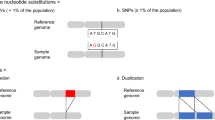
Abstract
Copy number variants (CNVs), defined as genome sequences of ≥50 bp that differ in copy number from that in a reference genome, are a common form of structural variation. Germline CNVs account for some of the missing heritability that single nucleotide polymorphisms could not account for. Recent technological advances have had a huge impact on CNV research. Microarray technology enables relatively low-cost, high-throughput, genome-wide measurements, and short-read sequencing technology enables the detection of short CNVs that cannot be detected by microarrays. As a result, large-scale genetic studies have been able to identify a variety of common and rare germline CNVs and their associations with diseases. Rare germline CNVs have been reported to be associated with neuropsychiatric disorders. In this review, we focused on germline CNVs and briefly described their functional characteristics, formation mechanisms, detection methods, related databases, and the latest findings. Finally, we introduced recent large-scale genetic studies to assess associations of CNVs with diseases, especially psychiatric disorders, and discussed the use of CNV-based animal models to investigate the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying these disorders. The development and implementation of improved detection methods, such as long-read single-molecule sequencing, are expected to provide additional insight into the molecular basis of psychiatric disorders and other complex diseases, thus facilitating basic and clinical research on CNVs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feuk L, Carson AR, Scherer SW. Structural variation in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:85–97.
Zarrei M, MacDonald JR, Merico D, Scherer SW. A copy number variation map of the human genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16:172–83.
Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ, Handsaker RE, Abyzov A, Huddleston J, et al. An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature. 2015;526:75–81.
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R, Feuk L, Gokcumen O, Zhang Y, et al. Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature. 2010;464:704–12.
Itsara A, Wu H, Smith JD, Nickerson DA, Romieu I, London SJ, et al. De novo rates and selection of large copy number variation. Genome Res. 2010;20:1469–81.
Roach JC, Glusman G, Smit AF, Huff CD, Hubley R, Shannon PT, et al. Analysis of genetic inheritance in a family quartet by whole-genome sequencing. Science. 2010;328:636–9.
Chiang C, Scott AJ, Davis JR, Tsang EK, Li X, Kim Y, et al. The impact of structural variation on human gene expression. Nat Genet. 2017;49:692–99.
Carvalho CM, Lupski JR. Mechanisms underlying structural variant formation in genomic disorders. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:224–38.
Hastings PJ, Lupski JR, Rosenberg SM, Ira G. Mechanisms of change in gene copy number. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:551–64.
Bailey JA, Gu Z, Clark RA, Reinert K, Samonte RV, Schwartz S, et al. Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science. 2002;297:1003–7.
Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet. 2002;18:74–82.
Lieber MR. The mechanism of double-strand DNA break repair by the nonhomologous DNA end-joining pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:181–211.
McVey M, Lee SE. MMEJ repair of double-strand breaks (director’s cut): deleted sequences and alternative endings. Trends Genet. 2008;24:529–38.
Lee JA, Carvalho CM, Lupski JR. A DNA replication mechanism for generating nonrecurrent rearrangements associated with genomic disorders. Cell. 2007;131:1235–47.
Hupe P, Stransky N, Thiery JP, Radvanyi F, Barillot E. Analysis of array CGH data: from signal ratio to gain and loss of DNA regions. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:3413–22.
Olshen AB, Venkatraman ES, Lucito R, Wigler M. Circular binary segmentation for the analysis of array-based DNA copy number data. Biostatistics. 2004;5:557–72.
Wang P, Kim Y, Pollack J, Narasimhan B, Tibshirani R. A method for calling gains and losses in array CGH data. Biostatistics. 2005;6:45–58.
Picard F, Robin S, Lavielle M, Vaisse C, Daudin JJ. A statistical approach for array CGH data analysis. BMC Bioinforma. 2005;6:27.
Karimpour-Fard A, Dumas L, Phang T, Sikela JM, Hunter LE. A survey of analysis software for array-comparative genomic hybridisation studies to detect copy number variation. Hum Genom. 2010;4:421–7.
Alkan C, Coe BP, Eichler EE. Genome structural variation discovery and genotyping. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:363–76.
Peiffer DA, Le JM, Steemers FJ, Chang W, Jenniges T, Garcia F, et al. High-resolution genomic profiling of chromosomal aberrations using Infinium whole-genome genotyping. Genome Res. 2006;16:1136–48.
