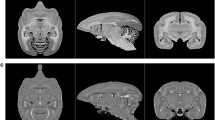
Abstract
Investigations of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) brain have shed light on the function and organization of the primate brain at a scale and resolution not yet possible in humans. A cornerstone of the linkage between non-human primate and human studies of the brain is magnetic resonance imaging, which allows for an association to be made between the detailed structural and physiological analysis of the non-human primate and that of the human brain. To further this end, we present a novel parcellation method and system for the rhesus monkey brain, referred to as the macaque Harvard-Oxford Atlas (mHOA), which is based on the human Harvard-Oxford Atlas (HOA) and grounded in an ontological and taxonomic framework. Consistent anatomical features were used to delimit and parcellate brain regions in the macaque, which were then categorized according to functional systems. This system of parcellation will be expanded with advances in technology and, like the HOA, will provide a framework upon which the results from other experimental studies (e.g., functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), physiology, connectivity, graph theory) can be interpreted.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGa:
-
anterior cingulate
- CGp:
-
posterior cingulate
- CP:
-
coronal plane
- COa:
-
central operculum- anterior
- COp:
-
central operculum - posterior
- F1dl:
-
dorso-lateral superior frontal
- F1dm:
-
dorso-medial superior frontal
- F2:
-
inferior frontal
- FOC:
-
fronto-orbital
- FP:
-
frontal pole
- INS:
-
insula
- ITG:
-
inferior temporal gyrus
- LPCi:
-
inferior portion of lateral parietal cortex
- LPCs:
-
superior portion of lateral parietal cortex
- MPC:
-
medial parietal cortex
- PO:
-
parietal operculum
- PoG:
-
postcentral gyrus
- PRL:
-
prelunate
- PHG:
-
parahippocampal gyrus
- PrG:
-
precentral gyrus
- SC:
-
subcallosal area
- STG:
-
superior temporal gyrus
- STP:
-
supratemporal plane
- STRdl:
-
dorsolateral portion of striate cortex
- STRm:
-
medial portion of striate cortex
- TP:
-
temporal pole
- VMO:
-
ventromedial occipital
References
Aggleton, J. P., Wright, N. F., Vann, S. D., & Saunders, R. C. (2012). Medial temporal lobe projections to the retrosplenial cortex of the macaque monkey. Hippocampus, 22(9), 1883–1900. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22024.
Akbarian, S., Grüsser, O. J., & Guldin, W. O. (1994). Corticofugal connections between the cerebral cortex and brainstem vestibular nuclei in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 339(3), 421–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903390309.
Allman, J. M., Tetreault, N. A., Hakeem, A. Y., Manaye, K. F., Semendeferi, K., Erwin, J. M., Park, S., Goubert, V., & Hof, P. R. (2010). The von Economo neurons in frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortex in great apes and humans. Brain Structure & Function, 214(5–6), 495–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0254-0.
Allman, J. M., Tetreault, N. A., Hakeem, A. Y., Manaye, K. F., Semendeferi, K., Erwin, J. M., et al. (2011). The von Economo neurons in the frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortex. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1225, 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06011.x.
Amaral, D. G., Insausti, R., & Cowan, W. M. (1987). The entorhinal cortex of the monkey: I. Cytoarchitectonic organization. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 264(3), 326–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902640305.
Amunts, K., Malikovic, A., Mohlberg, H., Schormann, T., & Zilles, K. (2000). Brodmann’s areas 17 and 18 brought into stereotaxic space-where and how variable? NeuroImage, 11(1), 66–84. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0516.
Amunts, K., Schleicher, A., Bürgel, U., Mohlberg, H., Uylings, H. B., & Zilles, K. (1999). Broca’s region revisited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 412(2), 319–341.
An, X., Bandler, R., Ongür, D., & Price, J. L. (1998). Prefrontal cortical projections to longitudinal columns in the midbrain periaqueductal gray in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 401(4), 455–479.
Andersen, R. A. (1995). Encoding of intention and spatial location in the posterior parietal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 5(5), 457–469. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/5.5.457.
Andersen, R. A., Asanuma, C., Essick, G., & Siegel, R. M. (1990). Corticocortical connections of anatomically and physiologically defined subdivisions within the inferior parietal lobule. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 296(1), 65–113. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902960106.
Augustinack, J. C., van der Kouwe, A. J. W., Blackwell, M. L., Salat, D. H., Wiggins, C. J., Frosch, M. P., Wiggins, C. J., Frosch, M. P., Wiggins, G. C., Potthast, A., Wald, L. L., & Fishl, B. R. (2005). Detection of entorhinal layer II using 7Tesla [corrected] magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology, 57(4), 489–494. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20426.
Augustine, J. R. (1996). Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews, 22(3), 229–244.
Autio, J. A., Glasser, M. F., Ose, T., Donahue, C. J., Bastiani, M., Ohno, M., Kawabata, Y., Urushibata, Y., Murata, K., Nishigori, K., Yamaguchi, M., Hori, Y., Toshida, A., Go, Y., Coalson, T. S., Jdabdi, S., Sotiropoulos, S. N., Kennedy, H., Smith, S., Van Essen, D. C., & Hayashi, T. (2020). Towards HCP-Style macaque connectomes: 24-Channel 3T multi-array coil, MRI sequences and preprocessing. Neuroimage, 215, 116800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116800.
Bailey, P., & von Bonin, G. (1951). The isocortex of man. Urbana, Illinois, USA: University of Illinois.
Bakola, S., Gamberini, M., Passarelli, L., Fattori, P., & Galletti, C. (2010). Cortical connections of parietal field PEc in the macaque: linking vision and somatic sensation for the control of limb action. Cerebral Cortex, 20(11), 2592–2604. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhq007.
Bakola, S., Passarelli, L., Gamberini, M., Fattori, P., & Galletti, C. (2013). Cortical connectivity suggests a role in limb coordination for macaque area PE of the superior parietal cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 33(15), 6648–6658. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4685-12.2013.
Barbas, H. (1993). Organization of cortical afferent input to orbitofrontal areas in the rhesus monkey. Neuroscience, 56(4), 841–864.
Barbas, H., & Pandya, D. N. (1989). Architecture and intrinsic connections of the prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 286(3), 353–375. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902860306.
Belmalih, A., Borra, E., Contini, M., Gerbella, M., Rozzi, S., & Luppino, G. (2009). Multimodal architectonic subdivision of the rostral part (area F5) of the macaque ventral premotor cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 512(2), 183–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21892.
Beul, S. F., Barbas, H., & Hilgetag, C. C. (2017). A predictive structural model of the primate connectome. Scientific Reports, 7, 43176. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43176.
Bigelow, J., Ng, C.-W., & Poremba, A. (2016). Local field potential correlates of auditory working memory in primate dorsal temporal pole. Brain Research, 1640(Pt B), 299–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.025.
Bizzi, E., & Schiller, P. H. (1970). Single unit activity in the frontal eye fields of unanesthetized monkeys during eye and head movement. Experimental Brain Research, 10(2), 150–158.
Black, K. J., Koller, J. M., Snyder, A. Z., & Perlmutter, J. S. (2004). Atlas template images for nonhuman primate neuroimaging: baboon and macaque. Methods in Enzymology, 385, 91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(04)85006-7.
