Abstract
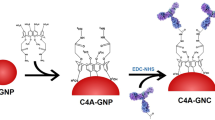
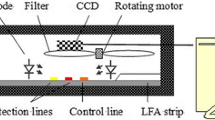
An on-site detection strategy is reported based on dual-color SiO2@quantum dot (QD)–integrated lateral flow immunoassay (LFA) strip to realize the quantitative and simultaneous detection of C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) in serum. The dual-color SiO2@QD nanotags with monodispersity and excellent luminescence were synthesized using polyethyleneimine-mediated electrostatic adsorption of dense red CdSe/ZnS-COOH (excitation/emission 365/625 nm) or green CdSe/ZnS-COOH (excitation/emission 365/525 nm) QDs on the surface of 180 nm SiO2 spheres and were conjugated with anti-PCT and anti-CRP monoclonal antibodies, as stable and fluorescent-enhanced QD nanotags in the LFA system. The use of SiO2@QDs with two different fluorescent signals caused the sensitivity and specificity of the multiplex LFA system. As a result, the proposed assay provided a wide logarithmic determination range with a CRP quantitative range of 0.5–103 ng/mL and PCT quantitative range of 0.05–103 ng/mL. The limits of detection (LODs) of CRP and PCT reached 0.5 and 0.05 ng/mL, respectively. The SiO2@QD-based LFA showed great potential as rapid detection tool for the simultaneous monitoring of CRP and PCT in serum sample.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prescott HC, Angus DC (2018) Enhancing recovery from sepsis: a review. Jama 319(1):62–75. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17687
Fleischmann-Struzek C, Goldfarb DM, Schlattmann P, Schlapbach LJ, Reinhart K, Kissoon N (2018) The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: a systematic review. Lancet Respir Med 6(3):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-2600(18)30063-8
Vincent J-L (2016) The clinical challenge of sepsis identification and monitoring. PLoS Med 13(5):e1002022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002022
Gao L, Liu X, Zhang D, Xu F, Chen Q, Hong Y, Feng G, Shi Q, Yang B, Xu L (2017) Early diagnosis of bacterial infection in patients with septicopyemia by laboratory analysis of PCT, CRP and IL-6. Exp Ther Med 13(6):3479–3483. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4417
Min J, Nothing M, Coble B, Zheng H, Park J, Im H, Weber GF, Castro CM, Swirski FK, Weissleder R, Lee H (2018) Integrated biosensor for rapid and point-of-care sepsis diagnosis. ACS Nano 12(4):3378–3384. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b08965
Dolin HH, Papadimos TJ, Stepkowski S, Chen X, Pan ZK (2018) A novel combination of biomarkers to herald the onset of sepsis prior to the manifestation of symptoms. Shock 49(4):364–370. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000001010
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D (2013) Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 13(12):862–874. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3552
Wang J, Wu H, Yang Y, Yan R, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Chen A, Shao S, Jiang P, Li YQ (2017) Bacterial species-identifiable magnetic nanosystems for early sepsis diagnosis and extracorporeal photodynamic blood disinfection. Nanoscale 10(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr06373c
Yi J, Qin Q, Wang Y, Zhang R, Bi H, Yu S, Liu B, Qiao L (2018) Identification of pathogenic bacteria in human blood using IgG-modified Fe3O4 magnetic beads as a sorbent and MALDI-TOF MS for profiling. Mikrochim Acta 185(12):542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3074-1
Serebrennikova KV, Samsonova JV, Osipov AP (2019) A semi-quantitative rapid multi-range gradient lateral flow immunoassay for procalcitonin. Mikrochim Acta 186(7):423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3550-2
Kim SW, Cho IH, Lim GS, Park GN, Paek SH (2017) Biochemical-immunological hybrid biosensor based on two-dimensional chromatography for on-site sepsis diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 98:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.06.032
Wu J, Chen Y, Yang M, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yang M, Sun J, Xie M, Jiang X (2017) Streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase nanocomplex-amplified microfluidics immunoassays for simultaneous detection of inflammatory biomarkers. Anal Chim Acta 982:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.031
Vijayan AL, Vanimaya RS, Saikant R, Lakshmi S, Kartik R (2017) Procalcitonin: a promising diagnostic marker for sepsis and antibiotic therapy. J Intensive Care 5:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-017-0246-8
Boonkaew S, Chaiyo S, Jampasa S, Rengpipat S, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O (2019) An origami paper-based electrochemical immunoassay for the C-reactive protein using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with graphene and gold nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 186(3):153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3245-8
Kumar S, Tripathy S, Jyoti A, Singh SG (2019) Recent advances in biosensors for diagnosis and detection of sepsis: a comprehensive review. Biosens Bioelectron 124-125:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.034
