Abstract
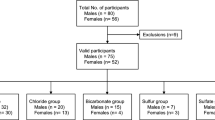
Aim to classify typical hot springs in Guizhou, China and their relevance to health. Assessing geochemical characters of typical hot springs of Guizhou and classifying through hierarchical cluster analysis, an epidemiologic study was conducted to analyze the correlation between hot spring types and health, which showed typical hot springs in Guizhou can be divided into two types, A and B. Type A is rich in fluorine, metasilicic acid, radon components and a large number of essential elements, such as Na, that the human body needs, with trace elements, such as Cr and V, that are essential or possibly essential. Type B is rich in fluorine, metasilicate, strontium components and a large number of essential elements, Ca, Mg, and S, with trace elements, Cu, Mn, Mo, Co, and Ni, that are essential or possibly essential. These hot springs’ effects on the health of those bathing in them showed both types were associated with bone and joint diseases. Having bathed in hot springs during the past year was associated with skin symptoms and bone and joint symptoms, and having bathed within the past two weeks was linked to sleep quality and levels of appetite and energy. However, differences do exist between the correlation between the two types and some chronic diseases, with Type A hot springs significantly related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and diabetes and Type B to hypertension. This classification of Guizhou’s hot springs can guide the future development and use of hot spring physiotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astashina, N. B., Rogozhnikov, G. I., Vladimirskiĭ, E. V., Rogozhnikov, A. G., & Nemenatov, I. G. (2013). The effectiveness of the application of mineral water from the klyuchi health resort in the programs of combined spa-based rehabilitation of the patients presenting with acquired jaw defects. Voprosy Kurortologii Fizioterapii I Lechebnoĭ Fizicheskoĭ Kultury, 14(1), 51–54.
Babaskin, D. V., Babaskina, L. I., & Pavlova, A. V. (2017). The marketing evaluation of the consumers' preference as regards the use of medicinal and medicinal table mineral waters. Voprosy Kurortologii Fizioterapii I Lechebno Fizichesko Kultury, 94(6), 26–31.
Ban, W. T., Duan, X. Q., Yang, Q., & Ding, J. P. (2018). A study of the occurrence law of zonal thermal reservoirs in the Gedong area of Guizhou. Geology and Exploration, 54(2), 0366–0375. (in Chinese).
Birke, M., Rauch, U., & Lorenz, H. (2009). Uranium in stream and mineral water of the Federal Republic of Germany. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31(6), 693–706.
Bundschuh, J., Maity, J. P., Mushtaq, S., Vithanage, M., Seneweera, S., Schneider, J., et al. (2017). Medical geology in the framework of the sustainable development goals. Science of the Total Environment, 581–582, 87–104.
Dai, C., G., Wang, X, H., Chen, J. S., Wang, M., Lu, D. B., Qin, S. R., et al. (2017). Guizhou geological survey regional geology of Guizhou Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese).
Di Marco, M., De Novellis, A. M. P., Carluccio, V., Bozzelli, R., Orlando, M., Lanuti, P., et al. (2019). Short- and long-term beneficial effects of medicinal mineral water administration. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(2), 1–12.
Dutheil, F., Chaplais, E., Vilmant, A., Courteix, D., Duche, P., Abergel, A., et al.(2019). Stress management in obesity during a thermal spa residential programme (ObesiStress): Protocol for a randomised controlled trial study. BMJ Open, 9(12), e027058.
Eva, H., Akter, Q. S., & Alam, M. K. (2020). Relationship between glycemic status and serum chromium level with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mymensingh Medical Journal, 29(1), 183–186.
Forestier, R., Erol, F. F., & Francon, A. (2016). Spa therapy and knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 59(3), 216–226.
Francon, A., & Forestier, R. (2009). Spa therapy in rheumatology. Indications based on the clinical guidelines of the French National Authority for health and the European League Against Rheumatism, and the results of 19 randomized clinical trials. Bulletin De Lacadémie Nationale De Médecine, 193(6), 1356–1358.
Fuge, R., & Johnson, C. C. (1986). The geochemistry of iodine—a review. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 8(2), 31–54.
Gáti, T., Tefner, I. K., Kovács, L., Hodosi, K., & Bender, T. (2018). The effects of the calcium-magnesium-bicarbonate content in thermal mineral water on chronic low back pain: A randomized, controlled follow-up study. International Journal of Biometeorology, 62(5), 897–905.
General administration of quality supervision, inspection and quarantine of the people's Republic of China and national standardization administration of China. (2010). Geologic exploration standard of geothermal resources (GB/T11615–2010).National standards of the People's Republic of China. (in Chinese).
Goovaerts, P. (2014). Geostatistics: A common link between medical geography, mathematical geology, and medical geology. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 114(8), 605–613.
Han, Z. J., & Jin, Z. S. (1996). Hydrogeological records of Guizhou province. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese).
Hanzel, A., Horvát, K., Molics, B., Berényi, K., Németh, B., Szendi, K., et al. (2018). Clinical improvement of patients with osteoarthritis using thermal mineral water at Szigetvar Spa-results of a randomised double-blind controlled study. International Journal of Biometeorology, 62(2), 253–259.
