Abstract
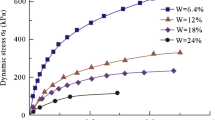
Earthquakes occur frequently in the Loess Plateau area, which result in damage to loess due to the disturbance of multiple cyclic loading. In this paper, the historical earthquake process is simulated by pre-dynamic loading treatment on undisturbed loess samples. Then cyclic tests are carried out on these treated samples to study the later liquefaction responses with different initial water content. The undisturbed sample is relative to the remold sample instead of the samples without disturbance. Results show that the axial deformation and pore pressure ratio of treated loess samples with initial water content of 5% are larger than those without treatment. For samples with initial water content of 10% and 15%, the cycle number required for liquefaction increases after treatment, but pore pressure ratio is between 0.18 and 0.36, which is less than the 5% water content samples. It means that liquefaction will have been formed before the excess pore pressure increases to large values. Combined with microstructural analysis, it is found that pre-dynamic treatment causes earthquake damage zone in loess with water content of 5%, which results in lower liquefaction stress ratio than non-treated ones. As for samples with water content of 10% and 15%, the internal voids become smaller and fine particles move into the gaps between large particles after treatment, resulting in denser structure which is hard to be liquefied. However, the increasing dynamic stress will aggravate the deterioration of loess at the water content from 5 to 15%. The changes of microstructure of loess samples are vulnerable to the dynamic stress amplitude and water sensitivity.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadi MS, Orense RP, Asadi MB, Pender MJ (2019) Post-liquefaction behavior of natural pumiceous sands. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 118:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.12.009
ASTM (2005) Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils. D4318-05, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM (2006) Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. D854-06, West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM (2007) Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils. D422-63 (reapproved 2007), West Conshohocken, PA
ASTM D854-10 (2010) Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, vol 8.04. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA
Bai MX, Zhang SM (1990) Liquefaction movement of loess strata during high intensity earthquakes. Geotech Invest Surv 20(6):1–5
Beyzaei CZ, Bray JD, Cubrinovski M, Bastin S, Stringer M, Jacka M, van Ballegooy S, Riemer M, Wentz R (2020) Characterization of silty soil thin-layering and groundwater conditions for liquefaction assessment. Can Geotech J 57(2):263–276. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2018-0287
Bouckovalas GD, Andrianopoulos KI, Papadimitriou AG (2003) A critical state interpretation for the cyclic liquefaction resistance of silty sands. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 23(2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0267-7261(02)00156-2
Castro G, Poulos SJ (1980) Factors affecting liquefaction and cyclic mobility. J Geotech Eng Div 106(2):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(77)90768-9
Chen WW, Liu W, Wang J, Sun GP, Wu WJ (2019) Relationship between saturation degree and B value for loess. Rock Soil Mech 40(3):834–842 (in Chinese)
Cheng GY (2003) Study on correlation between shear-wave velocity and liquefaction resistance of saturated sand. Tianjin University, PhD thesis (in Chinese)
Chiaradonna A, Reder A (2020) Influence of initial conditions on the liquefaction strength of an earth structure. Bull Eng Geol Env 79:687–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01594-z
Chiaradonna A, d’Onofrio A, Bilotta E (2019) Assessment of post-liquefaction consolidation settlement. Bull Earthq Eng 17:5825–5848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00695-0
Darby KM, Boulanger RW, DeJong JT, Bronner JD (2019) Progressive changes in liquefaction and cone penetration resistance across multiple shaking events in centrifuge tests. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001995
Derbyshire E, Dijkstra TA, Smalley IJ, Li Y (1994) Failure mechanisms in loess and the effects of moisture content changes on remolded strength. Quatern Int 24:5–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/1040-6182(94)90032-9
Ecemis N, Demirci HE, Karaman M (2015) Influence of consolidation properties on the cyclic re-liquefaction potential of sands. Bull Earthq Eng 13(6):1655–1673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-014-9677-y
Enomoto T (2019) Liquefaction and post-liquefaction properties of sand-silt mixtures and undisturbed silty sands. Soils Found 59(6):2311–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2019.09.005
Ertek MK, Demir G (2017) Evaluation of liquefaction potential and post-liquefaction settlements in a coastal region in Atakum. Arab J Geosci 10(11):232–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2998-9
Gao GR (1981) Classification of microstructure of loess in China and their collapsibility. Sci China Math 24(7):962–974