Blatt, G. J., & Rosene, D. L. (1998). Organization of direct hippocampal efferent projections to the cerebral cortex of the rhesus monkey: projections from CA1, prosubiculum, and subiculum to the temporal lobe. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 392(1), 92–114.
Blatt, G. J., Pandya, D. N., & Rosene, D. L. (2003). Parcellation of cortical afferents to three distinct sectors in the parahippocampal gyrus of the rhesus monkey: an anatomical and neurophysiological study. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 466(2), 161–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10866.
Blinkov, S. M., & Glezer, I. I. (1968). The human brain in figures and tables: A quantitative handbook. New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Bohland, J. W., Wu, C., Barbas, H., Bokil, H., Bota, M., Breiter, H. C., et al. (2009). A proposal for a coordinated effort for the determination of brainwide neuroanatomical connectivity in model organisms at a mesoscopic scale. PLoS Computational Biology, 5(3), e1000334. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000334.
Bonin, G. von, & Bailey, P. (1947). The neocortex of Macaca mulatta. Chicago: University of Illinois Press.
Bonini, L., Maranesi, M., Livi, A., Fogassi, L., & Rizzolatti, G. (2014). Space-dependent representation of objects and other’s action in monkey ventral premotor grasping neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 34(11), 4108–4119. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4187-13.2014.
Bonini, L., Ugolotti Serventi, F., Bruni, S., Maranesi, M., Bimbi, M., Simone, L., Rozzi, S., Ferrari, P. F., & Fogassi, L. (2012). Selectivity for grip type and action goal in macaque inferior parietal and ventral premotor grasping neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(6), 1607–1619. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01158.2011.
Borra, E., Belmalih, A., Calzavara, R., Gerbella, M., Murata, A., Rozzi, S., & Luppino, G. (2008). Cortical connections of the macaque anterior intraparietal (AIP) area. Cerebral Cortex, 18(5), 1094–1011.
Borra, E., & Luppino, G. (2017). Functional anatomy of the macaque temporo-parieto-frontal connectivity. Cortex, 97, 306–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.12.007.
Boussaoud, D., Ungerleider, L. G., & Desimone, R. (1990). Pathways for motion analysis: cortical connections of the medial superior temporal and fundus of the superior temporal visual areas in the macaque. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 296(3), 462–495. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902960311.
Bowden, D. M., & Martin, R. F. (1995). NeuroNames Brain Hierarchy. NeuroImage, 2(1), 63–83. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1995.1009.
Bowden, D. M., & Dubach, M. F. (2003). NeuroNames 2002. Neuroinformatics, 1(1), 43–59. https://doi.org/10.1385/NI:1:1:043.
Bowden, D. M., Dubach, M., & Park, J. (2007). Creating neuroscience ontologies. In C. J. Crasto & S. H. Koslow (Eds.), Neuroinformatics (pp. 67–87). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-520-6_5.
Bowden, D. M., Song, E., Kosheleva, J., & Dubach, M. F. (2012). NeuroNames: an ontology for the BrainInfo portal to neuroscience on the web. Neuroinformatics, 10(1), 97–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-011-9128-8.
Brodmann, K. (1909). Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde. Leipzig: Verlag.
Brodmann, K. (2006). Brodmann’s localisation in the cerebral cortex. (Translated by L. Garey), Berlin: Springer.
Braak, H. (1980). Architectonics of the human telencephalic cortex (Vol. 4). Berlin: Springer.
Bruce, C. J., & Goldberg, M. E. (1985). Primate frontal eye fields. I. Single neurons discharging before saccades. Journal of Neurophysiology, 53(3), 603–635. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1985.53.3.603.
Bruni, S., Giorgetti, V., Fogassi, L., & Bonini, L. (2017). Multimodal encoding of goal-directed actions in monkey ventral premotor grasping neurons. Cerebral Cortex, 27(1), 522–533. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv246.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(3), 186–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2575.
Calabrese, E., Badea, A., Coe, C. L., Lubach, G. R., Shi, Y., Styner, M. A., & Johnson, G. A. (2015). A diffusion tensor MRI atlas of the postmortem rhesus macaque brain. NeuroImage, 117, 408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.072.
Carmichael, S. T., & Price, J. L. (1995a). Limbic connections of the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 363(4), 615–641. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903630408.
Carmichael, S. T., & Price, J. L. (1995b). Sensory and premotor connections of the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 363(4), 642–664. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903630409.
Carmichael, S. T., & Price, J. L. (1996). Connectional networks within the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of macaque monkeys. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 371(2), 179–207. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960722)371:2<179::AID-CNE1>3.0.CO;2-#.
Carpenter, M., & Sutin, J. (1983). Human neuroanatomy (8th ed.). Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Cavada, C., & Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1989a). Posterior parietal cortex in rhesus monkey: I. Parcellation of areas based on distinctive limbic and sensory corticocortical connections. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 287(4), 393–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902870402.
Cavada, C., & Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1989b). Posterior parietal cortex in rhesus monkey: II. Evidence for segregated corticocortical networks linking sensory and limbic areas with the frontal lobe. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 287(4), 422–445. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902870403.
Caviness, V. S., Meyer, J., Makris, N., & Kennedy, D. N. (1996). MRI-Based topographic parcellation of human neocortex: an anatomically specified method with estimate of reliability. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 8(6), 566–587. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.1996.8.6.566.
Caviness, V. S., Filipek, P. A., & Kennedy, D. N. (1989). Magnetic resonance technology in human brain science: blueprint for a program based on morphometry. Brain Development, 11, 1–13.
Caviness, V. S., Lange, N. T., Makris, N., Herbert, M. R., & Kennedy, D. N. (1999). MRI-based brain volumetrics: emergence of a developmental brain science. Brain Development, 21, 289–295.
Chen, A., DeAngelis, G. C., & Angelaki, D. E. (2010). Macaque parieto-insular vestibular cortex: responses to self-motion and optic flow. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 30(8), 3022–3042. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4029-09.2010.
Chiba, T., Kayahara, T., & Nakano, K. (2001). Efferent projections of infralimbic and prelimbic areas of the medial prefrontal cortex in the Japanese monkey, Macaca fuscata. Brain Research, 888(1), 83–101.
Cieslik, E. C., Zilles, K., Caspers, S., Roski, C., Kellermann, T. S., Jakobs, O., et al. (2013). Is there “one” DLPFC in cognitive action control? Evidence for heterogeneity from co-activation-based parcellation. Cerebral Cortex, 23(11), 2677–2689. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhs256.
Cipolloni, P. B., & Pandya, D. N. (1991). Golgi, histochemical, and immunocytochemical analyses of the neurons of auditory-related cortices of the rhesus monkey. Experimental Neurology, 114(1), 104–122.
Colby, C. L., Gattass, R., Olson, C. R., & Gross, C. G. (1988). Topographical organization of cortical afferents to extrastriate visual area PO in the macaque: a dual tracer study. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 269(3), 392–413. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902690307.
Cowey, A., & Latto, R. M. (1971). Effects of frontal eye-field ablation on visual fields and on fixation in rhesus monkeys. Brain Research, 31(2), 375–376.