Houston, M. C., & Harper, K. J. (2010). Potassium, magnesium, and calcium: Their role in both the cause and treatment of hypertension. Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 10(7), 3–11.
Jack, L. J. (2019). PCD disseminates public health interventions addressing chronic disease prevention and health promotion. Preventing Chronic Disease, 16, e58.
Karagülle, M., Kardeş, S., Karagülle, O., Dişçi, R., & Karagülle, M. Z. (2017). Effect of spa therapy with saline balneotherapy on oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Biometeorology, 61(1), 169–180.
Kupper, H. (1958). Geology of the mineral springs in Baden. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift, 108(8), 175–176.
Latorre-Román, P., Rentero-Blanco, Á., & M., Laredo-Aguilera, J. A., & García-Pinillos, F., (2015). Effect of a 12-day balneotherapy programme on pain, mood, sleep, and depression in healthy elderly people. Psychogeriatrics, 15(1), 14–19.
Li, C., Chen, Z. S., Wang, G. L., Jin, T. F., Li, Y. K., Luo, T., et al. (2020). Geochemical characteristics and origin of geothermal water in Southeastern Guizhou. Petrology and Geochemistry: Bulletin of Mineralogy. (in Chinese).
Li, J., & Gao, Y. J. (2015). The composition of radioactive radon spring and its application in rehabilitation. World Latest Medicine Information, 15(99), 197. (in Chinese).
Liang, W., Mou, C. L., Zhou, K. K., Ge, X. Y., Chen, C., & Xu, P. H. (2015). Palaeogeography of the cambrian epoch 3-furongian in the middle and upper yangtze region. Journal of Palaeogeography, 17(2), 172–185. (in Chinese).
Lin, N. F., Tang, J., & Bian, J. M. (2004). Geochemical environment and health problems in China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26(1), 81–88.
Linhares, D., Pimentel, A., Borges, C., Cruz, J. V., & Garcia, p., & Rodrigues, A. S., (2019). Cobalt distribution in the soils of São Miguel Island (Azores): From volcanoes to health effects. Science of the Total Environment, 684(2019), 715–721.
Lopalco, M., Proia, A. R., Fraioli, A., Serio, A., Cammarella, I., Petraccia, L., et al. (2004). Therapeutic effect of the association between pulmonary ventilation and aerosol–inhalation with sulphureous mineral water in the chronic bronchopneumopathies. La Clinica Terapeutica, 155(4), 115–120.
Matsumoto, S. (2018). Evaluation of the role of balneotherapy in rehabilitation Medicine. Journal of Nippon Medical School, 85(4), 196–203.
McKenzie, B. L., Santos, J. A., Geldsetzer, P., Davies, J., Manne-Goehler, J., Gurung, M. S., et al. (2020). Evaluation of sex differences in dietary behaviours and their relationship with cardiovascular risk factors: A cross-sectional study of nationally representative surveys in seven low- and middle-income countries. Nutrition Journal, 19(1), 3.
Meng, F. T., & Yang, Y. L. (2015). Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of Jianhe hot spring in GuiZhou. China Mining Magazine, 24(7), 61–65. (in Chinese).
Morer, C., Roques, C. F., Françon, A., Forestier, R., & Maraver, F. (2017). The role of mineral elements and other chemical compounds used in balneology: Data from double-blind randomized clinical trials. International Journal of Biometeorology, 61(12), 2159–2173.
Nakamura, T., Hara, K., Miyagi, N., T., et al. (2019). Dietary calcium intake and hypertension: importance of serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin d. Nutrients, 11(4), 911.
National health committee of the People's Republic of China and state administration of market supervision. (2018). National food safety standard drinking natural mineral water (GB8537–2018). National standards of the People's Republic of China. (in Chinese).
NeÄmark, A. I., Davydov, A. V., & Lebedev, E. V. (1900). Silver-containing hydrocarbonate-calcium-magnesium mineral water in complex treatment of patients with chronic pyelonephritis. Voprosy Kurortologii Fizioterapii I Lechebnoĭ Fizicheskoĭ Kultury, 1900(4), 30–32.
Nuvolone, D., Maggiore, R. D., Maio, S., Fresco, R., Baldacci, S., Carrozzi, L., et al. (2011). Geographical information system and environmental epidemiology: A cross-sectional spatial analysis of the effects of traffic-related air pollution on population respiratory health. Environmental Health, 10(1), 1–12.
Petraccia, L., Liberati, G., Masciullo, S. G., Grassi, M., & Fraioli, A. (2006). Water, mineral waters and health. Clinical Nutrition, 25(3), 377–385.
Rapant, S., Cvečková, V., Dietzová, Z., Fajčíková, K., Hiller, E., Finkelman, R. B., et al. (2014). The potential impact of geological environment on health status of residents of the Slovak Republic. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(3), 543–561.
