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), p 41023
W. Yang, J. Li, P. Zhou, L. Zhu, and H. Tang, Superhydrophobic Copper Coating: Switchable Wettability, on-Demand Oil-Water Separation, and Antifouling, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 327, p 849-854
J. Zhang and Y. Han, A Topography/Chemical Composition Gradient Polystyrene Surface: Toward the Investigation of the Relationship Between Surface Wettability and Surface Structure and Chemical Composition, Langmuir, 2008, 24(3), p 796-801
L. Feng, Y. Zhang, Y. Cao, X. Ye, and L. Jiang, The Effect of Surface Microstructures and Surface Compositions on the Wettabilities of Flower Petals, Soft Matter, 2011, 7(6), p 2977-2980
Z. Li and Z. Guo, Bioinspired Surfaces with Wettability for Antifouling Application, Nanoscale, 2019, 11(47), p 22636-22663
C.H. Xue, X.J. Guo, J.Z. Ma, and S.T. Jia, Fabrication of Robust and Antifouling Superhydrophobic Surfaces via Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2015, 7(15), p 8251-8259
J.K. Pi, H.C. Yang, L.S. Wan, J. Wu, and Z.K. Xu, Polypropylene Microfiltration Membranes Modified with TiO2 Nanoparticles for Surface Wettability and Antifouling Property, J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 500, p 8-15
S. Qiu, W. Li, W. Zheng, H. Zhao, and L. Wang, Synergistic Effect of Polypyrrole-Intercalated Graphene for Enhanced Corrosion Protection of Aqueous Coating in 3.5% NaCI, Solution, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(39), p 34294-34304
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [21705158]; the National Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province [2015C01036]; and the International Scientific, Technological Cooperation Project of Ningbo [2016D10012].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, X., Huang, Q. et al. Dual Antifouling Mechanisms Induced by Cupric Ions and Needle-Like Alumina in Arc-Sprayed Composite Coatings. J Therm Spray Tech 29, 1784–1791 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-01076-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-01076-9