Belushkin A, Yesilkoy F, Gonzalez-Lopez JJ, Ruiz-Rodriguez JC, Ferrer R, Fabrega A, Altug H (2020) Rapid and digital detection of inflammatory biomarkers enabled by a novel portable nanoplasmonic imager. Small 16(3):e1906108. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201906108
Xianyu Y, Wu J, Chen Y, Zheng W, Xie M, Jiang X (2018) Controllable assembly of enzymes for multiplexed lab-on-a-chip bioassays with a tunable detection range. Angew Chem 57(25):7503–7507. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201801815
Mahmoudi T, de la Guardia M, Baradaran B (2020) Lateral flow assays towards point-of-care cancer detection: a review of current progress and future trends. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 125:115842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115842
Wang C, Wang C, Wang X, Wang K, Zhu Y, Rong Z, Wang W, Xiao R, Wang S (2019) Magnetic SERS strip for sensitive and simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(21):19495–19505. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03920
Zhang J, Yu Q, Qiu W, Li K, Qian L, Zhang X, Liu G (2019) Gold-platinum nanoflowers as a label and as an enzyme mimic for use in highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassays: application to detection of rabbit IgG. Mikrochim Acta 186(6):357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3464-z
Wang R, Zhang W, Wang P, Su X (2018) A paper-based competitive lateral flow immunoassay for multi beta-agonist residues by using a single monoclonal antibody labelled with red fluorescent nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 185(3):191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2730-9
Zhang Z, Shikha S, Liu J, Zhang J, Mei Q, Zhang Y (2019) Upconversion nanoprobes: recent advances in sensing applications. Anal Chem 91(1):548–568. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04049
Wang C, Shen W, Rong Z, Liu X, Gu B, Xiao R, Wang S (2019) Layer-by-layer assembly of magnetic-core dual quantum dot-shell nanocomposites for fluorescence lateral flow detection of bacteria. Nanoscale. 12:795–807. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr08509b
Guo L, Shao Y, Duan H, Ma W, Leng Y, Huang X, Xiong Y (2019) Magnetic quantum dot nanobead-based fluorescent immunochromatographic assay for the highly sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 in dark soy sauce. Anal Chem 91(7):4727–4734. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00223
Znoyko SL, Orlov AV, Pushkarev AV, Mochalova EN, Guteneva NV, Lunin AV, Nikitin MP, Nikitin PI (2018) Ultrasensitive quantitative detection of small molecules with rapid lateral-flow assay based on high-affinity bifunctional ligand and magnetic nanolabels. Anal Chim Acta 1034:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.07.012
Wang C, Xiao R, Wang S, Yang X, Bai Z, Li X, Rong Z, Shen B, Wang S (2019) Magnetic quantum dot based lateral flow assay biosensor for multiplex and sensitive detection of protein toxins in food samples. Biosens Bioelectron 146:111754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111754
Hu J, Jiang YZ, Wu LL, Wu Z, Bi Y, Wong G, Qiu X, Chen J, Pang DW, Zhang ZL (2017) Dual-signal readout nanospheres for rapid point-of-care detection of Ebola virus glycoprotein. Anal Chem 89(24):13105–13111. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02222
Wang C, Hou F, Ma Y (2015) Simultaneous quantitative detection of multiple tumor markers with a rapid and sensitive multicolor quantum dots based immunochromatographic test strip. Biosens Bioelectron 68:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.051
Qi X, Huang Y, Lin Z, Xu L, Yu H (2016) Dual-quantum-dots-labeled lateral flow strip rapidly quantifies procalcitonin and C-reactive protein. Nanoscale Res Lett 11(1):167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1383-z
Hu J, Jiang YZ, Tang M, Wu LL, Xie HY, Zhang ZL, Pang DW (2018) Colorimetric-fluorescent-magnetic nanosphere-based multimodal assay platform for Salmonella detection. Anal Chem 91:1178–1184. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05154
Galan-Malo P, Pellicer S, Perez MD, Sanchez L, Razquin P, Mata L (2019) Development of a novel duplex lateral flow test for simultaneous detection of casein and beta-lactoglobulin in food. Food Chem 293:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.FoodChem.2019.04.039
Li L, Feng D, Zhao J, Guo Z, Zhang Y (2015) Simultaneous fluoroimmunoassay of two tumor markers based on CdTe quantum dots and gold nanocluster coated-silica nanospheres as labels. RSC Adv 5(128):105992–105998. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra19262e
Duan H, Li Y, Shao Y, Huang X, Xiong Y (2019) Multicolor quantum dot nanobeads for simultaneous multiplex immunochromatographic detection of mycotoxins in maize. Sensors Actuators B Chem 291:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.04.101
Yang Y, Qian X, Zhang L, Miao W, Ming D, Jiang L, Huang H (2020) Enhanced imaging of glycan expressing cancer cells using poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-grafted silica nanospheres labeled with quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 1095:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.10.024