Rapolienė, L., Razbadauskas, A., Mockevičienė, D., Varžaitytė, L., & Skarbalienė, A. (2020). Balneotherapy for musculoskeletal pain: Does themineral content matter? International Journal of Biometeorology, 64, 965–979.
Rühle, P. F., Klein, G., Rung, T., Phan, H. T., Fournier, C., Fietkau, R., et al. (2019). Impact of radon and combinatory radon/carbon dioxide spa on pain and hypertension: Results from the explorative RAD-ON01 study. Modern Rheumatology, 29(1), 165–172.
Selinus, o., Ajloway, B., Centeno, J. A., Finkelman, R. B., Lindh, U., et al. Translated by Zheng, B. S., et al. (2009). Essentials of medical geology: Impacts of the natural environment on public health. Science Press,139–140. (in Chinese).
Silva, R. A., Rogers, K., & Buckley, T. J. (2018). Advancing environmental epidemiology to assess the beneficial influence of the natural environment on human health and well-being. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(17), 9545–9555.
Song, X. Q., Duan, Q. S., Meng, F. T., & Cao, Z. D. (2014). Geological genesis analysis of the Xifeng hot spring in Guizhou. Geological Science and Technology Information, 33(5), 216–220. (in Chinese).
Sun, X. T., Li, H. J., He, X. Y., Li, M. X., Yan, P. J., Xun, Y. Q., et al. (2019). The association between calcium supplement and preeclampsia and gestational hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hypertens Pregnancy, 38(2), 129–139.
Waheed, S., Rahman, S., Siddique, N., & Faiz, Y. (2013). Calcium supplements as additional source of trace elements in health and disease part 1: Adequacy and safety of chelated calcium supplements. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 298(2), 1453–1461.
Wang, C., Xu, J. Y., Yang, L., Xu, Y. J., Zhang, X. Y., Bai, C. X., et al. (2018). Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in china (the china pulmonary health [cph] study): A national cross-sectional study. Lancet, 391(10131), 1706–1717.
Wilkin, R. T., & Digiulio, D. C. (2010). Geochemical impacts to groundwater from geologic carbon sequestration: Controls on PH and inorganic carbon concentrations from reaction path and kinetic modeling. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(12), 4821–4827.
Xiao, X., Chen, M. L., & B. Y., & Liang, F., (2015). On chemistry characteristics and physiotherapy value of guizhou suiyang crystal spring water. Journal of Southwest China Normal University, 000(001), 129–134. (in Chinese).
Xiao, Z., Zhang, N. D., & Lin, M. (2017). The Chinese medical mineral mpring definition and classification scheme expert consensus. Chinese Journal of Convalescent Medicine, 26(6), 668–672. (in Chinese).
Xu, Y. Y., Huang, H., Zeng, Q. B., Yu, C., Yao, M. L., Hong, F., et al. (2017). The effect of elemental content on the risk of dental fluorosis and the exposure of the environment and population to fluoride produced by coal-burning. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 56, 329–339.
Yamaoka, K., Mitsunobu, F., Hanamoto, K., Shibuya, K., Mori, S., Tanizaki, Y., et al. (2004). Biochemical comparison between radon effects and thermal effects on humans in radon hot spring therapy. Journal of Radiation Research, 45(1), 83–88.
Yao, Z. Y., Cheng, Z. L., & Wang, J. W. (1982). A preliminary environmental geochemical study on the radon springs in Xifeng Guizhou Province. Geochemica, 1, 76–81. (in Chinese).
Zhang, J., He, Y. B., Luo, J. X., Gu, Z. X., Liu, X. F., & Nie, H. Y. (2018). Sedimentary characteristics of middle cambrian gypsum rock in middle-upper yangtze area. China Sciencepaper, 13(3), 28–37. (in Chinese).
Zhang, M. Y., He,Y. L., Wu, W. Y., Chen, Y. F., Zhu, C. M., Zou, Y. Z., et al. (2015). Psychiatric rating scale manual. Hunan Science and Technology Press, 352–358. (in Chinese).
Zhang, S. C. (1994). Basic types and characteristics of thermal mineral water in Guizhou Province. Guizhou Geology, 11(4), 330–333. (in Chinese).
Zhong, C. K., Zhu, Z. B., Wang, A. L., Xu, T., Bu, X. Q., Peng, H., et al. (2019). Multiple biomarkers covering distinct pathways for predicting outcomes after ischemic stroke. Neurology, 92(4), e295–e304.
Acknowledgement
The study was supported by the Geological Exploration Fund Project of Guizhou Province (Grant No.: QGTZZHH[2017]257), Geological Scientific Research Project of the Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Guizhou Province (Grant No.: QDKKH[2019]20), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 41662008), Fundamental Research Project of Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Province, (Grant No.: [2019]1080) and the NSFC Parent Program of Guizhou University (Grant No.: QKHRCPT[2018]5781-46).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Yang, J., Zhu, L. et al. Classification of typical hot springs and their relationship with health in Guizhou, China. Environ Geochem Health 43, 1287–1304 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00724-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00724-x