Wang K, Li M, Hadley D, Liu R, Glessner J, Grant SF, et al. PennCNV: an integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res. 2007;17:1665–74.
Korn JM, Kuruvilla FG, McCarroll SA, Wysoker A, Nemesh J, Cawley S, et al. Integrated genotype calling and association analysis of SNPs, common copy number polymorphisms and rare CNVs. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1253–60.
Pinto D, Pagnamenta AT, Klei L, Anney R, Merico D, Regan R, et al. Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders. Nature. 2010;466:368–72.
Colella S, Yau C, Taylor JM, Mirza G, Butler H, Clouston P, et al. QuantiSNP: an Objective Bayes Hidden-Markov Model to detect and accurately map copy number variation using SNP genotyping data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:2013–25.
Zhang X, Du R, Li S, Zhang F, Jin L, Wang H. Evaluation of copy number variation detection for a SNP array platform. BMC Bioinforma. 2014;15:50.
Zhang Z, Cheng H, Hong X, Di Narzo AF, Franzen O, Peng S, et al. EnsembleCNV: an ensemble machine learning algorithm to identify and genotype copy number variation using SNP array data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:e39.
Zhao M, Wang Q, Wang Q, Jia P, Zhao Z. Computational tools for copy number variation (CNV) detection using next-generation sequencing data: features and perspectives. BMC Bioinforma. 2013;14(Suppl 11):S1.
Kosugi S, Momozawa Y, Liu X, Terao C, Kubo M, Kamatani Y. Comprehensive evaluation of structural variation detection algorithms for whole genome sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019;20:117.
Cameron DL, Schroder J, Penington JS, Do H, Molania R, Dobrovic A, et al. GRIDSS: sensitive and specific genomic rearrangement detection using positional de Bruijn graph assembly. Genome Res. 2017;27:2050–60.
Layer RM, Chiang C, Quinlan AR, Hall IM. LUMPY: a probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R84.
Zhang J, Wang J, Wu Y. An improved approach for accurate and efficient calling of structural variations with low-coverage sequence data. BMC Bioinforma. 2012;13(Suppl 6):S6.
Bartenhagen C, Dugas M. Robust and exact structural variation detection with paired-end and soft-clipped alignments: SoftSV compared with eight algorithms. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17:51–62.
Chen X, Schulz-Trieglaff O, Shaw R, Barnes B, Schlesinger F, Kallberg M, et al. Manta: rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:1220–2.
Kronenberg ZN, Osborne EJ, Cone KR, Kennedy BJ, Domyan ET, Shapiro MD, et al. Wham: identifying structural variants of biological consequence. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015;11:e1004572.
Tan R, Wang Y, Kleinstein SE, Liu Y, Zhu X, Guo H, et al. An evaluation of copy number variation detection tools from whole-exome sequencing data. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:899–907.
Lappalainen I, Lopez J, Skipper L, Hefferon T, Spalding JD, Garner J, et al. DbVar and DGVa: public archives for genomic structural variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D936–41.
Collins RL, Brand H, Karczewski KJ, Zhao X, Alfoldi J, Francioli LC, et al. A structural variation reference for medical and population genetics. Nature. 2020;581:444–51.
MacDonald JR, Ziman R, Yuen RK, Feuk L, Scherer SW. The database of genomic variants: a curated collection of structural variation in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D986–92.
Bragin E, Chatzimichali EA, Wright CF, Hurles ME, Firth HV, Bevan AP, et al. DECIPHER: database for the interpretation of phenotype-linked plausibly pathogenic sequence and copy-number variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D993–D1000.
Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Benson M, Brown G, Chao C, Chitipiralla S, et al. ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D862–8.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ, et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature. 2009;461:747–53.
de Cid R, Riveira-Munoz E, Zeeuwen PL, Robarge J, Liao W, Dannhauser EN, et al. Deletion of the late cornified envelope LCE3B and LCE3C genes as a susceptibility factor for psoriasis. Nat Genet. 2009;41:211–5.
McCarroll SA, Huett A, Kuballa P, Chilewski SD, Landry A, Goyette P, et al. Deletion polymorphism upstream of IRGM associated with altered IRGM expression and Crohn’s disease. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1107–12.
Wheeler E, Huang N, Bochukova EG, Keogh JM, Lindsay S, Garg S, et al. Genome-wide SNP and CNV analysis identifies common and low-frequency variants associated with severe early-onset obesity. Nat Genet. 2013;45:513–7.