Foubert A, Beloglazova NV, Gordienko A, Tessier MD, Drijvers E, Hens Z, De Saeger S (2017) Development of a rainbow lateral flow immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of four mycotoxins. J Agric Food Chem 65(33):7121–7130. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04157
Huang Z, Peng J, Han J, Zhang G, Huang Y, Duan M, Liu D, Xiong Y, Xia S, Lai W (2019) A novel method based on fluorescent magnetic nanobeads for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Chem 276:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.164
Zhang H, Luo J, Beloglazova N, Yang S, De Saeger S, Mari GM, Zhang S, Shen J, Wang Z, Yu X (2019) Portable multiplex immunochromatographic assay for quantitation of two typical algae toxins based on dual-color fluorescence microspheres. J Agric Food Chem 67(21):6041–6047. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00011
Yen CW, de Puig H, Tam JO, Gomez-Marquez J, Bosch I, Hamad-Schifferli K, Gehrke L (2015) Multicolored silver nanoparticles for multiplexed disease diagnostics: distinguishing dengue, yellow fever, and Ebola viruses. Lab Chip 15(7):1638–1641. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc00055f
Di Nardo F, Baggiani C, Giovannoli C, Spano G, Anfossi L (2017) Multicolor immunochromatographic strip test based on gold nanoparticles for the determination of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisins. Microchim Acta 184(5):1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2121-7
Lee S, Mehta S, Erickson D (2016) Two-color lateral flow assay for multiplex detection of causative agents behind acute febrile illnesses. Anal Chem 88(17):8359–8363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01828
Rong Z, Bai Z, Li J, Tang H, Shen T, Wang Q, Wang C, Xiao R, Wang S (2019) Dual-color magnetic-quantum dot nanobeads as versatile fluorescent probes in test strip for simultaneous point-of-care detection of free and complexed prostate-specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 145:111719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111719
Hu J, Zhang ZL, Wen CY, Tang M, Wu LL, Liu C, Zhu L, Pang DW (2016) Sensitive and quantitative detection of C-reaction protein based on immunofluorescent nanospheres coupled with lateral flow test strip. Anal Chem 88(12):6577–6584. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01427
Rong Z, Xiao R, Xing S, Xiong G, Yu Z, Wang L, Jia X, Wang K, Cong Y, Wang S (2018) SERS-based lateral flow assay for quantitative detection of C-reactive protein as an early bio-indicator of a radiation-induced inflammatory response in nonhuman primates. Analyst 143(9):2115–2121. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00160j
Liu P, Li C, Zhang R, Tang Q, Wei J, Lu Y, Shen P (2019) An ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for procalcitonin detection based on the gold nanoparticles-enhanced tyramide signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 126:543–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.048
Molinero-Fernandez A, Moreno-Guzman M, Arruza L, Lopez MA, Escarpa A (2020) Polymer-based micromotor fluorescence immunoassay for on-the-move sensitive procalcitonin determination in very low birth weight infants’ plasma. ACS Sensors 5(5):1336–1344. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b02515
Molinero-Fernandez A, Moreno-Guzman M, Arruza L, Lopez MA, Escarpa A (2019) Toward early diagnosis of late-onset sepsis in preterm neonates: dual magnetoimmunosensor for simultaneous procalcitonin and C-reactive protein determination in diagnosed clinical samples. ACS Sensors 4(8):2117–2123. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00890
Acknowledgments
We thank Beijing Zhongkebaice Technology Service Co., for helping to conduct TEM and SEM analysis.
Funding
This research was supported by Major Infectious Diseases such as AIDS and Viral Hepatitis Prevention and Control Technology Major Projects (2018ZX10712-001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81830101, 81471994, 81871734), and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant no. 1908085QB85).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.Q.W., C.W.W. and R.X. designed and managed the project. X.S.Y., X.X.L., B.G. and H.F.L. performed all the experiments. B.G. provided clinical samples and did the analysis of ECL immunoassay results. C.W.W., X.S.Y. and X.X.L wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All experimental operations were performed following the guidelines approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University (approval ID: XYFY2020-KL017-01). Informed consents were obtained from human participants of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1410 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Liu, X., Gu, B. et al. Quantitative and simultaneous detection of two inflammation biomarkers via a fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay using dual-color SiO2@QD nanotags. Microchim Acta 187, 570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04555-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04555-6