Abstract
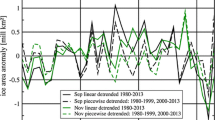
The rapid decrease in Arctic sea ice cover and thickness not only has a linkage with extreme weather in the mid-latitudes but also brings more opportunities for Arctic shipping routes and polar resource exploration, both of which motivate us to further understand causes of sea-ice variations and to obtain more accurate estimates of sea-ice cover in the future. Here, a novel data-driven method, the causal effect networks algorithm, is applied to identify the direct precursors of September sea-ice extent covering the Northern Sea Route and Transpolar Sea Route at different lead times so that statistical models can be constructed for sea-ice prediction. The whole study area was also divided into two parts: the northern region covered by multiyear ice and the southern region covered by seasonal ice. The forecast models of September sea-ice extent in the whole study area (TSIE) and southern region (SSIE) at lead times of 1–4 months can explain over 65% and 79% of the variances, respectively, but the forecast skill of sea-ice extent in the northern region (NSIE) is limited at a lead time of 1 month. At lead times of 1–4 months, local sea-ice concentration and sea-ice thickness have a larger influence on September TSIE and SSIE than other teleconnection factors. When the lead time is more than 4 months, the surface meridional wind anomaly from northern Europe in the preceding autumn or early winter is dominant for September TSIE variations but is comparable to thermodynamic factors for NSIE and SSIE. We suggest that this study provides a complementary approach for predicting regional sea ice and is helpful in evaluating and improving climate models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Årthun M, Eldevik T, Smedsrud L H, et al. 2012. Quantifying the influence of Atlantic heat on Barents Sea ice variability and retreat. Journal of Climate, 25(13): 4736–4743, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00466.1
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E, Bitz C M, Holland M M. 2011. Influence of initial conditions and climate forcing on predicting Arctic sea ice. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(18): L18503
Boisvert L N, Petty A A, Stroeve J C. 2016. The impact of the extreme winter 2015/16 Arctic cyclone on the Barents-Kara Seas. Monthly Weather Review, 144(11): 4279–4287, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-16-0234.1
Borovikov A, Cullather R, Kovach R, et al. 2019. GEOS-5 seasonal forecast system. Climate Dynamics, 53(12): 7335–7361, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3835-2
Bushuk M, Msadek R, Winton M, et al. 2017. Skillful regional prediction of Arctic sea ice on seasonal timescales. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(10): 4953–4964, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL073155
Chevallier M, Salasy Mélia D, Voldoire A, et al. 2013. Seasonal forecasts of the pan-Arctic sea ice extent using a GCM-based seasonal prediction system. Journal of Climate, 26(16): 6092–6104, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00612.1
Cohen J, Screen J A, Furtado J C, et al. 2014. Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather. Nature Geoscience, 7(9): 627–637, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2234
Collow T W, Wang Wanqiu, Kumar A, et al. 2015. Improving Arctic sea ice prediction using PIOMAS initial sea ice thickness in a coupled ocean-atmosphere model. Monthly Weather Review, 143(11): 4618–4630, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-15-0097.1
Comiso J C. 2017. Bootstrap sea ice concentrations from nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS, version 3. [1979–2017] Boulder, Colorado USA: NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center, doi: https://doi.org/10.5067/7Q8HCCWS4I0R[2019-02-17]
Dee D P, Uppala S M, Simmons A J, et al. 2011. The ERA-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137(656): 553–597, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828
Drobot S D, Maslanik J A, Fowler C. 2006. A long-range forecast of Arctic summer sea-ice minimum extent. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(10): L10501
Ebert-Uphoff I, Deng Yi. 2012. Causal discovery for climate research using graphical models. Journal of Climate, 25(17): 5648–5665, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00387.1
Ellingsen I H, Dalpadado P, Slagstad D, et al. 2008. Impact of climatic change on the biological production in the Barents Sea. Climatic Change, 87(1–2): 155–175, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-007-9369-6
