Abstract
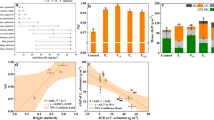
Suaeda species are widely distributed in the coastal areas and are commonly selected as candidates for coastal saline–alkaline soil restoration. In this study, a pot experiment was carried out to investigate the effects of different nutrient levels and salt stresses on the growth and physiological characteristics of Suaeda salsa and Suaeda glauca, two coexisting species exhibiting a spatial segregation in the Yellow River Delta (YRD), China. Our results showed that both Suaeda species can adapt to a high salinity environment (21 g kg−1 NaCl) and display similar regulation strategies, including increased shoot–root ratio, maintaining leaf succulence, and relying on proline and metal ions as osmotic regulators. However, nutrients had a different impact on the salt tolerance of the two species. Under low soil salinity levels, nutrient addition was more beneficial for S. salsa, while under high soil salinity levels, nutrient addition was more beneficial for S. glauca. Our results reveal that the spatial segregation of the two Suaeda species was not driven by salinity. Both species can be used in coastal restoration projects for their high salt-tolerant abilities, but the nutrient addition management should be specific to the species and site soil levels.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri B, Rasouli B (2011) How does the root of Salicornia herbacea response to salinity in comparison to the shoot. International Conference on Biotechnology and Environment Management 88–92
Andres K, Savarese M, Bovard B, Parsons M (2019) Coastal wetland geomorphic and vegetative change: effects of sea-level rise and water management on brackish marshes. Estuaries and Coasts 42:1308–1327
Barbier EB, Hacker SD, Kennedy C, Koch EW, Stier AC, Silliman BR (2011) The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecological Monographs 81:169–193
Bargaz A, Nassar RMA, Rady MM, Gaballah MS, Thompson SM, Brestic M, Schmidhalter U, Abdelhamid MT (2016) Improved salinity tolerance by phosphorus fertilizer in two Phaseolus vulgaris recombinant inbred lines contrasting in their P-efficiency. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 202:497–507
Barker AV, Pilbeam DJ (2015) Handbook of plant nutrition. CRC press, Boca Raton
Barrett-Lennard EG (2002) Restoration of saline land through revegetation. Agricultural Water Management 53:213–226
Brisson J, Chazarenc F (2009) Maximizing pollutant removal in constructed wetlands: should we pay more attention to macrophyte species selection? Science of the Total Environment 407:3923–3930
Chang ER, Veeneklaas RM, Bakker JP, Daniels P, Esselink P (2016) What factors determined restoration success of a salt marsh ten years after de-embankment? Applied Vegetation Science 19:66–77
Crain CM, Silliman BR, Bertness SL, Bertness MD (2004) Physical and biotic drivers of plant distribution across estuarine salinity gradients. Ecology 85:2539–2549
Cui B, He Q, Zhao X (2008) Researches on the ecological thresholds of Suaeda salsa to the environmental gradients of water table depth and soil salinity. Acta Gcologica Sinica 28:1408–1418
Cui L, Li G, Ouyang N, Mu F, Yan F, Zhang Y, Huang X (2018) Analyzing coastal wetland degradation and its key restoration technologies in the coastal area of Jiangsu, China. Wetlands 38:525–537
Deegan LA, Johnson DS, Warren RS, Peterson BJ, Fleeger JW, Fagherazzi S, Wollheim WM (2012) Coastal eutrophication as a driver of salt marsh loss. Nature 490(7420):388–392
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2015) Effectiveness of organic wastes as fertilizers and amendments in salt-affected soils. Agriculture-Basel 5:221–230
Duan H, Ma Y, Liu R, Li Q, Yang Y, Song J (2018) Effect of combined waterlogging and salinity stresses on euhalophyte Suaeda glauca. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 127:231–237
Elliott M, Burdon D, Hemingway KL, Apitz SE (2007) Estuarine, coastal and marine ecosystem restoration: confusing management and science-a revision of concepts. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 74:349–366