Craig, A. D. B. (2014). Topographically organized projection to posterior insular cortex from the posterior portion of the ventral medial nucleus in the long-tailed macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 522(1), 36–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23425.
Croxson, P. L., Forkel, S. J., Cerliani, L., & Thiebaut de Schotten, M. (2018). Structural variability across the primate brain: a cross-species comparison. Cerebral Cortex, 28(11), 3829–3841. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx244.
Cunningham, D. J. (1892). Contribution to the surface anatomy of the cerebral hemispheres. Dublin, Ireland: Royal Irish Academy.
Daniel, P. M., & Whitteridge, D. (1961). The representation of the visual field on the cerebral cortex in monkeys. The Journal of Physiology, 159, 203–221. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006803.
Dejerine JJ, & Dejerine-Klumpke A(1895) Anatomie des centres nerveus. Tome 1° Paris: Rueff.
Desikan, R. S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., Buckner, R. L., Dale, A. M., Maguire, R. P., Hyman, B. T., Albert, M. S., & Killiany, R. J. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage, 31(3), 968–980.
Desimone, R., Albright, T. D., Gross, C. G., & Bruce, C. (1984). Stimulus-selective properties of inferior temporal neurons in the macaque. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 4(8), 2051–2062.
Devinsky, O., Morrell, M. J., & Vogt, B. A. (1995). Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 118(Pt 1), 279–306. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/118.1.279.
Dong, W. K., Chudler, E. H., Sugiyama, K., Roberts, V. J., & Hayashi, T. (1994). Somatosensory, multisensory, and task-related neurons in cortical area 7b (PF) of unanesthetized monkeys. Journal of Neurophysiology, 72(2), 542–564. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.542.
Dreyer, D. A., Loe, P. R., Metz, C. B., & Whitsel, B. L. (1975). Representation of head and face in postcentral gyrus of the macaque. Journal of Neurophysiology, 38(3), 714–733. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1975.38.3.714.
Dreyer, D. A., Schneider, R. J., Metz, C. B., & Whitsel, B. L. (1974). Differential contributions of spinal pathways to body representation in postcentral gyrus of Macaca mulatta. Journal of Neurophysiology, 37(1), 119–145. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1974.37.1.119.
Duffy, F. H., & Burchfiel, J. L. (1971). Somatosensory system: organizational hierarchy from single units in monkey area 55. Science (New York, N.Y.), 172(3980), 273–227.
Eberstaller, O. (1890). Das Stirnhirn. Ein Beitrag zur Anatomie der Oberflache des Gehirns. Wien-Liepzig: Urban and Schwarzenberg.
Eickhoff, S. B., Paus, T., Caspers, S., Grosbras, M.-H., Evans, A. C., Zilles, K., & Amunts, K. (2007). Assignment of functional activations to probabilistic cytoarchitectonic areas revisited. NeuroImage, 36(3), 511–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.03.060.
Eidelberg, D., & Galaburda, A. M. (1984). Inferior parietal lobule: divergent architectonic asymmetries in the human brain. Archives of Neurology, 41(8), 843–852.
Evrard, H. C., Forro, T., & Logothetis, N. K. (2012). Von Economo neurons in the anterior insula of the macaque monkey. Neuron, 74(3), 482–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.003.
Evrard, H. C., Logothetis, N. K., & Craig, A. D. B. (2014). Modular architectonic organization of the insula in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 522(1), 64–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23436.
Fattori, P., Breveglieri, R., Bosco, A., Gamberini, M., & Galletti, C. (2017). Vision for prehension in the medial parietal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 27(2), 1149–1163. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bh302.
Feng, L., Jeon, T., Yu, Q., Ouyang, M., Peng, Q., Mishra, V., Pletikos, M., Sestan, N., Miller, M. I., Mori, S., Hsiao, S., Liu, S., & Huang, H. (2017). Population-averaged macaque brain atlas with high-resolution ex vivo DTI integrated into in vivo space. Brain Structure & Function, 222(9), 4131–4147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1463-6.
Filipek, P. A., Richelme, C., Kennedy, D. N., & Caviness, V. S. (1994). The young adult human brain: an MRI-based morphometric analysis. Cerebral Cortex, 4(4), 344–360. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/4.4.344.
Fischl, B., Rajendran, N., Busa, E., Augustinack, J., Hinds, O., Yeo, B. T. T., et al. (2008). Cortical folding patterns and predicting cytoarchitecture. Cerebral Cortex, 18(8), 1973–1980. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhm225.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Ségonne, F., Salat, D. H., et al. (2004). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 14(1), 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhg087.
Frazier, J. A., Chiu, S., Breeze, J. L., Makris, N., Lange, N., Kennedy, D. N., Herbert, M. R., Bent, E. K., Koneru, V. K., Dieterich, M. E., Hodge, S. M., Rauch, S. L., Grant, P. E., Cohen, B. M., Seidman, L. J., Caviness, V. S., & Biederman, J. (2005). Structural brain magnetic resonance imaging of limbic and thalamic volumes in pediatric bipolar disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(7), 1256–1265.
Ferraina, S., Johnson, P. B., Garasto, M. R., Battaglia-Mayer, A., Ercolani, L., Bianchi, L., Lacquaniti, F., & Caminiti, R. (1997). Combination of hand and gaze signals during reaching: activity in parietal area 7m of the monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology, 77(2), 1034–1038.
Freedman, L. J., Insel, T. R., & Smith, Y. (2000). Subcortical projections of area 25 (subgenual cortex) of the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 421(2), 172–188.
Frey, S., Pandya, D. N., Chakravarty, M. M., Bailey, L., Petrides, M., & Collins, D. L. (2011). An MRI based average macaque monkey stereotaxic atlas and space (MNI monkey space). NeuroImage, 55(4), 1435–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.040.
Friedman, H. R., & Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1994). Coactivation of prefrontal cortex and inferior parietal cortex in working memory tasks revealed by 2DG functional mapping in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 14(5 Pt 1), 2775–2788.
Fujita, I., Tanaka, K., Ito, M., & Cheng, K. (1992). Columns for visual features of objects in monkey inferotemporal cortex. Nature, 360(6402), 343–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/360343a0.
Galaburda, A. M., & Pandya, D. N. (1983). The intrinsic architectonic and connectional organization of the superior temporal region of the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 221(2), 169–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902210206.
Galletti, C., & Fattori, P. (2018). The dorsal visual stream revisited: Stable circuits or dynamic pathways? Cerebral Cortex, 98, 203–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2017.01009.
Galletti, C., Gamberini, M., Kutz, D. F., Fattori, P., Luppino, G., & Matelli, M. (2001). The cortical connections of area V6: an occipito-parietal network processing visual information. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 13(8), 1572–1588.
Galletti, C., Gamberini, M., Kutz, D. F., Baldinotti, I., & Fattori, P. (2005). The relationship between V6 and PO in macaque extrastriate cortex. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 21(4), 959–970. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03911.x.
Galletti, C., Kutz, D. F., Gamberini, M., Breveglieri, R., & Fattori, P. (2003). Role of the medial parieto-occipital cortex in the control of reaching and grasping movements. Experimental Brain Research, 153(2), 158–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1589-z.
