Abstract
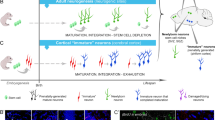
Mammalian taste bud cells have a limited lifespan and differentiate into type I, II, and III cells from basal cells (type IV cells) (postmitotic precursor cells). However, little is known regarding the cell lineage within taste buds. In this study, we investigated the cell fate of Mash1-positive precursor cells utilizing the Cre-loxP system to explore the differentiation of taste bud cells. We found that Mash1-expressing cells in Ascl1CreERT2::CAG-floxed tdTomato mice differentiated into taste bud cells that expressed aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) and carbonic anhydrase IV (CA4) (type III cell markers), but did not differentiate into most of gustducin (type II cell marker)-positive cells. Additionally, we found that Mash1-expressing cells could differentiate into phospholipase C β2 (PLCβ2)-positive cells, which have a shorter lifespan compared with AADC- and CA4-positive cells. These results suggest that Mash1-positive precursor cells could differentiate into type III cells, but not into most of type II cells, in the taste buds.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beidler LM, Smallman RL (1965) Renewal of cells within taste buds. J Cell Biol 27:263–272
Bertrand N, Castro DS, Guilemot F (2002) Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat Rev Neurosci 475:128–141
Boughter JD Jr, Pumplin DW, Yu C, Christy RC, Smith DV (1997) Differential expression of α-gustducin in taste bud populations of the rat and hamster. J Neurosci 17:2852–2858
Chandrashekar J, Yarmolinsky D, von Buchholtz L, Oka Y, Sly W, Ryba NJ, Zucker CS (2009) The taste of carbonation. Science 326:443–445
Clapp TR, Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon SC, Kinnamon JC (2004) Morphologic characterization of rat taste receptor cells that express components of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Comp Neurol 468:311–321
DeFazio RA, Dvoryanchikov G, Maruyama Y, Kim JW, Pereira E, Roper SD, Chaudhari N (2006) Separate populations of receptor cells and presynaptic cells in mouse taste buds. J Neurosci 26:3971–3980
Delay RJ, Kinnamon JC, Roper SD (1986) Ultrastructure of mouse vallate taste buds: II. Cell types and cell lineage. J Comp Neurol 253:242–252
Farbman AI (1965a) Fine structure of the taste bud. J Ultrastruct Res 12:242–252
Farbman AI (1965b) Electron microscope study of developing taste buds in rat fungiform papillae. Dev Biol 11:55–68
Farbman AI (1980) Renewal of taste bud cells in rat circumvallate papillae. Cell Tissue Kinet 13:349–357
Finger TE, Simon SA (2000) Cell biology of taste epithelium. In: Finger TE, Silver WL, Restrepo D (eds) The neurobiology of taste and smell. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 287–314
Fujimoto S, Murray RG (1970) Fine structure of degeneration and regeneration in denerved rabbit vallate taste buds. Anat Rec 168:393–413
Guillemot F, Lo LC, Johnson JE, Auerbach A, Anderson DJ, Joyner AL (1993) Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell 75:463–476
Johnson JE, Birren SJ, Anderson DJ (1990) Two rat homologues of Drosophila achaete-scute specifically expressed in neuronal precursors. Nature 346:858–861
Kim MR, Kusakabe Y, Miura H, Shindo Y, Ninomiya Y, Hino A (2003) Regional expression patterns of taste receptors and gustducin in the mouse tongue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:500–506
Kito-Shingaki A, Seta Y, Toyono T, Kataoka S, Kakinoki Y, Yanagawa Y, Toyoshima K (2014) Expression of GAD67 and Dlx5 in the taste buds of mice genetically lacking Mash1. Chem Senses 39:403–414
Lindeman B (1996) Taste reception. Physiol Rev 76:719–766
Lo LC, Johnson JE, Wuenschell CW, Saito T, Anderson DJ (1991) Mammalian achaete-scyte homolog 1 is transiently expressed by specially-restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev 5:1524–1537
Miura H, Kusakabe Y, Harada S (2006) Cell lineage and differentiation in taste buds. Arch Histol Cytol 69:209–225
Miura H, Scott JK, Harada S, Barlow LA (2014) Sonic hedgehog-expressing basal cells are general post-mitotic precursor of functional taste receptor cells. Dev Dyn 243:1286–1297
Murray RG (1986) The mammalian taste bud type III cell: a critical analysis. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res 95:175–188
Perea-Martinez I, Nagai T, Chaudhari N (2013) Functional cell types in taste buds have distinct longevities. PLoS One 8:e53399
Pumplin DW, Yu C, Smith DV (1997) Light and dark cells of rat vallate taste buds are morphologically distinct cell types. J Comp Neurol 378:389–410
Rössler P, Kroner C, Freitag J, Noè J, Breer H (1998) Identification of a phospholipase C β subtype in rat taste cells. Eur J Cell Biol 77:253–261
Seta Y, Stoick-Cooper CL, Toyono T, Kataoka S, Toyoshima K, Barlow LA (2006) The bHLH transcription factors, Hes6 and Mash1, are expressed in distinct subsets of cells within adult mouse taste buds. Arch Histol Cytol 69:189–198
Seta Y, Kataoka S, Toyono T, Toyoshima T (2007) Immunohistochemical localization of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in mouse taste buds and developing taste papillae. Histochem Cell Biol 127:415–422
Seta Y, Oda M, Kataoka S, Toyono T, Toyoshima K (2011) Mash1 is required for the differentiation of AADC-positive type III cells in mouse taste buds. Dev Dyn 240:775–784
Stone LM, Finger TE, Tam PP, Tan SS (1995) Taste receptor cells arise from local epithelium, not neurogenic ectoderm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:1916–1920
Stone LM, TanS-S TPPL, Finger TE (2002) Analysis of cell lineage relationships in taste buds. J Neurosci 22:4522–4529
Takagi T, Seta Y, Kataoka S, Nakatomi M, Toyono T, Kawamoto K (2018) Mash1-expressing cells could differentiate to type III cells in adult mouse taste buds. Anat Sci Int 93:422–429
Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon JC (2004) Synaptobrevin-2-like immunoreactivity is associate with vesicles at synapses in rat circumvallate taste buds. J Comp Neurol 471:59–71
Yee CL, Yang R, Bottger B, Finger TE, Kinnamon JC (2001) "Type III" cells of rat taste buds: Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies of neuron-specific enolase, protein gene product 9.5, and serotonin. J Comp Neurol 440:97–108
Yee CL, Jones KR, Finger TE (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is present in adult mouse taste cells with synapses. J Comp Neurol 459:15–24
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Funding
The work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research number 18 K09525 to Y.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All of the animals used in this study were maintained and handled according to the protocols approved by Kyushu Dental University Animal Care (Certification No: 17–010).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, CC., Seta, Y., Matsuyama, K. et al. Mash1-expressing cells may be relevant to type III cells and a subset of PLCβ2-positive cell differentiation in adult mouse taste buds. Cell Tissue Res 383, 667–675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03283-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03283-w