Abstract
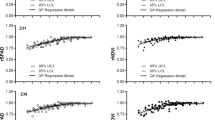
Rapid non-destructive estimation of the plant nitrogen (N) status is needed for the precise management of N in small-scale farms. Our objectives were to describe the responses of the soil–plant analyses development (SPAD) measurements to the plant N status of winter wheat, and to evaluate whether the SPAD index is more precise than SPAD readings in estimating the plant N status. During 2009–2011, a field experiment with winter wheat was conducted in the North China Plain. There were eight N supply levels ranging from 0 to 420 kg N ha−1 to create gradients of leaf greenness. The SPAD readings were measured on the topmost fully expanded leaf; the SPAD index was expressed relative to the SPAD readings of sufficiently fertilized plants. Combing over years, significant quadratic responses of SPAD reading to the plant N concentration (PNC) occurred at each/similar Zadoks growth stage (ZGS) but differed largely from ZGS 39/43 to ZGS 58/59, the r2 varied between 0.88 and 0.97; the SPAD readings exhibited a high logarithmic correlation to plant N accumulation (PNA, r2 = 0.94) irrespective of growth stages. Compared with SPAD readings, the SPAD index showed the same precision in response to PNC and PNA at each growth stage in each year, but presented less precision for the combined datasets across years, indicating that the SPAD index is not a more preferable tool in estimating plant N status. In addition, both the SPAD readings and SPAD index demonstrated poor to moderate responses to basal stem nitrate content (BSNC) with large differences among ZGS 39–59 and between the 2 years, indicating that the SPAD measurements could not be effectively used to estimate the BSNC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S. U. (2011). Effects of soil water deficit on leaf nitrogen, chlorophylls and SPAD chlorphyll meter reading on growth stages of soybean. Bangladesh Journal of Botany,40(2), 171–175.
Arunyanark, A., Jogloy, S., Akkasaeng, C., Vorasoot, N., Kesmala, T., Nageswara Rao, R. C., et al. (2008). Chlorophyll stability is an indicator of drought tolerance in peanut. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,194(2), 113–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2008.00299.x.
Barraclough, P. B., & Kyte, J. (2001). Effect of water stress on chlorophyll meter readings in winter wheat. In W. J. Horst, M. K. Schenk, A. Bürkert, N. Claassen, H. Flessa, W. B. Frommer, et al. (Eds.), Plant nutrition: food security and sustainability of agro-ecosystems through basic and applied research (pp. 722–723). Dordrecht: Springer.
Barutcular, C., Yıldırım, M., Koç, M., Akıncı, C., Toptaş, I., Albayrak, O., et al. (2016). Evaluation of SPAD chlorophyll in spring wheat genotypes under different environments. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin,25(4), 1258–1266.
Byju, G., & Anand, M. H. (2009). Leaf color chart and chlorophyll-meter-based leaf nitrogen estimation and their threshold values for real-time nitrogen management in Cassava. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis,40(17–18), 2816–2832. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620903173830.
Chen, P., Haboudane, D., Tremblay, N., Wang, J., Vigneault, P., & Li, B. (2010). New spectral indicator assessing the efficiency of crop nitrogen treatment in corn and wheat. Remote Sensing of Environment,114(9), 1987–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.04.006.
Debaeke, P., Rouet, P., & Justes, E. (2006). Relationship between the normalized SPAD index and the nitrogen nutrition index: application to durum wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition,29(1), 75–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160500416471.
Dunn, B. L., Singh, H., & Goad, C. (2018). Relationship between chlorophyll meter readings and nitrogen in poinsettia leaves. Journal of Plant Nutrition,41(12), 1–10.
Feng, W., Zhu, Y., Yao, X., Tian, Y., Zhuang, S., & Cao, W. (2008). Monitoring plant nitrogen accumulation dynamics with hyperspectral remote sensing in wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,41(7), 1937–1946.
Hawkins, J. A., Sawyer, J. E., Barker, D. W., & Lundvall, J. P. (2007). Using relative chlorophyll meter values to determine nitrogen application rates for corn. Agronomy Journal,99(4), 1034–1040. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2006.0309.
Horneck, D. A., & Miller, R. O. (1998). Determination of total nitrogen in plant tissue. Handbook of reference methods for plant analysis,2, 75–83.
Jarrell, W., & Beverly, R. (1981). The dilution effect in plant nutrition studies. Advances in Agronomy,34(1), 197–224.
Jia, L., Yu, Z., Li, F., Gnyp, M., Koppe, W., Bareth, G., et al. (2012). Nitrogen status estimation of winter wheat by using an IKONOS satellite image in the North China Plain. In D. Li & Y. Chen (Eds.), Computer and computing technologies in agriculture V (pp. 174–184). Berlin: Springer.
Kasahara, M., Kagawa, T., Oikawa, K., Suetsugu, N., Miyao, M., & Wada, M. (2002). Chloroplast avoidance movement reduces photodamage in plants. Nature,420(6917), 829–832.
Li, F., Gnyp, M. L., Jia, L., Miao, Y., Yu, Z., Koppe, W., et al. (2008). Estimating N status of winter wheat using a handheld spectrometer in the North China Plain. Field Crops Research,106(1), 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.11.001.
Li, Z., Liu, H., & Zhang, F. (2003). Research of nitrogen nutrition status for winter wheat based on chlorophyll meter. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,9(4), 401–405.
Li, D., Wang, X., Zheng, H., Zhou, K., Yao, X., Tian, Y., et al. (2018). Estimation of area- and mass-based leaf nitrogen contents of wheat and rice crops from water-removed spectra using continuous wavelet analysis. Plant Methods,14(1), 76.