Engelsen O, Hegseth E N, Hop H, et al. 2002. Spatial variability of chlorophyll-a in the Marginal Ice Zone of the Barents Sea, with relations to sea ice and oceanographic conditions. Journal of Marine Systems, 35(1–2): 79–97, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00077-5
Falk-Petersen S, Hop H, Budgell W P, et al. 2000. Physical and ecological processes in the marginal ice zone of the northern Barents Sea during the summer melt period. Journal of Marine Systems, 27(1–3): 131–159, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-7963(00)00064-6
Guemas V, Chevallier M, Déqué M, et al. 2016. Impact of sea ice initialization on sea ice and atmosphere prediction skill on seasonal timescales. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(8): 3889–3896, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL066626
Hegseth E N. 1998. Primary production of the northern Barents Sea. Polar Research, 17(2): 113–123, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1751-8369.1998.tb00266.x
Hilmer M, Harder M, Lemke P. 1998. Sea ice transport: a highly variable link between Arctic and North Atlantic. Geophysical Research Letters, 25(17): 3359–3362, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/98GL52360
Holland M M, Stroeve J. 2011. Changing seasonal sea ice predictor relationships in a changing Arctic climate. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(18): L18501
Horvat C, Tziperman E. 2015. A prognostic model of the sea-ice floe size and thickness distribution. The Cryosphere, 9(6): 2119–2134, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-9-2119-2015
Huang Yi, Chou G, Xie Yan, et al. 2019. Radiative control of the inter-annual variability of Arctic sea ice. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(16): 9899–9908, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL084204
Humpert M, Raspotnik A. 2012. The future of Arctic shipping along the transpolar sea route. In: Heininen L, Exner-Pirot H, Plouffe J, eds. Arctic Yearbook. Akureyri: Northern Research Forum, 281–307
Kapsch M L, Graversen R G, Economou T, et al. 2014. The importance of spring atmospheric conditions for predictions of the Arctic summer sea ice extent. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(14): 5288–5296, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL060826
Kapsch M L, Graversen R G, Tjernström M. 2013. Springtime atmospheric energy transport and the control of Arctic summer sea-ice extent. Nature Climate Change, 3(8): 744–748, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1884
Kapsch M L, Graversen R G, Tjernström M, et al. 2016. The effect of downwelling longwave and shortwave radiation on Arctic summer sea ice. Journal of Climate, 29(3): 1143–1159, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0238.1
Kauker F, Kaminski T, Ricker R, et al. 2015. Seasonal sea ice predictions for the Arctic based on assimilation of remotely sensed observations. The Cryosphere Discussions, 9(5): 5521–5554, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/tcd-9-5521-2015
Koenigk T, Mikolajewicz U. 2009. Seasonal to interannual climate predictability in mid and high northern latitudes in a global coupled model. Climate Dynamics, 32(6): 783–798, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0419-1
Kretschmer M, Coumou D, Donges J F, et al. 2016. Using causal effect networks to analyze different arctic drivers of midlatitude winter circulation. Journal of Climate, 29(11): 4069–4081, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0654.1
Kretschmer M, Runge J, Coumou D. 2017. Early prediction of extreme stratospheric polar vortex states based on causal precursors. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(16): 8592–8600, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL074696
Levitus S, Antonov J I, Boyer T P, et al. 2012. World ocean heat content and thermosteric sea level change (0–2 000 m), 1955–2010. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(10): L10603
Li Sha, Wang Muyin, Bond N A, et al. 2018. Precursors of September arctic sea-ice extent based on causal effect networks. Atmosphere, 9(11): 437, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110437
Lindsay R W, Zhang Jinlun, Schweiger A J, et al. 2008. Seasonal predictions of ice extent in the Arctic Ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113(C2): C02023
Liu Jiping, Chen Zhiqiang, Hu Yongyun, et al. 2019. Towards reliable Arctic sea ice prediction using multivariate data assimilation. Science Bulletin, 64(1): 63–72, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2018.11.018
Liu Jiping, Curry J A, Wang Huijun, et al. 2012. Impact of declining Arctic sea ice on winter snowfall. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(11): 4074–4079, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114910109