Fan L, Wang Y, Shao X, Geng Y, Wang Z, Ma Y, Liu J (2012) Effects of combined nitrogen fertilizer and nano-carbon application on yield and nitrogen use of rice grown on saline-alkali soil. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment 10:558–562
Farooq M, Hussain M, Wakeel A, Siddique KHM (2015) Salt stress in maize: effects, resistance mechanisms, and management. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 35:461–481
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2015) Plant salt tolerance: adaptations in halophytes. Annals of Botany 115:327–331
Foret JD (2002) Nutrient limitation of tidal marshes on the Chenier plain, Louisiana. Dissertation, University of Louisiana at Lafayette
Forlani G, Bertazzini M, Cagnano G (2019) Stress-driven increase in proline levels, and not proline levels themselves, correlates with the ability to withstand excess salt in a group of 17 Italian rice genotypes. Plant Biology 21:336–342
Gu J, Luo M, Zhang X, Christakos G, Agusti S, Duarte CM, Wu J (2018) Losses of salt marsh in China: trends, threats and management. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 214:98–109
Gutierrez-Boem FH, Thomas GW (1998) Phosphorus nutrition affects wheat response to water deficit. Agronomy Journal 90:166–171
Hansel FD, Amado TJC, Diaz DAR, Rosso LHM, Nicoloso FT, Schorr M (2017) Phosphorus fertilizer placement and tillage affect soybean root growth and drought tolerance. Agronomy Journal 109:2936–2944
He Q, Cui B, Zhao X, Fu H, Xiong X, Feng G (2007) Vegetation distribution patterns to the gradients of water depth and soil salinity in wetlands of Yellow River delta, China. Wetland Science 5:208–214
He Q, Cui B, Zhao X, Fu H, Liao X (2009) Relationships between salt marsh vegetation distribution/diversity and soil chemical factors in the Yellow River estuary, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 29(2):676–687
He Q, Cui B, Bertness MD, An Y (2012) Testing the importance of plant strategies on facilitation using congeners in a coastal community. Ecology 93:2023–2029
Hoagland D (1920) Optimum nutrient solutions for plants. Science 52:562–564
Hou B, Ma F, Xing S, Song Y, Liu Y (2007) Soil and vegetation characteristics of wetland communities at different successive stages in the Huanghe River Delta. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College 24:313–318
Iqbal N, Umar S, Khan NA, Khan MIR (2014) A new perspective of phytohormones in salinity tolerance: regulation of proline metabolism. Environmental and Experimental Botany 100:34–42
Jia J, Huang C, Bai J, Zhang G, Zhao Q, Wen X (2018) Effects of drought and salt stresses on growth characteristics of euhalophyte Suaeda salsa in coastal wetlands. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 103:68–74
Jouyban Z (2012) The effects of salt stress on plant growth. Technical Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences 2:7–10
Kronvang B, Jeppesen E, Conley DJ, Sondergaard M, Larsen SE, Ovesen NB, Carstensen J (2005) Nutrient pressures and ecological responses to nutrient loading reductions in Danish streams, lakes and coastal waters. Journal of Hydrology 304:274–288
Li C, Sun Y, Fan J, Zhai Z, Yang S, Fan J, Wang T, Wang S, Zhang H (2015) Ecological significance of planting Suaeda salsa in saline /alkali soils in the Lop Nur potash mine. Arid Zone Research 32:1160–1166
Li J, Guo K, Li X, Feng X, Liu X (2018a) Effects of PEG, NaCl and Na2CO3 stresses on Suaeda glauca and Suaeda salsa seed germination. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture 26:1011–1018
Li M, Guo W, Du N, Xu Z, Guo X (2018b) Nitrogen deposition does not affect the impact of shade on Quercus acutissima seedlings. PLoS One 13:e0194261
Liu X, Wang G, Yu J, Ran Y, Guan B, Han G, Wang A, Zhao Y (2018a) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus supply on plant community structure of coastal wetland in the Yellow River Delta. Chinese Journal of Ecology 37:801–809