Gamberini, M., Fattori, P., & Galletti, C. (2015). The medial parietal occipital areas in the macaque monkey. Visual Neuroscience, 32, e013. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0952523815000103.
Gamberini, M., Passarelli, L., Fattori, P., & Galletti, C. (2020). Structural connectivity and functional properties of the macaque superior parietal lobule. Brain Structure & Function. 225, 1349–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01976-9.
García-Cabezas, M. Á., & Barbas, H. (2014). Area 4 has layer IV in adult primates. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 39(11), 1824–1834. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12585.
Gattass, R., Gross, C. G., & Sandell, J. H. (1981). Visual topography of V2 in the macaque. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 201(4), 519–539. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902010405.
Gerbella, M., Belmalih, A., Borra, E., Rozzi, S., & Luppino, G. (2010). Cortical connections of the macaque caudal ventrolateral prefrontal areas 45A and 45B. Cerebral Cortex, 20(1), 141–168. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp087.
Geyer, S., Matelli, M., Luppino, G., & Zilles, K. (2000a). Functional neuroanatomy of the primate isocortical motor system. Anatomy and Embryology, 202(6), 443–474.
Geyer, S., Schormann, T., Mohlberg, H., & Zilles, K. (2000b). Areas 3a, 3b, and 1 of human primary somatosensory cortex. Part 2. Spatial normalization to standard anatomical space. NeuroImage, 11(6 Pt 1), 684–696. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2000.0548.
Glasser, M. F., Coalson, T. S., Robinson, E. C., Hacker, C. D., Harwell, J., Yacoub, E., et al. (2016). A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex. Nature, 536(7615), 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18933.
Glasser, M. F., & Van Essen, D. C. (2011). Mapping human cortical areas in vivo based on myelin content as revealed by T1- and T2-weighted MRI. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 31(32), 11597–11616. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2180-11.2011.
Goldstein, J. M., Seidman, L. J., Makris, N., Ahern, T., O'Brien, L. M., Caviness Jr., V. S., Kennedy, D. N., Faraone, S. V., & Tsuang, M. T. (2007). Hypothalamic abnormalities in schizophrenia: sex effects and genetic vulnerability. Biological Psychiatry, 61, 935–945. PMID 17046727.
Goodale, M. A., & Milner, A. D. (1992). Separate visual pathways for perception and action. Trends in Neurosciences, 15(1), 20–25.
Gottlieb, J. P., Kusunoki, M., & Goldberg, M. E. (1998). The representation of visual salience in monkey parietal cortex. Nature, 391(6666), 481–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/35135.
Goulas, A., Zilles, K., & Hilgetag, C. C. (2018). Cortical gradients and laminar projections in mammals. Trends in Neurosciences, 41(11), 775–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2018.06.003.
Gower, E. C. (1989). Efferent projections from limbic cortex of the temporal pole to the magnocellular medial dorsal nucleus in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 280(3), 343–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902800303.
Gregoriou, G. G., Borra, E., Matelli, M., & Luppino, G. (2006). Architectonic organization of the inferior parietal convexity of the macaque monkey. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 496(3), 422–451.
Gross, C. G., Bender, D. B., & Rocha-Miranda, C. E. (1969). Visual receptive fields of neurons in inferotemporal cortex of the monkey. Science (New York, N.Y.), 166(3910), 1303–1306.
Gross, C. G., Rocha-Miranda, C. E., & Bender, D. B. (1972). Visual properties of neurons in inferotemporal cortex of the macaque. Journal of Neurophysiology, 35(1), 96–111. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1972.35.1.96.
Hadjidimitrakis, K., Dal Bo’, G., Breveglieri, R., Galletti, C., & Fattori, P. (2015). Overlapping representations for reach depth and direction in caudal superior parietal lobule of macaques. Journal of Neurophysiology, 114(4), 2340–2352. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00486.2015.
Hilgetag, C. C., Medalla, M., Beul, S. F., & Barbas, H. (2016). The primate connectome in context: Principles of connections of the cortical visual system. NeuroImage, 134, 685–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.04.017.
Hinds, O. P., Rajendran, N., Polimeni, J. R., Augustinack, J. C., Wiggins, G., Wald, L. L., Diana Rosas, H., Potthast, A., Schwartz, E. L., & Fischl, B. (2008). Accurate prediction of V1 location from cortical folds in a surface coordinate system. NeuroImage, 39(4), 1585–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.033.
Horel, J. A., Voytko, M. L., & Salsbury, K. G. (1984). Visual learning suppressed by cooling the temporal pole. Behavioral Neuroscience, 98(2), 310–324.
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1969). Anatomical demonstration of columns in the monkey striate cortex. Nature, 221(5182), 747–750.
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1974a). Sequence regularity and geometry of orientation columns in the monkey striate cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 158(3), 267–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901580304.
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1974b). Uniformity of monkey striate cortex: A parallel relationship between field size, scatter, and magnification factor. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 158(3), 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901580305.
Hyvärinen, J. (1981). Regional distribution of functions in parietal association area 7 of the monkey. Brain Research, 206(2), 287–303.
Hyvärinen, J., & Poranen, A. (1974). Function of the parietal associative area 7 as revealed from cellular discharges in alert monkeys. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 97(4), 673–692. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/97.1.673.
Imam, F. T., Larson, S., Grethe, J. S., Gupta, A., Bandrowski, A., & Martone, M. E. (2012). Development and use of ontologies inside the neuroscience information framework: a practical approach. Frontiers in Genetics, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00111.
Insausti, R., & Amaral, D. G. (2008). Entorhinal cortex of the monkey: IV. Topographical and laminar organization of cortical afferents. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 509(6), 608–641. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21753.
Jones, E. G., & Powell, T. P. S. (1970). An anatomical study of converging sensory pathways within the cerebral cortex of the monkey. Brain, 93(4), 793–820. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/93.4.793.
Joyce, M. K. P., & Barbas, H. (2018). Cortical connections position primate area 25 as a keystone for interoception, emotion, and memory. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 38(7), 1677–1698. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2363-17.2017.
Kaas, J. H., & Hackett, T. A. (2000). Subdivisions of auditory cortex and processing streams in primates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(22), 11793–11799. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.22.11793.
Kennedy D. N., Makris N., Bates J. F., & Caviness V. S. (1997). Structural morphometry in the developing brain. In R.W. Thatcher, G. R. Lyon, J. Rumsey, N. Krasnegor (Eds.), Development neuroimaging: mapping the development of brain and behavior (pp 3–14). New York: Academic Press.
Kennedy, D. N., Lange, N., Makris, N., Bates, J., Meyer, J., & Caviness, V. S. (1998). Gyri of the human neocortex: an MRI-based analysis of volume and variance, Cerebral Cortex, 8(4), 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/8.4.372.
Kobatake, E., & Tanaka, K. (1994). Neuronal selectivities to complex object features in the ventral visual pathway of the macaque cerebral cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 71(3), 856–867. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1994.71.3.856.
Kobayashi, Y., & Amaral, D. G. (2003). Macaque monkey retrosplenial cortex: II. Cortical afferents. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 466(1), 48–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10883.