Wellcome Trust Case Control C, Craddock N, Hurles ME, Cardin N, Pearson RD, Plagnol, et al. Genome-wide association study of CNVs in 16,000 cases of eight common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature. 2010;464:713–20.
Cooper GM, Coe BP, Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Vu TH, Baker C, et al. A copy number variation morbidity map of developmental delay. Nat Genet. 2011;43:838–46.
Betancur C. Etiological heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: more than 100 genetic and genomic disorders and still counting. Brain Res. 2011;1380:42–77.
Lionel AC, Crosbie J, Barbosa N, Goodale T, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Rickaby J, et al. Rare copy number variation discovery and cross-disorder comparisons identify risk genes for ADHD. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:95ra75.
Marshall CR, Howrigan DP, Merico D, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Wu W, Greer DS, et al. Contribution of copy number variants to schizophrenia from a genome-wide study of 41,321 subjects. Nat Genet. 2017;49:27–35.
Olson H, Shen Y, Avallone J, Sheidley BR, Pinsky R, Bergin AM, et al. Copy number variation plays an important role in clinical epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 2014;75:943–58.
Soemedi R, Wilson IJ, Bentham J, Darlay R, Topf A, Zelenika D, et al. Contribution of global rare copy-number variants to the risk of sporadic congenital heart disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;91:489–501.
Verbitsky M, Westland R, Perez A, Kiryluk K, Liu Q, Krithi-vasan P, et al. The copy number variation landscape of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. Nat Genet. 2019;51:117–27.
Crawford K, Bracher-Smith M, Owen D, Kendall KM, Rees E, Pardinas AF, et al. Medical consequences of pathogenic CNVs in adults: analysis of the UK Biobank. J Med Genet. 2019;56:131–38.
Owen MJ, Sawa A, Mortensen PB. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2016;388:86–97.
Lord C, Elsabbagh M, Baird G, Veenstra-Vanderweele J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet. 2018;392:508–20.
Hilker R, Helenius D, Fagerlund B, Skytthe A, Christensen K, Werge TM, et al. Heritability of schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum based on the nationwide danish twin register. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;83:492–98.
Colvert E, Tick B, McEwen F, Stewart C, Curran SR, Woodhouse E, et al. Heritability of autism spectrum disorder in a UK population-based twin sample. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:415–23.
Rees E, Walters JT, Georgieva L, Isles AR, Chambert KD, Richards AL, et al. Analysis of copy number variations at 15 schizophrenia-associated loci. Br J Psychiatry. 2014;204:108–14.
Hu Z, Xiao X, Zhang Z, Li M. Genetic insights and neurobiological implications from NRXN1 in neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1400–14.
McDonald-McGinn DM, Sullivan KE, Marino B, Philip N, Swillen A, Vorstman JA, et al. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2015;1:15071.
Fiksinski AM, Schneider M, Murphy CM, Armando M, Vicari S, Canyelles JM, et al. Understanding the pediatric psychiatric phenotype of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2018;176:2182–91.
Schneider M, Debbane M, Bassett AS, Chow EW, Fung WL, van den Bree M, et al. Psychiatric disorders from childhood to adulthood in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: results from the International Consortium on Brain and Behavior in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 2014;171:627–39.
Jonas RK, Montojo CA, Bearden CE. The 22q11.2 deletion syndrome as a window into complex neuropsychiatric disorders over the lifespan. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:351–60.
Mok KY, Sheerin U, Simon-Sanchez J, Salaka A, Chester L, Escott-Price V, et al. Deletions at 22q11.2 in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a combined analysis of genome-wide association data. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:585–96.
Sobanski E. Psychiatric comorbidity in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006;256(Suppl 1):i26–31.
Cerda M, Sagdeo A, Johnson J, Galea S. Genetic and environmental influences on psychiatric comorbidity: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2010;126:14–38.
Leyfer OT, Folstein SE, Bacalman S, Davis NO, Dinh E, Morgan J, et al. Comorbid psychiatric disorders in children with autism: interview development and rates of disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2006;36:849–61.
Buckley PF, Miller BJ, Lehrer DS, Castle DJ. Psychiatric comorbidities and schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2009;35:383–402.
Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Coe BP, Parikh S, Friedman N, Goldstein A, et al. Phenotypic heterogeneity of genomic disorders and rare copy-number variants. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1321–31.
Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Cooper GM, Antonacci F, Siswara P, Itsara A, et al. A recurrent 16p12.1 microdeletion supports a two-hit model for severe developmental delay. Nat Genet. 2010;42:203–9.