Liu Y, Li B, Jun Y, Sun W, Yu Y (2018b) Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on osmotic adjustment and soil microorganisms of maize in saline-alkali soil. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 31:1013–1018
Liu M, Wang C, Wang F, Xie Y (2019) Vermicompost and humic fertilizer improve coastal saline soil by regulating soil aggregates and the bacterial community. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 65:281–293
Males J (2017) Secrets of succulence. Journal of Experimental Botany 68:2121–2134
Milic D, Lukovic J, Zoric L, Vasin J, Ninkov J, Zeremski T, Milic S (2013) Halophytes relations to soil ionic composition. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society 78:1259–1268
Mitsch WJ, Gosselink JG (2015) Wetlands. Wiley, Hoboken
Ogburn RM, Edwards EJ (2010) The ecological water-use strategies of succulent plants. In: Kader JC, Delseny M (eds) Advances in botanical research, vol 55. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 179–225
Ottow EA, Brinker M, Teichmann T, Fritz E, Kaiser W, Brosché M, Kangasjärvi J, Jiang X, Polle A (2005) Populus euphratica displays apoplastic sodium accumulation, osmotic adjustment by decreases in calcium and soluble carbohydrates, and develops leaf succulence under salt stress. Plant Physiology 139:1762–1772
Per TS, Khan NA, Reddy PS, Masood A, Hasanuzzaman M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA (2017) Approaches in modulating proline metabolism in plants for salt and drought stress tolerance: Phytohormones, mineral nutrients and transgenics. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 115:126–140
Pottosin I, Dobrovinskaya O (2014) Non-selective cation channels in plasma and vacuolar membranes and their contribution to K+ transport. Journal of Plant Physiology 171:732–742
R Core Team (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Rabhi M, Ferchichi S, Jouini J, Hamrouni MH, Koyro HW, Ranieri A, Abdelly C, Smaoui A (2010) Phytodesalination of a salt-affected soil with the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum L. to arrange in advance the requirements for the successful growth of a glycophytic crop. Bioresource Technology 101:6822–6828
Sannigrahi S, Chakraborti S, Joshi PK, Keesstra S, Sen S, Paul SK, Kreuter U, Sutton PC, Jha S, Dang KB (2019) Ecosystem service value assessment of a natural reserve region for strengthening protection and conservation. Journal of Environmental Management 244:208–227
Sdouga D, Ben Amor F, Ghribi S, Kabtni S, Tebini M, Branca F, Trifi-Farah N, Marghali S (2019) An insight from tolerance to salinity stress in halophyte Portulaca oleracea L.: Physio-morphological, biochemical and molecular responses. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 172:45–52
Shamsutdinov NZ, Shamsutdinova EZ, Orlovsky NS, Shamsutdinov ZS (2017) Halophytes: ecological features, global resources, and outlook for multipurpose use. Herald of the Russian Academy of Sciences 87:1–11
Shao J, Zheng Q, Liu Z, Ning J (2005) Effects of phosphorus application on ion distribution in aloe seedlings under seawater stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica 25:3167–3171
Smith RS, Shiel RS, Bardgett RD, Millward D, Corkhill P, Rolph G, Hobbs PJ, Peacock S (2003) Soil microbial community, fertility, vegetation and diversity as targets in the restoration management of a meadow grassland. Journal of Applied Ecology 40:51–64
Song J, Fan H, Zhao Y, Jia Y, Du X, Wang B (2008) Effect of salinity on germination, seedling emergence, seedling growth and ion accumulation of a euhalophyte Suaeda salsa in an intertidal zone and on saline inland. Aquatic Botany 88:331–337
Song J, Shi G, Xing S, Yin C, Fan H, Wang B (2009) Ecophysiological responses of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa to the interactive effects of salinity and nitrate availability. Aquatic Botany 91:311–317
Sundareshwar PV, Morris JT, Koepfler EK, Fornwalt B (2003) Phosphorus limitation of coastal ecosystem processes. Science 299:563–565