Loeng H. 1991. Features of the physical oceanographic conditions of the Barents Sea. Polar Research, 10(1): 5–18, doi: https://doi.org/10.3402/polar.v10i1.6723
MacLachlan C, Arribas A, Peterson K A, et al. 2015. Global Seasonal forecast system version 5 (GloSea5): a high-resolution seasonal forecast system. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 141(689): 1072–1084, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2396
Massonnet F, Fichefet T, Goosse H, et al. 2011. On the influence of model physics on simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice. The Cryosphere, 5(3): 687–699, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-5-687-2011
Massonnet F, Fichefet T, Goosse H. 2015. Prospects for improved seasonal Arctic sea ice predictions from multivariate data assimilation. Ocean Modelling, 88: 16–25, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2014.12.013
Melia N, Haines K, Hawkins E. 2016. Sea ice decline and 21st century trans-Arctic shipping routes. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(18): 9720–9728, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL069315
Metzger E J, Smedstad O M, Thoppil P G, et al. 2014. US Navy operational global ocean and Arctic ice prediction systems. Oceanography, 27(3): 32–43, doi: https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2014.66
Msadek R, Vecchi G A, Winton M, et al. 2014. Importance of initial conditions in seasonal predictions of Arctic sea ice extent. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(14): 5208–5215, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL060799
Perovich D K, Light B, Eicken H, et al. 2007. Increasing solar heating of the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas, 1979–2005: attribution and role in the ice-albedo feedback. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(19): L19505, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031480
Runge J, Petoukhov V, Donges J F, et al. 2015. Identifying causal gateways and mediators in complex spatio-temporal systems. Nature Communications, 6: 8502, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9502
Saha S, Moorthi S, Pan Hualu, et al. 2010. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 91(8): 1015–1058, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3001.1
Sakshaug E. 1997. Biomass and productivity distributions and their variability in the Barents Sea. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 54(3): 341–350, doi: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.1996.0170
Sandø A B, Nilsen J E Ø, Gao Y, et al. 2010. Importance of heat transport and local air-sea heat fluxes for Barents Sea climate variability. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C7): C07013
Schlichtholz P. 2011. Influence of oceanic heat variability on sea ice anomalies in the Nordic Seas. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(5): L05705
Schröder D, Feltham D L, Flocco D, et al. 2014. September Arctic sea-ice minimum predicted by spring melt-pond fraction. Nature Climate Change, 4(5): 353–357, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2203
Smith L C, Stephenson S R. 2013. New trans-Arctic shipping routes navigable by midcentury. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(13): E1191–E1195, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1214212110
Stroeve J, Hamilton L C, Bitz C M, et al. 2014. Predicting September sea-ice: ensemble skill of the SEARCH sea ice outlook 2008–2013. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(7): 2411–2418, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL059388
Tamelander T, Renaud P E, Hop H, et al. 2006. Trophic relationships and pelagic-benthic coupling during summer in the Barents Sea Marginal Ice Zone, revealed by stable carbon and nitrogen isotope measurements. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 310: 33–46, doi: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps310033
Tilling R L, Ridout A, Shepherd A, et al. 2015. Increased Arctic sea ice volume after anomalously low melting in 2013. Nature Geoscience, 8(8): 643–646, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2489
Tivy A, Howell S E L, Alt B, et al. 2011. Origins and levels of seasonal forecast skill for sea ice in Hudson Bay using canonical correlation analysis. Journal of Climate, 24(5): 1378–1395, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3527.1
Vinje T. 2001. Anomalies and trends of sea-ice extent and atmospheric circulation in the Nordic seas during the period 1864–1998. Journal of Climate, 14(3): 255–267, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<0255:AATOSI>2.0.CO;2
