Abstract
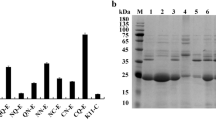
An efficient expression-secretion system for heterologous protein production in food-grade hosts, Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus subtilis, is still required to broaden their applications. The optimal signal peptide compatible with both the desired protein and the target host is important for the system. Here, we constructed new expression-secretion vectors to be used in both bacteria. A natural plasmid originating from food-grade L. plantarum BCC9546 was used as a core vector combined with a strong constitutive promoter, L-ldh promoter, and various signal peptides from several types of L. plantarum proteins: ABC transporter, cell wall-associated and extracellular proteins. A gene encoding 88-kDa amylase isolated from starch-related L. plantarum TBRC470 was used as a gene model to evaluate the systems. By comparing the amounts of secreted amylase from the recombinant strains to that of wild type, all signal peptides gave higher yields of secreted amylase in recombinant B. subtilis. Interestingly, two ABC transporter signal peptides from glutamine and mannose ABC transporters provided noticeably high levels of secreted amylase in recombinant L. plantarum. Moreover, these signal peptides also gave high yields of secreted amylase in recombinant B. subtilis. From the results, the signal peptide of glutamine ABC transporter, which functions in essential amino acid transportation that is a precursor for synthesis of nitrogen-containing compounds and nitrogen homeostasis, has a potential use in development of an efficient expression-secretion system for heterologous protein production in both food-grade hosts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Börner RA, Kandasamy V, Axelsen AM, Nielsen AT, Bosma EF (2019) Genome editing of lactic acid bacteria: opportunities for food, feed, pharma and biotech. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(1):fny191
Cui W, Han L, Suo F, Liu Z, Zhou L, Zhou Z (2018) Exploitation of Bacillus subtilis as a robust workhorse for production of heterologous proteins and beyond. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(10):145
Fath MJ, Kolter R (1993) ABC transporters: bacterial exporters. Microbiol Rev 57(4):995–1017
Forchhammer K (2007) Glutamine signaling in bacteria. Front Biosci 12:358–370
Freudl R (2018) Signal peptides for recombinant protein secretion in bacterial expression systems. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):52
Froger A, Hall JE (2007) Transformation of plasmid DNA into E. coli using the heat shock method. J Vis Exp 6:253
Giraud E, Cuny G (1997) Molecular characterization of the alpha-amylase genes of Lactobacillus plantarum A6 and Lactobacillus amylovorus reveals an unusual 3' end structure with direct tandem repeats and suggests a common evolutionary origin. Gene 198(1–2):149–157
Karlskås IL, Maudal K, Axelsson L, Rud I, Eijsink VG, Mathiesen G (2014) Heterologous protein secretion in Lactobacilli with modified pSIP vectors. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91125
Kunst F, Msadek T, Rapoport G (1994) In: Piggot PJ, Moran CP Jr., Youngman P (eds) In regulation of bacterial differentiation. The American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 1–20
Landete JM (2017) A review of food-grade vectors in lactic acid bacteria: from the laboratory to their application. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37(3):296–308
Liu L, Liu Y, Shin HD, Chen RR, Wang NS, Li J, Du G, Chen J (2013) Developing Bacillus spp. as a cell factory for production of microbial enzymes and industrially important biochemical in the context of systems and synthetic biology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(14):6113–6127
Mathiesen G, Sveen A, Brurberg MB, Fredriksen L, Axelsson L, Eijsink VGH (2009) Genome-wide analysis of signal peptide functionality in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. BMC Genomics 10(10):425
Mathiesen G, Sveen A, Piard JC, Axelsson L, Eijsink VG (2008) Heterologous protein secretion by Lactobacillus plantarum using homologous signal peptides. J Appl Microbiol 105(1):215–226
Miller GL (1959) Using dinitrosalicylic acid for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Phanaksri T, Luxananil P, Panyim S, Tirasophon W (2015) Synergism of regulatory elements in σB- and σA-dependent promoters enhances recombinant protein expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Biosci Bioeng 120(4):470–475
Plavec TV, Berlec A (2019) Engineering of lactic acid bacteria for delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(5):2053–2066
Promchai R, Boonchalearn A, Visessanguan W, Luxananil P (2018) Rapid production of extracellular thermostable alkaline halophilic protease originating from an extreme haloarchaeon, Halobacterium salinarum by recombinant Bacillus subtilis. Biocat Agri Biotechnol 15:192–198
Promchai R, Promdonkoy B, Tanapongpipat S, Visessanguan W, Eurwilaichitr L, Luxananil P (2016) A novel salt-inducible vector for efficient expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 222:86–93
Schallmey M, Singh A, Ward OP (2004) Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can J Microbiol 50(1):1–17
Siezen RJ, Francke C, Renckens B, Boekhorst J, Wels M, Kleerebezem M, van Hijum SA (2012) Complete resequencing and reannotation of the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 genome. J Bacteriol 194(1):195–196
Song Y, Nikoloff JM, Fu G, Chen J, Li Q, Xie N, Zheng P, Sun J, Zhang D (2016) Promoter screening from Bacillus subtilis in various conditions hunting for synthetic biology and industrial applications. PLoS ONE 11(7):e0158447
Valyasevi R, Smitinond T, Praphailog W, Chowalitnitithum C, Kunawasen S, Chavasith V (1999) The microbiology and development of starter culture for Nham, the traditional Thai pork sausage. In: Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference of the International Committee on Food Microbiology and Hygience (ICFMH), Veldhoven, The Netherlands, pp 709–711
Wang LF, Doi RH (1987) Promoter switching during development and the termination site of the sigma 43 operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet 207(1):114–119
Wu SC, Yeung JC, Duan Y, Ye R, Szarka SJ, Habibi HR, Wong SL (2002) Functional production and characterization of a fibrin-specific single-chain antibody fragment from Bacillus subtilis: effects of molecular chaperones and a wall-bound protease on antibody fragment production. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(7):3261–3269
Gu Y, Xu X, Wu Y, Niu T, Liu Y, Li J, Du G, Liu L (2018) Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: from rational design to industrial applications. Metab Eng 50:109–121
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, National Science and Technology Development Agency, Thailand (P-14-50499). We thank Dr. Peera Jaru-Ampornpan for valuable comments, suggestions and proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animal and human rights
There is no human participants and/or animals involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Promchai, R., Visessanguan, W. & Luxananil, P. An efficient ABC transporter signal peptide directs heterologous protein secretion in food-grade hosts. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02932-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02932-0