Oetjens MT, Kelly MA, Sturm AC, Martin CL, Ledbetter DH. Quantifying the polygenic contribution to variable expressivity in eleven rare genetic disorders. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4897.
Kirov G, Rees E, Walters JT, Escott-Price V, Georgieva L, Richards AL, et al. The penetrance of copy number variations for schizophrenia and developmental delay. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;75:378–85.
Stefansson H, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Steinberg S, Magnusdottir B, Morgen K, Arnarsdottir S, et al. CNVs conferring risk of autism or schizophrenia affect cognition in controls. Nature. 2014;505:361–6.
Kendall KM, Rees E, Escott-Price V, Einon M, Thomas R, Hewitt J, et al. Cognitive performance among carriers of pathogenic copy number variants: analysis of 152,000 UK biobank subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82:103–10.
Kendall KM, Bracher-Smith M, Fitzpatrick H, Lynham A, Rees E, Escott-Price V, et al. Cognitive performance and functional outcomes of carriers of pathogenic copy number variants: analysis of the UK Biobank. Br J Psychiatry. 2019;214:297–304.
Writing Committee for the E-CNVWG, van der Meer D, Sonderby IE, Kaufmann T, Walters GB, Abdellaoui A, et al. Association of copy number variation of the 15q11.2 BP1-BP2 region with cortical and subcortical morphology and cognition. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;77:1–11.
Kirov G, Pocklington AJ, Holmans P, Ivanov D, Ikeda M, Ruderfer D, et al. De novo CNV analysis implicates specific abnormalities of postsynaptic signalling complexes in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17:142–53.
Pinto D, Delaby E, Merico D, Barbosa M, Merikangas A, Klei L, et al. Convergence of genes and cellular pathways dysregulated in autism spectrum disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94:677–94.
Kushima I, Aleksic B, Nakatochi M, Shimamura T, Okada T, Uno Y, et al. Comparative analyses of copy-number variation in autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia reveal etiological overlap and biological insights. Cell Rep. 2018;24:2838–56.
Sullivan PF, Magnusson C, Reichenberg A, Boman M, Dalman C, Davidson M, et al. Family history of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder as risk factors for autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:1099–103.
Zheng Z, Zheng P, Zou XB. Association between schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autism Res. 2018;11:1110–19.
Kushima I, Aleksic B, Nakatochi M, Shimamura T, Shiino T, Yoshimi A, et al. High-resolution copy number variation analysis of schizophrenia in Japan. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:430–40.
De Rubeis S, He X, Goldberg AP, Poultney CS, Samocha K, Cicek AE, et al. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature. 2014;515:209–15.
Gilman SR, Chang J, Xu B, Bawa TS, Gogos JA, Karayiorgou M, et al. Diverse types of genetic variation converge on functional gene networks involved in schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:1723–8.
Rossignol DA, Frye RE. Evidence linking oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation in the brain of individuals with autism. Front Physiol. 2014;5:150.
Forsingdal A, Jorgensen TN, Olsen L, Werge T, Didriksen M, Nielsen J. Can animal models of copy number variants that predispose to schizophrenia elucidate underlying biology? Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:13–24.
Nakatani J, Tamada K, Hatanaka F, Ise S, Ohta H, Inoue K, et al. Abnormal behavior in a chromosome-engineered mouse model for human 15q11-13 duplication seen in autism. Cell. 2009;137:1235–46.
Isshiki M, Tanaka S, Kuriu T, Tabuchi K, Takumi T, Okabe S. Enhanced synapse remodelling as a common phenotype in mouse models of autism. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4742.
Tamada K, Tomonaga S, Hatanaka F, Nakai N, Takao K, Miyakawa T, et al. Decreased exploratory activity in a mouse model of 15q duplication syndrome; implications for disturbance of serotonin signaling. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e15126.
Baba M, Yokoyama K, Seiriki K, Naka Y, Matsumura K, Kondo M, et al. Psychiatric-disorder-related behavioral phenotypes and cortical hyperactivity in a mouse model of 3q29 deletion syndrome. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:2125–35.
Fujitani M, Zhang S, Fujiki R, Fujihara Y, Yamashita T. A chromosome 16p13.11 microduplication causes hyperactivity through dysregulation of miR-484/protocadherin-19 signaling. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:364–74.
Toyoshima M, Akamatsu W, Okada Y, Ohnishi T, Balan S, Hisano Y, et al. Analysis of induced pluripotent stem cells carrying 22q11.2 deletion. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:e934.