Wallace J M, Gutzler D S. 1981. Teleconnections in the geopotential height field during the Northern Hemisphere winter. Monthly Weather Review, 109(4): 784–812, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1981)109<0784:TITGHF>2.0.CO;2
Wang Lei, Yuan Xiaojun, Ting Mingfang, et al. 2016. Predicting summer arctic sea ice concentration intraseasonal variability using a vector autoregressive model. Journal of Climate, 29(4): 1529–1543, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0313.1
Wassmann P, Reigstad M, Haug T, et al. 2006. Food webs and carbon flux in the Barents Sea. Progress in Oceanography, 71(2–4): 232–287, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2006.10.003
Wayand N E, Bitz C M, Blanchard-Wrigglesworth E. 2019. A year-round subseasonal-to-seasonal sea ice prediction portal. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(6): 3298–3307, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL081565
Williams J, Tremblay B, Newton R, et al. 2016. Dynamic preconditioning of the minimum September sea-ice extent. Journal of Climate, 29(16): 5879–5891, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0515.1
Winton M. 2003. On the climatic impact of ocean circulation. Journal of Climate, 16(17): 2875–2889, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<2875:OTCIOO>2.0.CO;2
Wu Xingren, Grumbine R. 2014. Sea Ice in the NCEP Climate Forecast System. Climate Prediction S&T Digest. Science and Technology Infusion Climate Bulletin Supplement February 2014, 28–35
Yang Shili, Dong Wenjie, Chou Jieming, et al. 2016. Global warming projections using the human-earth system model BNU-HESM1.0. Science Bulletin, 61(23): 1833–1838, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1176-x
Yuan Xiaojun, Chen Dake, Li Cuihua, et al. 2016. Arctic sea ice seasonal prediction by a linear Markov model. Journal of Climate, 29(22): 8151–8173, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0858.1
Zhang Yongfei, Bitz C M, Anderson J L, et al. 2018a. Insights on sea ice data assimilation from perfect model observing system simulation experiments. Journal of Climate, 31(15): 5911–5926, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0904.1
Zhang Yuanyuan, Cheng Xiao, Liu Jiping, et al. 2018b. The potential of sea ice leads as a predictor for summer Arctic sea ice extent. The Cryosphere, 12(12): 3747–3757, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-12-3747-2018
Zhang Jinlun, Lindsay R, Schweiger A, et al. 2013. The impact of an intense summer cyclone on 2012 Arctic sea ice retreat. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(4): 720–726, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50190
Zhang Jinlun, Rothrock D A. 2003. Modeling global sea ice with a thickness and enthalpy distribution model in generalized curvilinear coordinates. Monthly Weather Review, 131(5): 845–861, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2003)131<0845:MGSIWA>2.0.CO;2
Zhang Jinlun, Rothrock D A. 2005. Effect of sea ice rheology in numerical investigations of climate. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110(C8): C08014
Zhang Jinlun, Schweiger A, Steele M, et al. 2015. Sea ice floe size distribution in the marginal ice zone: theory and numerical experiments. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120(5): 3484–3498
Zhang Jinlun, Steele M, Lindsay A, et al. 2008. Ensemble 1-Year predictions of arctic sea ice for the spring and summer of 2008. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(8): L08502
Zhang Xia, Tu Jingfang, Guo Peiqing, et al. 2009. The economic estimate of arctic sea routes and its strategic significance for the development of Chinese economy. China Soft Science (in Chinese), (S2): 86–93
Acknowledgements
The causal effect networks algorithm has been developed by Jakob Runge, and the TIGRAMITE software package is available through https://github.com/jakobrunge/tigramite. Thank all of the data development organizations and data websites for data-sets available online, including NSIDC, APL/PSC, ECMWF, OCL/NOAA and CPC/NOAA. We are also grateful to Lu Zhou for her help with uncertainty analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Key Research and Development Program of China under contract Nos 2016YFF0202705 and 2018YFA0605904; the Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere and Ocean (JISAO) under contract NOAA Cooperative Agreement NA15OAR4320063, contribution No. 2019-1044, and PMEL contribution No. 5052.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wang, M., Huang, W. et al. Using a skillful statistical model to predict September sea ice covering Arctic shipping routes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 39, 11–25 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-020-1595-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-020-1595-z