Kobayashi, Y., & Amaral, D. G. (2007). Macaque monkey retrosplenial cortex: III. Cortical efferents. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 502(5), 810–833. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21346.
Kondo, H., Saleem, K. S., & Price, J. L. (2003). Differential connections of the temporal pole with the orbital and medial prefrontal networks in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 465(4), 499–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10842.
Kosaki, H., Hashikawa, T., He, J., & Jones, E. G. (1997). Tonotopic organization of auditory cortical fields delineated by parvalbumin immunoreactivity in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 386(2), 304–316.
Krieg, W. (1975). Interpretative atlas of the monkey’s brain: 89 cell- and fiber-stained sections of the brain of the macaque, with an illustrated textbook. Evanston, IL: BrainBooks.
Krubitzer, L., Clarey, J., Tweedale, R., Elston, G., & Calford, M. (1995). A redefinition of somatosensory areas in the lateral sulcus of macaque monkeys. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 15(5 Pt 2), 3821–3839.
Latto, R., & Cowey, A. (1971). Visual field defects after frontal eye-field lesions in monkeys. Brain Research, 30(1), 1–24.
Lavenex, P., Suzuki, W. A., & Amaral, D. G. (2002). Perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices of the macaque monkey: projections to the neocortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 447(4), 394–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10243.
Leichnetz, G. R. (2001). Connections of the medial posterior parietal cortex (area 7m) in the monkey. Anatomical Record, 263(2), 215–236.
Leinonen, L., Hyvärinen, J., Nyman, G., & Linnankoski, I. (1979). I. Functional properties of neurons in lateral part of associative area 7 in awake monkeys. Experimental Brain Research, 34(2), 299–320.
Leon, M. I., & Shadlen, M. N. (2003). Representation of time by neurons in the posterior parietal cortex of the macaque. Neuron, 38(2), 317–327.
Luppino, G., Matelli, M., Camarda, R., & Rizzolatti, G. (1993). Corticocortical connections of area F3 (SMA-proper) and area F6 (pre-SMA) in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 338(1), 114–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903380109.
Lynall, M.-E., Bassett, D. S., Kerwin, R., McKenna, P. J., Kitzbichler, M., Muller, U., & Bullmore, E. (2010). Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 30(28), 9477–9487. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0333-10.2010.
Maier-Hein, K. H., Neher, P. F., Houde, J.-C., Côté, M.-A., Garyfallidis, E., Zhong, J., et al. (2017). The challenge of mapping the human connectome based on diffusion tractography. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01285-x.
Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., Boriel, D. L., & Rosene, D. L. (2010). Methods of MRI-based structural imaging in the aging monkey. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 50(3), 166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.06.007.
Makris, N., Meyer, J. W., Bates, J. F., Yeterian, E. H., Kennedy, D. N., & Caviness, V. S. (1999). MRI-Based topographic parcellation of human cerebral white matter and nuclei. II. Rationale and applications with systematics of cerebral connectivity. NeuroImage, 9(1), 18–45. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0384.
Makris, N., Papadimitriou, G. M., Worth, A. J., Jenkins, B., Garrido, L., Sorensen, A. G., et al. (2002). Diffusion tensor imaging. In K.L., Davis, D.D. Charney, J.T. Coyle & C. Nemeroff (Eds.), Neuropharmacology - 5th generation of progress (pp. 357-71). New York, NY: Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins.
Makris, N., Worth, A. J., Sorensen, A. G., Papadimitriou, G. M., Wu, O., Reese, T. G., et al. (1997). Morphometry of in vivo human white matter association pathways with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology, 42(6), 951–962. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410420617.
Makris, N., Hodge, S.M., Haselgrove, C., Kennedy, D.N., Dale, A., Fischl, B., Rosen, B.R., Harris, G., Caviness, V.S., Schmahmann, J.D. (2003). Human cerebellum: surface-assisted cortical parcellation and volumetry with magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15(4), 584–599.
Makris, N., Gasic, G. P., Seidman, L. J., Goldstein, J. M., Gastfriend, D. R., Elman, I., et al. (2004). Decreased absolute amygdala volume in cocaine addicts. Neuron, 44(4), 729–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.027.
Makris, N., Schlerf, J. E., Hodge, S. M., Haselgrove, C., Albaugh, M. D., Seidman, L. J., et al. (2005). MRI-based surface-assisted parcellation of human cerebellar cortex: an anatomically specified method with estimate of reliability. NeuroImage, 25(4), 1146–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.12.056.
Makris, N., Goldstein, J. M., Kennedy, D., Hodge, S. M., Caviness, V. S., Faraone, S. V., Tsuang, M. T., & Seidman, L. J. (2006). Decreased volume of left and total anterior insular lobule in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 155–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2005.11.020.
Markowitsch, H. J., Emmans, D., Irle, E., Streicher, M., & Preilowski, B. (1985). Cortical and subcortical afferent connections of the primate’s temporal pole: a study of rhesus monkeys, squirrel monkeys, and marmosets. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 242(3), 425–458. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902420310.
Martin, R. F., & Bowden, D. M. (1996). A stereotaxic template atlas of the macaque brain for digital imaging and quantitative neuroanatomy. NeuroImage, 4(2), 119–150. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1996.0036.
Matelli, M., Camarda, R., Glickstein, M., & Rizzolatti, G. (1986). Afferent and efferent projections of the inferior area 6 in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 251(3), 281–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902510302.
Matelli, M., Luppino, G., & Rizzolatti, G. (1985). Patterns of cytochrome oxidase activity in the frontal agranular cortex of the macaque monkey. Behavioural Brain Research, 18(2), 125–136.
Matelli, M., Luppino, G., & Rizzolatti, G. (1991). Architecture of superior and mesial area 6 and the adjacent cingulate cortex in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 311(4), 445–462.
Maunsell, J. H., & Van Essen, D. C. (1987). Topographic organization of the middle temporal visual area in the macaque monkey: representational biases and the relationship to callosal connections and myeloarchitectonic boundaries. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 266(4), 535–555. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902660407.
McLaren, D. G., Kosmatka, K. J., Oakes, T. R., Kroenke, C. D., Kohama, S. G., Matochik, J. A., et al. (2009). A population-average MRI-based atlas collection of the rhesus macaque. NeuroImage, 45(1), 52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.058.
Medalla, M., & Barbas, H. (2014). Specialized prefrontal “auditory fields”: organization of primate prefrontal-temporal pathways. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 8, 77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2014.00077.
Mesulam, M. M., & Mufson, E. J. (1982a). Insula of the old world monkey. I. Architectonics in the insulo-orbito-temporal component of the paralimbic brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 212(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902120102.
Mesulam, M. M., & Mufson, E. J. (1982b). Insula of the old world monkey. III: Efferent cortical output and comments on function. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 212(1), 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902120104.
Mesulam, M.-M. (2000). Principles of behavioral and cognitive neurology. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Mesulam, M.-M. (2012). The evolving landscape of human cortical connectivity: facts and inferences. Neuroimage, 62, 2182–2189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.033.
Mettler, F. A. (1933). Brain of pithecus rhesus (M. rhesus). American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 17(3), 309–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.1330170315.