Li, Y. X., Xu, D. F., Xie, X. J., Shen, S. H., & Pan, W. B. (2009). Spatial distribution of winter wheat leaf SPAD value and its relationship with nitrogen nutrition status. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,30(2), 164–168.
Li, J. W., Yang, J. P., Li, D. S., Fei, P. P., Guo, T. T., Ge, C. S., et al. (2011). Chlorophyll meter’s estimate of weight-based nitrogen concentration in rice leaf is influenced by leaf thickness. Plant Production Science,14(2), 177–183.
Lopez-Bellido, R. J., Shepherd, C. E., & Barraclough, P. B. (2004). Predicting post-anthesis N requirements of bread wheat with a Minolta SPAD meter. European Journal of Agronomy,20(3), 313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1161-0301(03)00025-x.
Marenco, R. A., Antezana-Vera, S. A., & Nascimento, H. C. S. (2009). Relationship between specific leaf area, leaf thickness, leaf water content and SPAD-502 readings in six Amazonian tree species. Photosynthetica,47(2), 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-009-0031-6.
Monostori, I., Árendás, T., Hoffman, B., Galiba, G., Gierczik, K., Szira, F., et al. (2016). Relationship between SPAD value and grain yield can be affected by cultivar, environment and soil nitrogen content in wheat. Euphytica,211(1), 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1741-z.
Munoz-Huerta, R. F., Guevara-Gonzalez, R. G., Contreras-Medina, L. M., Torres-Pacheco, I., Prado-Olivarez, J., & Ocampo-Velazquez, R. V. (2013). A review of methods for sensing the nitrogen status in plants: advantages, disadvantages and recent advances. Sensors (Basel),13(8), 10823–10843. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130810823.
Oppelt, N. (2002). Monitoring of plant chlorophyll and nitrogen status using the airborne imaging spectrometer AVIS. Dissertation, LMU München.
Peltonen, J., Virtanen, A., & Haggrèn, E. (1995). Using a chlorophyll meter to optimize nitrogen fertilizer application for intensively-managed small-grain cereals. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,174(5), 309–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.1995.tb01118.x.
Prost, L., & Jeuffroy, M. H. (2007). Replacing the nitrogen nutrition index by the chlorophyll meter to assess wheat N status. Agronomy for Sustainable Development,27(4), 321–330. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2007032.
Ravier, C., Quemada, M., & Jeuffroy, M.-H. (2017). Use of a chlorophyll meter to assess nitrogen nutrition index during the growth cycle in winter wheat. Field Crops Research,214, 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.08.023.
Schächtl, J., Huber, G., Maidl, F.-X., Sticksel, E., Schulz, J., & Haschberger, P. (2005). Laser-induced chlorophyll fluorescence measurements for detecting the nitrogen status of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) canopies. Precision Agriculture,6(2), 143–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-004-1031-y.
Schlemmer, M., Gitelson, A., Schepers, J., Ferguson, R., Peng, Y., Shanahan, J., et al. (2013). Remote estimation of nitrogen and chlorophyll contents in maize at leaf and canopy levels. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,25, 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2013.04.003.
Spaner, D., Todd, A. G., Navabi, A., McKenzie, D. B., & Goonewardene, L. A. (2005). Can leaf chlorophyll measures at differing growth stages be used as an indicator of winter wheat and spring barley nitrogen requirements in eastern Canada? Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,191(5), 393–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2005.00175.x.
Tian, Y. C., Zhu, Y., Cao, W. X., Fan, X. M., & Liu, X. J. (2003). Monitoring protein and starch accumulation in wheat grains with leaf SPAD and canopy spectral reflectance. Agricultural Sciences in China,2(11), 1205–1211.
Uchino, H., Watanabe, T., Ramu, K., Sahrawat, K. L., Marimuthu, S., Wani, S. P., et al. (2013). Calibrating chlorophyll meter (SPAD-502) reading by specific leaf area for estimating leaf nitrogen concentration in sweet sorghum. Journal of Plant Nutrition,36(10), 1640–1646. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2013.799190.
Varvel, G. E., Schepers, J. S., & Francis, D. D. (1997). Ability for in-season correction of nitrogen deficiency in corn using chlorophyll meters. Soil Science Society of America Journal,61(4), 1233–1239.
Yu, W., Miao, Y., Feng, G., Yue, S., & Liu, B. (2012). Evaluating different methods of using chlorophyll meter for diagnosing nitrogen status of summer maize. In 2012 First International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics, (pp. 1–4): IEEE.
Yue, X. L., Hu, Y. C., Zhang, H. Z., & Schmidhalter, U. (2015). Green Window approach for improving nitrogen management by farmers in small-scale wheat fields. The Journal of Agricultural Science,153(03), 446–454. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0021859614000203.
Yue, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., & Schmidhalter, U. (2019). Optimizing the nitrogen management strategy for winter wheat in the North China Plain using rapid soil and plant nitrogen measurements. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis,50(11), 1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1604738.
Zadoks, J. C., Chang, T. T., & Konzak, C. F. (1974). A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research,14(6), 415–421.
Zhang, Y., Chen, X. M., Shao, F. C., Wang, D. S., & He, Z. H. (2012). Analysis on quality stability of steamed bread and noodle by wheat cultivar Zhongmai 175. Journal of Triticeae Crops,32(3), 440–447.
Zhang, F. S., Wang, J. Q., Zhang, W. F., Cui, Z. L., Ma, W. Q., Chen, X. P., et al. (2008). Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement. Acta Pedologica Sinica,45(5), 915–924.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, Project Number: FKZ 0330800A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to authorship or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Evaluation of Both SPAD Reading and SPAD Index on Estimating the Plant Nitrogen Status of Winter Wheat. Int. J. Plant Prod. 14, 67–75 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00068-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00068-2