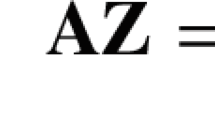Abstract
The method of Principal Informative Components (PIC) is presented for problems of statistical measurements, where the signal to be measured cannot be directly observed. Such situations include image reconstruction, system identification, communication channel reversal, media tomography, etc. The common feature of such problems, usually, is instability of their solutions to small variations of initial data that generally require the attraction of special methods of regularization. The basic principle of PIC method consists in employing decomposition of signals in special bases that were formed from eigenvectors of Fischer’s information operator. These bases are related to the method of Principal Components Analysis (PCA), which is well known in statistics, however, they have a somewhat different meaning as compared to the PCA method. The review indicates that by using the special procedures for selecting coordinate vectors, it is possible, first, to guarantee the signal estimation stability to unpredictable factors of problem and, second, to ensure a significant reduction of total measurement error as compared to the “direct” signal estimation, i.e., without the use of basis notions. The review presents a substantiation of PIC method application for problems of linear and nonlinear estimation. The composite technique of coordinate basis optimization is also considered that combines advantages of the physical approach (obviousness and effectiveness) with advantages of statistically informative approach (minimization of statistical errors). The specified technique is based on projecting the arbitrary coordinate basis on PIC subspace. As a result, the range of possible fluctuations of signal estimation is reduced and the upper bound of statistical error of signal measurement is lowered. Some numerical estimates of the PIC method efficiency are given using the example of problem of medium acoustic tomography that confirms the general theoretical conclusions. The review includes the analysis of some information technologies, where the ideas of PIC method hold a good promise for practical application. In particular, it is suggested that one of such promising fields can be MIMO systems that play an important part in 5G wireless access systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Oppenheim, R. W. Schaffer, J. R. Buck, Discrete-Time Signal Processing, 2nd ed. (Prentice Hall, NJ, 1999). ISBN 0-13-754920-2.
I. T. Jolliffe, Principal Component Analysis/Springer Series in Statistics, 2nd ed. (Springer-Verlag Inc., New York, 2010). ISBN 0-387-95442-2.
A. Papoulis, S. P. Pillai, Probability, Random Variables and Stochastic Processes, 4th ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002). ISBN 0-07-112256-7.
R. C. Aster, B. Borchers, C. H. Thurber, Parameter Estimation and Inverse Problems, 2nd ed. (Academic Press, New York, 2012). ISBN 978-0-12-385048-5.
V. Yu. Terebizh, Introduction to the Statistical Theory of Inverse Problems [in Russian] (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2005). ISBN 5-9221-0562-0.
V. Yu. Terebizh, “Image restoration with minimum a priori information,” Physics-Uspekhi38, 137 (1995). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1070/PU1995v038n02ABEH000068.
A. Ya. Kalyuzhnyi, “An algebraization of the acoustic tomography problem using the principal informative components,” Akustychnyi Visnyk1, No. 4, 19 (1998). URI: http://dspace.nbuv.gov.ua/handle/123456789/894.
A. Y. Kalyuzhny, L. G. Krasny, “Method of the main informative components for acoustic tomography,” J. Acoustical Soc. America105, No. 2, 1178 (1999). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1121/1.425573.
A. Y. Kalyuzhny, A. A. Kovtonyuk, “Method of the principal informative components for reconstruction problems,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process, ICASSP-2000, 5–7 June 2000, Istanbul, Turkey (IEEE, 2000), Vol. 1, pp. 169–172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2000.861902.
A. Y. Kalyuzhny, A. A. Kovtonyuk, “Optimal algebraic coding of noisy and distorted images,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Information Technology: Coding and Computing, ITCC-2001, 2–4 Apr. 2001, Las Vegas, USA (IEEE, 2001), pp. 537–541. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ITCC.2001.918852.
A. Y. Kalyuzhny, A. A. Kovtonyuk, “PIC-projection technique for decreasing of statistical error in signals reconstruction problems,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process, ICASSP-2001, 7–11 May 2001, Salt-Lake City, USA (IEEE, 2001), Vol. 6, pp. 3917–3920. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2001.940700.
A. Y. Kalyuzhny, A. A. Kovtonyuk, “Basis of the Principal Informative Components for signal estimation problems,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process, ICASSP-2002, 13–17 May 2002, Orlando, USA (IEEE, 2002), Vol. 1, pp. 335–338. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2002.5744937.
L. Zhao, H. Zhao, K. Zheng, W. Xiang, Massive MIMO in 5G Networks: Selected Applications / SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering (Springer International Publishing AG, 2012). ISBN 978-3-319-68408-6.
A. F. Molisch, Wireless Communication, 2nd ed. (John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2011). ISBN 9780470666692.
S. M. Kay, Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory. University of Rhode Island (Prentice Hall, NJ, 1998). ISBN 0-13-345711-7.
R. A. Horn, C. R. Johnson, Matrix Analysis, 2nd ed. (Cambridge University Press, 2013). ISBN 9780521548236.
R. E. Kaiman, “Contributions to the theory of optimal control,” Bol. Soc. Mat. Mexicana5, 102 (1960).
A. P. Sage, C. C. White, Optimum System Control, 2nd ed. (Prentice-Hall, Inc., NJ, 1977). ISBN 0-13-638296-7.
A. Y. Carmi, L. S. Mihaylova, S. J. Godsill, Compressed Sensing & Sparse Filtering (Springer Heidelberg, New York, Dordrecht, London, 2014). ISBN 978-3-642-38397-7.
G. E. Pfander (ed.). Sampling Theory, a Renaissance. Compressive Sensing and Other Developments (Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2015). ISBN 978-3-319-19748-7.
I. Andras, P. Dolinsky, L. Michaeli, J. Saliga, “Sparse signal acquisition via compressed sensing and principal component analysis,” Meas. Sci. Rev.18, No. 5, 175 2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/msr-2018-0025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2019, published in Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radioelektronika, 2019, Vol. 62, No. 11, pp. 643–661.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaliuzhnyi, O.Y. Method of Principal Informative Components in Problems of Statistical Measurements of Signal Parameters (Systematic Review). Radioelectron.Commun.Syst. 62, 541–558 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0735272719110013
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0735272719110013