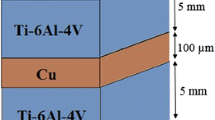
Abstract
Solid-state diffusion bonding (DB) of TiAl alloy and Ti2AlNb alloy was carried out using pure Ti as an interlayer at 1000 °C under 20 MPa for 60–120 min. The effects of bonding times on the interfacial microstructure and mechanical performance of the TiAl/Ti/Ti2AlNb bonded joints at room temperature (RT) were investigated detailly. The results demonstrated that the diffusion layers (DLs) mainly consisted of four characteristic layers, (I) single coarse α2 phase adjacent TiAl alloy, (II) single refined α2 phase at the bonding interface, (III) equiaxed/acicular α2 phase embedded in β phase adjacent Ti2AlNb alloy and (IV) both equiaxed α2 phase and acicular O phase embedded in β phase adjacent Ti2AlNb alloy, respectively. The thickness of the four layers increased with the increasing of the bonding time. The growth of DLs is controlled by diffusion and the reaction rate constant k for region I, II, III and IV are 1.22 × 10−6, 1.27 × 10−6, 2.6 × 10−7 and 7.7 × 10−7 m·s−1/2, respectively. Meanwhile, the interface α2 grain grows up without texture. The maximum tensile strength of 281 MPa was maintained at 1000 °C for 90 min under the pressure of 20 MPa. Consequently, the phase transformation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of the DLs were discussed.
Graphic abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemens H, Mayer S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 2013;15(4):191.
Shao HP, Wang Z, Lin T, Ye Q, Guo ZM. Preparation of TiAl alloy powder by high-energy ball milling and diffusion reaction at low temperature. Rare Met. 2018;37(1):21.
Williams JC, Starke EA. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Mater. 2003;51(19):5775.
Tetsui T, Shindo K, Kaji S, Kobayashi S, Takeyama M. Fabrication of TiAl components by means of hot forging and machining. Intermetallics. 2005;13(9):971.
Wu XH. Review of alloy and process development of TiAl alloys. Intermetallics. 2006;14(10–11):1114.
Yang Y, Chen RR, Fang HZ, Guo JJ, Ding HS, Su YQ, Fu HZ. Improving microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti43Al5Nb0.1B alloy by addition of Fe. Rare Metals. 2019;38(11):1024.
Tang B, Zhao FT, Chu YD, Kou HC, Li JS. Hot workability and superplasticity of low-Al and high-Nb containing TiAl alloys. JOM. 2017;69(12):2610.
He YS, Hu R, Luo WZ, He T, Liu XH. Oxidation behavior of a novel multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy in the temperature range of 650 °C to 850 °C. Rare Met. 2018;37(10):838.
He YS, Hu R, Luo WZ, He T, Lai YJ, Du YJ, Liu XH. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a new Ti2AlNb-based alloy after aging treatment. Rare Met. 2018;37(11):942.
Zou GS, Xie EH, Bai HL, Wu AP, Wang Q, Ren JL. A study on transient liquid phase diffusion bonding of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;499(499):101.
Wang Y, Cai XQ, Yang ZW, Qiu QW, Wang DP, Liu YC. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy joints brazed with Ti-Ni-Nb alloy. Mater Chem Phys. 2016;182:488.
Ren HS, Xiong HP, Chen B, Pang SJ, Wu X, Cheng YY, Chen BQ. Transient liquid phase diffusion bonding of Ti–24Al–15Nb–1Mo alloy to TiAl intermetallics. Mater Sci Eng A. 2016;651:45.
Chen GQ, Zhang G, Yin QX, Zhang BG, Feng JC. Microstructure evolution of electron beam welded joints of Ti-43Al-9V-0.3Y and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Mater Lett. 2018;233:336.
Li ZF, Wu GQ, Huang Z, Ruan ZJ. Diffusion bonding of laser surface modified TiAl alloy/Ni alloy. Mater Lett. 2004;58(27):3470.