Miyashita, T., & Rockland, K. S. (2007). GABAergic projections from the hippocampus to the retrosplenial cortex in the rat. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 26(5), 1193–1204. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05745.x.
Morán, M. A., Mufson, E. J., & Mesulam, M. M. (1987). Neural inputs into the temporopolar cortex of the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 256(1), 88–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902560108.
Morecraft, R. J., Cipolloni, P. B., Stilwell-Morecraft, K. S., Gedney, M. T., & Pandya, D. N. (2004). Cytoarchitecture and cortical connections of the posterior cingulate and adjacent somatosensory fields in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 469(1), 37–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10980.
Morecraft, R. J., Geula, C., & Mesulam, M. M. (1992). Cytoarchitecture and neural afferents of orbitofrontal cortex in the brain of the monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 323(3), 341–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903230304.
Morecraft, R. J., Stilwell-Morecraft, K. S., Cipolloni, P. B., Ge, J., McNeal, D. W., & Pandya, D. N. (2012). Cytoarchitecture and cortical connections of the anterior cingulate and adjacent somatomotor fields in the rhesus monkey. Brain Research Bulletin, 87(4–5), 457–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.12.005.
Morecraft, R. J., Stilwell-Morecraft, K. S., Ge, J., Cipolloni, P. B., & Pandya, D. N. (2015). Cytoarchitecture and cortical connections of the anterior insula and adjacent frontal motor fields in the rhesus monkey. Brain Research Bulletin, 119(Pt A), 52–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.10.004.
Morel, A., Garraghty, P. E., & Kaas, J. H. (1993). Tonotopic organization, architectonic fields, and connections of auditory cortex in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 335(3), 437–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903350312.
Morris, R., Petrides, M., & Pandya, D. N. (1999). Architecture and connections of retrosplenial area 30 in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). The European Journal of Neuroscience, 11(7), 2506–2518.
Mufson, E. J., & Mesulam, M. M. (1982). Insula of the old world monkey. II: Afferent cortical input and comments on the claustrum. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 212(1), 23–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902120103.
Murata, A., Gallese, V., Kaseda, M., & Sakata, H. (1996). Parietal neurons related to memory-guided hand manipulation. Journal of Neurophysiology, 75(5), 2180–2186. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1996.75.5.2180.
Nelson, R. J., Sur, M., Felleman, D. J., & Kaas, J. H. (1980). Representations of the body surface in postcentral parietal cortex of Macaca fascicularis. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 192(4), 611–643. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901920402.
Nichols, B. N., Mejino, J. L., Detwiler, L. T., Nilsen, T. T., Martone, M. E., Turner, J. A., Rubin, D. L., & Brinkley, J. F. (2014). Neuroanatomical domain of the foundational model of anatomy ontology. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, 5(1), 1.
Nieuwenhuys, R., Voogd, J., & van Huijzen, C. (2008). The human central nervous system (4th ed.). Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Ongür, D., An, X., & Price, J. L. (1998). Prefrontal cortical projections to the hypothalamus in macaque monkeys. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 401(4), 480–505.
Ono, M., Kubik, S., & Abernathy, C. D. (1990). Atlas of the cerebral sulci. New York, NY: Thieme.
Ortiz-Rios, M., Azevedo, F. A. C., Kuśmierek, P., Balla, D. Z., Munk, M. H., Keliris, G. A., et al. (2017). Widespread and opponent fmri signals represent sound location in macaque auditory cortex. Neuron, 93(4), 971–983.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.013.
Pandya, D. N., & Kuypers, H. G. J. M. (1969). Cortico-cortical connections in the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 13(1), 13–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(69)90141-3.
Pandya, D. N., Dye, P., & Butters, N. (1971). Efferent cortico-cortical projections of the prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 31(1), 35–46.
Pandya, D. N., Seltzer, B., Petrides, M., & Cipolloni, P. B. (2015). Cerebral cortex: architecture, connections, and the dual origin concept. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Pandya, D. N., & Sanides, F. (1973). Architectonic parcellation of the temporal operculum in rhesus monkey and its projection pattern. Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte, 139(2), 127–161.
Pandya, D. N., & Yeterian, E. H. (1985). Architecture and connections of cortical association areas. In E. Jones and A. Peters (Eds.), Cerebral cortex (pp. 3-61). New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Passarelli, L., Rosa, M. G. P., Bakola, S., Gamberini, M., Worthy, K. H., Fattori, P., & Galletti, C. (2018). Uniformity and diversity of cortical projections to precuneate areas in the macaque monkey: what defines area PGm? Cerebral Cortex, 28(5), 1700–1717. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx067.
Paul, R. L., Merzenich, M., & Goodman, H. (1972). Representation of slowly and rapidly adapting cutaneous mechanoreceptors of the hand in Brodmann’s areas 3 and 1 of Macaca mulatta. Brain Research, 36(2), 229–249.
Paus, T. (2001). Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(6), 417–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/35077500.
Paxinos, G., Huang, X.-F., Petrides, M., & Toga, A. W. (2008). The rhesus monkey brain: in stereotaxic coordinates (2nd ed.) San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Pereira-Pedro, A. S., Rilling, J. K., Chen, X., Preuss, T. M., & Bruner, E. (2017). Midsagittal brain variation among non-human primates: insights into evolutionary expansion of the human precuneus. Brain, Behavior and Evolution, 90(3), 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481085.
Perrett, D. I., Rolls, E. T., & Caan, W. (1982). Visual neurones responsive to faces in the monkey temporal cortex. Experimental Brain Research, 47(3), 329–342.
Petersen, M. V., Mlakar, J., Haber, S. H., Parent, M., Smith, Y., Strick, P. L., Griswold, M. A., & McIntyre, C. C. (2019). Holographic reconstruction of axonal pathways in the human brain. Neuron, S0896-6273(19), 30832–30833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.09.030.
Petrides, M., & Pandya, D. N. (1984). Projections to the frontal cortex from the posterior parietal region in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 228(1), 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902280110.
Petrides, M., & Pandya, D. N. (2002). Comparative cytoarchitectonic analysis of the human and the macaque ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and corticocortical connection patterns in the monkey. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 16(2), 291–310.
Petrides, M., & Pandya, D. N. (2007). Efferent association pathways from the rostral prefrontal cortex in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(43), 11573–11586. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2419-07.2007.
Piserchia, V., Breveglieri, R., Hadjidimitrakis, K., Bertozzi, F., Galletti, C., & Fattori, P. (2017). Mixed body/hand reference frame for reaching in 3D space in macaque parietal area PEc. Cerebral Cortex, 27(3), 1976–1990. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw039.
Platt, M. L., & Glimcher, P. W. (1999). Neural correlates of decision variables in parietal cortex. Nature, 400(6741), 233–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/22268.
Polimeni, J. R., Balasubramanian, M., & Schwartz, E. L. (2006). Multi-area visuotopic map complexes in macaque striate and extra-striate cortex. Vision Research, 46(20), 3336–3359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2006.03.006.
Polyak, S. (1957). The vertebrate visual system. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Powell, T. P., Cowan, W. M., & Raisman, G. (1965). The central olfactory connexions. Journal of Anatomy, 99(Pt 4), 791–813.