Tang A, Liu R, Xu L, Wang J, Liu Y (2011) Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and distribution of plant community in Changyi marine ecological special protection area. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation 31:88–93
Verhoeven JTA, Laanbroek HJ, Rains MC, Whigham DF (2014) Effects of increased summer flooding on nitrogen dynamics in impounded mangroves. Journal of Environmental Management 139:217–226
Wang Z, Zhao G, Gao M, Chang C, Jiang S, Jia J, Li J (2016) Spatial variation of soil water and salt and microscopic variation of soil salinity in summer in typical area of the Yellow River Delta in Kenli County. Acta Ecologica Sinica 36:1040–1049
Wang L, Bu X, Chen J, Huang D, Luo T (2018) Effects of NaCl on plant growth, root ultrastructure, water content, and ion accumulation in a halophytic seashore beach plum (Prunus maritima). Pakistan Journal of Botany 50:863–869
Waraich EA, Ahmad R, Saifullah, Ashraf MY, Ehsanullah (2011) Role of mineral nutrition in alleviation of drought stress in plants. Australian Journal of Crop Science 5:764–777
White E, Kaplan D (2017) Restore or retreat? Saltwater intrusion and water management in coastal wetlands. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability 3:e01258
Wolters M, Garbutt A, Bekker RM, Bakker JP, Carey PD (2008) Restoration of salt-marsh vegetation in relation to site suitability, species pool and dispersal traits. Journal of Applied Ecology 45:904–912
Wu Z, Zhao S, Zhang X (1994) Studies on interrelation between salt vegetation and soil salinity in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Phytoecological Sinica 18:184–193
Wu W, Yang Z, Tian B, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang T (2018) Impacts of coastal reclamation on wetlands: loss, resilience, and sustainable management. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 210:153–161
Xia J, Ren J, Zhang S, Wang Y, Fang Y (2019) Forest and grass composite patterns improve the soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta, China. Geoderma 349:25–35
Xu W, Cui K, Xu A, Nie L, Huang J, Peng S (2015) Drought stress condition increases root to shoot ratio via alteration of carbohydrate partitioning and enzymatic activity in rice seedlings. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 37
Yang X, Zhang T, Wu Q (2002) The relationship between biodiversity and soil fertility characteristics on abandoned fields in the tropical region of southern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 22:190–196
Yang C, Shi D, Wang D (2008) Comparative effects of salt and alkali stresses on growth, osmotic adjustment and ionic balance of an alkali-resistant halophyte Suaeda glauca (Bge.). Plant Growth Regulation 56:179–190
Zhang A, Pang Q, Yan X (2013) Advances in salt-tolerance mechanisms of Suaeda plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica 33:3575–3583
Zhang H, Qin F, Qin P, Pan S (2014) Evidence that arbuscular mycorrhizal and phosphate-solubilizing fungi alleviate NaCl stress in the halophyte Kosteletzkya virginica: nutrient uptake and ion distribution within root tissues. Mycorrhiza 24:383–395
Zhao K, Fan H, Ungar I (2002) Survey of halophyte species in China. Plant Science (Shannon) 163:491–498
Zmihorski M, Part T, Gustafson T, Berg A (2016) Effects of water level and grassland management on alpha and beta diversity of birds in restored wetlands. Journal of Applied Ecology 53:587–595
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (2019GSF109070), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0505905), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770361; 31970347). We thank Zhaowei He and Feng Wang for field and lab assistance, and Huijia Song for suggestions that improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, QH., Sairebieli, K., Zhao, MM. et al. Nutrients Have a Different Impact on the Salt Tolerance of Two Coexisting Suaeda Species in the Yellow River Delta. Wetlands 40, 2811–2823 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-020-01382-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-020-01382-6