Wu GQ, Huang Z, Chen CQ, Ruan ZJ, Zhang Y. Superplastic diffusion bonding of γ-TiAl-based alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2004;380(1):402.
Song XG, Cao J, Liu JK, Zhao LY, Feng JC. Reaction-diffusion bonding of high Nb containing TiAl alloy. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2014;43(1):28.
Chu Y, Li JS, Zhu L, Tang B, Kou HC. Characterization of the interfacial-microstructure evolution and void shrinkage of Ti-22Al-25Nb orthorhombic alloy with different surface roughness during diffusion bonding. Intermetallics. 2017;90:119.
Zhu L, Li JS, Tang B, Liu Y, Zhang MQ, Li L, Kou HC. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of diffusion bonding high Nb containing TiAl alloy to Ti2AlNb alloy. Vacuum. 2019;164:140.
Bian H, Lei YZ, Fu W, Hu SP, Song XG, Feng JC. Diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb alloy and high-Nb-containing TiAl alloy: interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties. Metals. 2018;8(12):1061.
Wang ZC, Li C, Qi JL, Feng JC, Cao J. Characterization of hydrogenated niobium interlayer and its application in TiAl/Ti2AlNb diffusion bonding. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2019;44(13):6929.
Simoes S, Ramos AS, Viana F, Vieira MT, Vieira MF. TiAl diffusion bonding using Ni/Ti multilayers. Weld World. 2017;61(6):1267.
Wang Y, Cai XQ, Yang ZW, Wang DP, Liu XG, Liu YC. Diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb alloy using pure Ti foil as an interlayer. J Alloy Compd. 2018;756:163.
Li X, Wang GF, Gu YB, Yang JL. Electrically assisted diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb alloy sheet using CP-Ti foil interlayer: microstructural characterization and mechanical tests. Mater Sci Eng A. 2019;744:733.
Li HQ, Wang QM, Gong J, Sun C. Interfacial reactions and oxidation behavior of Al2O3 and Al2O3/Al coatings on an orthorhombic Ti2AlNb alloy. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257(9):4105.
Ramos AS, Vieira MT, Duarte LI, Vieira MF, Viana F, Calinas R. Nanometric multilayers: a new approach for joining TiAl. Intermetallics. 2006;14(10):1157.
Liu J, Cao J, Lin X, Chen H, Wang J, Feng JC. Interfacial microstructure and joining properties of TiAl/Ti3AlC2 diffusion bonded joints using Zr and Ni foils as interlayer. Vacuum. 2014;102:16.
Sun LX, Li MQ, Li H. Interface characteristics and recrystallization mechanism of dissimilar titanium bonds. J Mater Sci. 2018;53(7):5380.
Tang B, Qi XS, Kou HC, Li JS, Milenkovic S. Recrystallization behavior at diffusion bonding interface of high Nb containing TiAl alloy. Adv Eng Mater. 2016;18(4):657.
Jia L, Yang F, Lu ZL, Wang J, Liu PY. W-Al2O3 heterogeneous bonding by hot-press sintering: Cr diffusion and mechanical strength. Mater Lett. 2018;211:216.
Wang Q, Chen GQ, Wang K, Fu XS, Zhou WL. Microstructural evolution and growth kinetics of interfacial compounds in TiAl/Ti3SiC2 diffusion bonding joints. Mater Sci Eng A. 2019;756:149.
He P, Feng JC, Zhang BG, Qian YY. A new technology for diffusion bonding intermetallic TiAl to steel with composite barrier layers. Mater Charact. 2003;50(1):87.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51771150), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0701303), the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (No. 201936053001) and the Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Solidification (NWPU), China (No. 2019-TS-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Tang, B., Ding, MX. et al. Interface characteristic and mechanical performance of TiAl/Ti2AlNb diffusion bonding joint with pure Ti interlayer. Rare Met. 39, 1402–1412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01548-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01548-5