Price, J. L., & Powell, T. P. (1971). Certain observations on the olfactory pathway. Journal of Anatomy, 110(Pt 1), 105–126.
Pritchard, T. C., Hamilton, R. B., Morse, J. R., & Norgren, R. (1986). Projections of thalamic gustatory and lingual areas in the monkey, Macaca fascicularis. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 244(2), 213–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902440208.
Quallo, M. M., Price, C. J., Ueno, K., Asamizuya, T., Cheng, K., Lemon, R. N., & Iriki, A. (2010). Creating a population-averaged standard brain template for Japanese macaques (M. fuscata). NeuroImage, 52(4), 1328–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.006.
Rademacher, J., Caviness, V. S., Steinmetz, H., & Galaburda, A. M. (1993). Topographical variation of the human primary cortices: implications for neuroimaging, brain mapping, and neurobiology. Cerebral Cortex, 3(4), 313–329. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/3.4.313.
Rademacher, J., Galaburda, A. M., Kennedy, D. N., Filipek, P. A., & Caviness, V. S. (1992). Human cerebral cortex: localization, parcellation, and morphometry with magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 4(4), 352–374. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.1992.4.4.352.
Rajkowska, G., & Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1995a). Cytoarchitectonic definition of prefrontal areas in the normal human cortex: I. Remapping of areas 9 and 46 using quantitative criteria. Cerebral Cortex, 5(4), 307–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/5.4.307.
Rajkowska, G., & Goldman-Rakic, P. S. (1995b). Cytoarchitectonic definition of prefrontal areas in the normal human cortex: II. Variability in locations of areas 9 and 46 and relationship to the Talairach Coordinate System. Cerebral Cortex, 5(4), 323–337. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/5.4.323.
Raos, V., Umiltá, M.-A., Murata, A., Fogassi, L., & Gallese, V. (2006). Functional properties of grasping-related neurons in the ventral premotor area F5 of the macaque monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology, 95(2), 709–729. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00463.2005.
Rauschecker, J. P., & Tian, B. (2000). Mechanisms and streams for processing of “what” and “where” in auditory cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(22), 11800–11806. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.22.11800.
Rauschecker, J. P., & Scott, S. K. (2009). Maps and streams in the auditory cortex: nonhuman primates illuminate human speech processing. Nature Neuroscience, 12(6), 718–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2331.
Recanzone, G. H., & Cohen, Y. E. (2010). Serial and parallel processing in the primate auditory cortex revisited. Behavioural Brain Research, 206(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.08.015.
Rempel-Clower, N. L., & Barbas, H. (1998). Topographic organization of connections between the hypothalamus and prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 398(3), 393–419.
Reveley, C., Gruslys, A., Ye, F. Q., Glen, D., Samaha, J., E Russ, B., et al. (2017). Three-dimensional digital template atlas of the macaque brain. Cerebral Cortex, 27(9), 4463–4477. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw248.
Rizzolatti, G., Fadiga, L., Gallese, V., & Fogassi, L. (1996). Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 3(2), 131–141.
Rizzolatti, G., & Matelli, M. (2003). Two different streams form the dorsal visual system: anatomy and functions. Experimental Brain Research, 153(2), 146–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1588-0.
Rohlfing, T., Kroenke, C. D., Sullivan, E. V., Dubach, M. F., Bowden, D. M., Grant, K., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2012). The INIA19 template and neuromaps atlas for primate brain image parcellation and spatial normalization. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2012.00027.
Rolls, E. T., & Baylis, L. L. (1994). Gustatory, olfactory, and visual convergence within the primate orbitofrontal cortex. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 14(9), 5437–5452.
Rolls, E. T., Critchley, H. D., & Treves, A. (1996). Representation of olfactory information in the primate orbitofrontal cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 75(5), 1982–1996. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1996.75.5.1982.
Rolls, E. T., Verhagen, J. V., & Kadohisa, M. (2003). Representations of the texture of food in the primate orbitofrontal cortex: neurons responding to viscosity, grittiness, and capsaicin. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90(6), 3711–3724. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00515.2003.
Romanski, L. M., Tian, B., Fritz, J., Mishkin, M., Goldman-Rakic, P. S., & Rauschecker, J. P. (1999). Dual streams of auditory afferents target multiple domains in the primate prefrontal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 2(12), 1131–1136. https://doi.org/10.1038/16056.
Rosene, D. L., & Van Hoesen, G. W. (1977). Hippocampal efferents reach widespread areas of cerebral cortex and amygdala in the rhesus monkey. Science, 198(4314), 315–317.
Rozzi, S., Calzavara, R., Belmalih, A., Borra, E., Gregoriou, G. G., Matelli, M., & Luppino, G. (2006). Cortical connections of the inferior parietal cortical convexity of the macaque monkey. Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1389–1417. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhj076.
Rozzi, S., Ferrari, P. F., Bonini, L., Rizzolatti, G., & Fogassi, L. (2008). Functional organization of inferior parietal lobule convexity in the macaque monkey: electrophysiological characterization of motor, sensory and mirror responses and their correlation with cytoarchitectonic areas. European Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 1569–1588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06395.x.
Rushmore, R. J., Bouix, S., Kubicki, M., Rathi, Y., Yeterian, E. H., & Makris, N. (2019). MRI-based parcellation and morphometry of the individual rhesus monkey brain: a translational system referencing a standardized ontology. bioRxiv, 699710. https://doi.org/10.1101/699710.
Rushmore, R. J., Bouix, S., Kubicki, M., Rathi, Y., Yeterian, E. H., & Makris, N. (2020). How human is human connectional neuroanatomy? Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 14: 18 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2020.00018.
Sakata, H., Takaoka, Y., Kawarasaki, A., & Shibutani, H. (1973). Somatosensory properties of neurons in the superior parietal cortex (area 5) of the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 64, 85–102.
Saleem, K. S., Kondo, H., & Price, J. L. (2008). Complementary circuits connecting the orbital and medial prefrontal networks with the temporal, insular, and opercular cortex in the macaque monkey. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 506(4), 659–693. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21577.
Saleem, K. S., & Logothetis, N. K. (2012). A combined MRI and histology atlas of the rhesus monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates (2nd ed.). London, UK: Academic Press.
Sanides, F. (1968). The architecture of the cortical taste nerve areas in squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus) and their relationships to insular, sensorimotor and prefrontal regions. Brain Research, 8(1), 97–124.
Sanides, F. (1962). Die Architektonik des menschlichen Stirnhirns. Berlin: Springer.
Sasaki, K., & Gemba, H. (1986). Effects of premotor cortex cooling upon visually initiated hand movements in the monkey. Brain Research, 374(2), 278–286.
Schilling, K. G., Nath, V., Hansen, C., Parvathaneni, P., Blaber, J., Gao, Y., et al. (2019). Limits to anatomical accuracy of diffusion tractography using modern approaches. NeuroImage, 185, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.10.029.