Zhao DJ, Lin MY, Chen J, Pedrosa E, Hrabovsky A, Fourcade HM, et al. MicroRNA profiling of neurons generated using induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, and 22q11.2 Del. Plos ONE. 2015;10:e0132387.
Yoon KJ, Nguyen HN, Ursini G, Zhang FY, Kim NS, Wen ZX, et al. Modeling a genetic risk for schizophrenia in iPSCs and mice reveals neural stem cell deficits associated with adherens junctions and polarity. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15:79–91.
Sedlazeck FJ, Lee H, Darby CA, Schatz MC. Piercing the dark matter: bioinformatics of long-range sequencing and mapping. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19:329–46.
Cao H, Hastie AR, Cao D, Lam ET, Sun Y, Huang H, et al. Rapid detection of structural variation in a human genome using nanochannel-based genome mapping technology. Gigascience. 2014;3:34.
Lam ET, Hastie A, Lin C, Ehrlich D, Das SK, Austin MD, et al. Genome mapping on nanochannel arrays for structural variation analysis and sequence assembly. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30:771–6.
Merker JD, Wenger AM, Sneddon T, Grove M, Zappala Z, Fresard L, et al. Long-read genome sequencing identifies causal structural variation in a Mendelian disease. Genet Med. 2018;20:159–63.
Audano PA, Sulovari A, Graves-Lindsay TA, Cantsilieris S, Sorensen M, Welch AE, et al. Characterizing the major structural variant alleles of the human genome. Cell. 2019;176:663–75 e19.
Chaisson MJP, Sanders AD, Zhao X, Malhotra A, Porubsky D, Rausch T, et al. Multi-platform discovery of haplotype-resolved structural variation in human genomes. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1784.
Levy-Sakin M, Pastor S, Mostovoy Y, Li L, Leung AKY, McCaffrey J, et al. Genome maps across 26 human populations reveal population-specific patterns of structural variation. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1025.
Green EK, Rees E, Walters JT, Smith KG, Forty L, Grozeva D, et al. Copy number variation in bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:89–93.
Nelis E, Van Broeckhoven C, De Jonghe P, Lofgren A, Vandenberghe A, Latour P, et al. Estimation of the mutation frequencies in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1 and hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies: a European collaborative study. Eur J Hum Genet. 1996;4:25–33.
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, et al. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature. 1998;392:605–8.
Hooli BV, Mohapatra G, Mattheisen M, Parrado AR, Roehr JT, Shen Y, et al. Role of common and rare APP DNA sequence variants in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2012;78:1250–7.
Kunkel LM, Hejtmancik JF, Caskey CT, Speer A, Monaco AP, Middlesworth W, et al. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986;322:73–7.
Gejman PV, Sanders AR, Kendler KS. Genetics of schizophrenia: new findings and challenges. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 2011;12:121–44.
Kirov G. CNVs in neuropsychiatric disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:R45–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by AMED under grant nos. JP20km0405216, JP20dm0107087, JP20dm0207075, JP20ak0101113, JP20dk0307075, JP20dk0307081, JP20dm0107160, and JP20ek0109411; and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI grant nos. 17H05090, 15K19720, and 18H04040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
NO has received research support and speakers’ honoraria from, or consulted for Sumitomo Dainippon, Otsuka, DAIICHI SANKYO, Tsumura, Nihon Medi-Physics, Pfizer, KAITEKI, Eli Lilly, Mochida, Eisai, Takeda, Novartis, Astellas, MSD, Meiji Seika Pharma, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Kyowa, Taisho Pharma, EA Pharma, UCB and Shionogi, outside the submitted work. MN and IK declare no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakatochi, M., Kushima, I. & Ozaki, N. Implications of germline copy-number variations in psychiatric disorders: review of large-scale genetic studies. J Hum Genet 66, 25–37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-020-00838-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-020-00838-1
This article is cited by
-
Characterization of loss of chromosome Y in peripheral blood cells in male Han Chinese patients with schizophrenia
BMC Psychiatry (2023)
-
The genetic architecture of schizophrenia: review of large-scale genetic studies
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
Copy Number Variations and Schizophrenia
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Exome sequencing analysis of Japanese autism spectrum disorder case-control sample supports an increased burden of synaptic function-related genes
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Genetics of autosomal mosaic chromosomal alteration (mCA)
Journal of Human Genetics (2021)