Schmahmann, J., & Pandya, D. (2006). Fiber pathways of the brain. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Schmahmann, J.D., Pandya, D.N., Wang, R., Dai, G., D'Arceuil, H.E., de Crespigny, A.J. et al. (2007). Association fibre pathways of the brain: parallel observations from diffusion spectrum imaging and autoradiography. Brain, 130(3):630–653. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl359
Schneider, R. J., Friedman, D. P., & Mishkin, M. (1993). A modality-specific somatosensory area within the insula of the rhesus monkey. Brain Research, 621(1), 116–120.
Scott, B. H., Leccese, P. A., Saleem, K. S., Kikuchi, Y., Mullarkey, M. P., Fukushima, M., et al. (2017). Intrinsic connections of the core auditory cortical regions and rostral supratemporal plane in the macaque monkey. Cerebral Cortex, 27(1), 809–840. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv277.
Seiditz, J., Sponheim, C., Glen, D., Ye, F. Q., Saleem, K. S., Leopold, D. A., Ungerleider, L., & Messinger, A. (2018). A population MRI brain template and analysis tools for the macaque. Neuroimage, 170, 121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.063.
Sinclair, R. J., & Burton, H. (1993). Neuronal activity in the second somatosensory cortex of monkeys (Macaca mulatta) during active touch of gratings. Journal of Neurophysiology, 70(1), 331–350. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1993.70.1.331.
Stanton, G. B., Cruce, W. L., Goldberg, M. E., & Robinson, D. L. (1977). Some ipsilateral projections to areas PF and PG of the inferior parietal lobule in monkeys. Neuroscience Letters, 6(2–3, 243), –250.
Suzuki, W. A., & Amaral, D. G. (1994). Perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices of the macaque monkey: cortical afferents. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 350(4), 497–533. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903500402.
Swanson, L. W. (2012). Brain architecture: understanding the basic plan (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Swanson, L. W. (2014). Neuroanatomical terminology: a lexicon of classical origins and historical foundations. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Tanaka, K., Saito, H., Fukada, Y., & Moriya, M. (1991). Coding visual images of objects in the inferotemporal cortex of the macaque monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology, 66(1), 170–189. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.170.
Ten Donkelaar, H. J., Broman, J., Neumann, P. E., Puelles, L., Riva, A., Tubbs, R. S., & Kachlik, D. (2017). Towards a Terminologia Neuroanatomica. Clinical Anatomy, 30(2), 145–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.22809.
Ten Donkelaar, H. J., Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., & Mai, J. K. (2018). Toward a common terminology for the gyri and sulci of the human cerebral cortex. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 12, 93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00093.
Tian, B., Reser, D., Durham, A., Kustov, A., & Rauschecker, J. P. (2001). Functional specialization in rhesus monkey auditory cortex. Science, 292(5515), 290–293. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1058911.
Tootell, R. B., Switkes, E., Silverman, M. S., & Hamilton, S. L. (1988). Functional anatomy of macaque striate cortex. II. Retinotopic organization. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 8(5), 1531–1568.
Ungerleider, L. G., & Mishkin, M. (1982). Two cortical visual systems. In D.J. Ingle, M.A. Goodale & R.J.W. Mansfield (Eds.), Analysis of visual behavior Cambridge, MA. : The MIT Press.
Ungerleider, L. G., Galkin, T. W., Desimone, R., & Gattass, R. (2008). Cortical connections of area V4 in the macaque. Cerebral Cortex, 18(3), 477–499. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhm061.
Uylings, H. B. M., Rajkowska, G., Sanz-Arigita, E., Amunts, K., & Zilles, K. (2005). Consequences of large interindividual variability for human brain atlases: converging macroscopical imaging and microscopical neuroanatomy. Anatomy and Embryology, 210(5–6), 423–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-005-0042-4.
Van Der Gucht, E., Youakim, M., Arckens, L., Hof, P. R., & Baizer, J. S. (2006). Variations in the structure of the prelunate gyrus in Old World monkeys. The Anatomical Record. Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology, 288(7), 753–775. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.a.20350.
Van Essen, D. C., Maunsell, J. H. R., & Bixby, J. L. (1981). Organization of extrastriate visual areas in the macaque monkey. In C. N. Woosley (Ed.), Multiple visual areas (pp. 157–170). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-5814-8_6.
Van Essen, D. C., Newsome, W. T., & Maunsell, J. H. (1984). The visual field representation in striate cortex of the macaque monkey: asymmetries, anisotropies, and individual variability. Vision Research, 24(5), 429–448.
Van Essen, D. C., Glasser, M. F., Dierker, D. L., & Harwell, J. (2012). Cortical parcellations of the macaque monkey analyzed on surface-based atlases. Cerebral Cortex, 22(10), 2227–2240. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr290.
Van Hoesen, G., & Pandya, D. N. (1975). Some connections of the entorhinal (area 28) and perirhinal (area 35) cortices of the rhesus monkey. I. Temporal lobe afferents. Brain Research, 95(1), 1–24.
Van Hoesen, G. W. (1982). The parahippocampal gyrus: new observations regarding its cortical connections in the monkey. Trends in Neurosciences, 5, 345–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-2236(82)90201-6.
Vogt, B. A., & Pandya, D. N. (1987). Cingulate cortex of the rhesus monkey: II. Cortical afferents. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 262(2), 271–289. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.902620208.
Vogt, B. A., Vogt, L., Farber, N. B., & Bush, G. (2005). Architecture and neurocytology of monkey cingulate gyrus. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 485(3), 218–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20512.
Werner, G., & Whitsel, B. L. (1968). Topology of the body representation in somatosensory area I of primates. Journal of Neurophysiology, 31(6), 856–869. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1968.31.6.856.
Wiesel, T. N., & Hubel, D. H. (1974). Ordered arrangement of orientation columns in monkeys lacking visual experience. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 158(3), 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901580306.
Woolsey, C. N., Marshall, W. H., & Bard, P. (1942). Representation of cutaneous tactile sensibility in the cerebral cortex of the monkey as indicated by evoked potentials. Johns Hopkins Hospital Bulletin, 70, 399–441.
Yeterian, E. H., Pandya, D. N., Tomaiuolo, F., & Petrides, M. (2012). The cortical connectivity of the prefrontal cortex in the monkey brain. Cortex; a Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior, 48(1), 58–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2011.03.004.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from the National Institutes of Health (R01 MH112748, R01 AG042512, RF1-AG062831, K24 MH116366) and from NSF (Grant PHY1505000). NM was a Fellow at the Hanse-Wissenschaftskolleg Institute for Advanced Study, Delmenhorst, Germany while working on this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
ESM 2
Cortical Parcellation (CP) Results – Images for the cortical parcellations for each coronal section. Each coronal section is shown in native view (no overlay), with parcellation borders shown as overlaid lines, and then as overlaid filled objects. Abbreviations are in the margin, and correspond to those in Figure 6. (PDF 72334 kb)
ESM 3
General Segmentation (GS) Results – Images of the general segmentation. Image conventions as in CP Results (PDF 83218 kb)
ESM 4
(PDF 83 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rushmore, R.J., Bouix, S., Kubicki, M. et al. MRI-based Parcellation and Morphometry of the Individual Rhesus Monkey Brain: the macaque Harvard-Oxford Atlas (mHOA), a translational system referencing a standardized ontology. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 1589–1621 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00357-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00357-9