Gao GR (1996) The distribution and geotechnical properties of loess soils, lateritic soils and clayey soils in China. Eng Geol 42(1):95–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(95)00056-9
GB (1999) Specification of soil test, SL237-032-1999. China Water Power Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
GB (2010) Code for seismic design of buildings, 50011-2010. China Building Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
GB (2015) Seismic ground motion parameters zonation map of China, 18306-2015. China Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
GB (2018) Standard for building construction in collapsible loess regions, 50025-2018. China Building Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Howells DA, Yegian MK, Oweis IS (1976) Liquefaction and cyclic mobility of saturated sands discussion. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 102:265–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(75)92422-5
Hu R, Yeung M, Lee C, Wang SJ (2001) Mechanical behavior and microstructural variation of loess under dynamic compaction. Eng Geol 59:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00074-0
Huang QB, Jia XN, Peng JB, Liu Y, Wang T (2019) Seismic response of loess-mudstone slope with bedding fault zone. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 123:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.05.009
Hughes FE, Madabhushi SPG (2019) Liquefaction induced displacement and rotation of structures with wide basements. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 120:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.01.006
Huie C, Yaling J, Cencen N, Leng GJ, Tian GL (2019) Dynamic characteristics of saturated loess under different confining pressures: a microscopic analysis. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(2):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1101-9
Ishihara K, Okusa S, Oyagi N, Ischuk A (1990) Liquefaction-induced flow slide in the collapsible loess deposit in Soviet Tajik. Soils Found 30(4):73–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(91)90223-9
Ishihara K, Harada K, Lee WF, Chan CC, Safiullah AMM (2016) Post-liquefaction settlement analyses based on the volume change characteristics of undisturbed and reconstituted samples. Soils Found 56(3):533–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2016.04.019
Iwasaki T (1986) Soil liquefaction studies in Japan: state of the art. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 5(1):2–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0267-7261(86)90024-2
Jiang CH, Wang YZ, Huang SS, Tao GL (2020) Properties and microstructure of cementing material made with waste silty clay soil. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 24(7):849–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2018.1426499
Karakan E, Tanrinian N, Sezer A (2019) Cyclic undrained behavior and post liquefaction settlement of a nonplastic silt. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 120:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.01.040
Kayabasi A, Gokceoglu C (2018) Liquefaction potential assessment of a region using different techniques (Tepebasi, Eskişehir, Turkey). Eng Geol 246:139–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.09.029
Leng Y, Peng J, Wang Q, Meng ZJ, Huang WL (2018) A fluidized landslide occurred in the Loess Plateau: a study on loess landslide in South Jingyang tableland. Eng Geol 236:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.05.006
Li P, Xie WL, Pak RYS, Vanapalli SK (2019) Microstructural evolution of loess soils from the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 173:276–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.10.006
Liu W, Chen WW, Wang Q, Wang J, Lin GC (2020) Effect of pre-dynamic loading on static liquefaction of undisturbed loess. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.105915
Lombardi D, Bhattacharya S, Hyodo M, Kaneko T (2014) Undrained behaviour of two silica sands and practical implications for modelling SSI in liquefiable soils. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 66:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.07.010
Ma F, Yang J, Bai X (2017) Water sensitivity and microstructure of compacted loess. Transp Geotech 11:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2017.03.003
Mele L, Tan Tian J, Lirer S, Flora A, Koseki J (2019) Liquefaction resistance of unsaturated sands: experimental evidence and theoretical interpretation. Géotechnique. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.18.P.042
Mohamad R, Dobry R (1986) Undrained monotonic and cyclic triaxial strength of sand. J Geotech Eng 112(10):941–958. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9410(1986)112:10(941)
Ng CWW, Akinniyi DB, Zhou C (2020) Influence of structure on the compression and shear behaviour of a saturated lateritic clay. Acta Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-00981-1
Ni S, Anderson J, Siddharthan R (1997) Characteristics of nonlinear response of deep saturated soil deposits. Bull Seismol Soc Am 87(2):342–355. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB03113
Okamura M, Soga Y (2006) Effects of pore fluid compressibility on liquefaction resistance of partially saturated sand. Soils Found 46(5):695–700. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.46.695
Pei X, Zhang X, Guo B, Wang GH, Zhang FY (2017) Experimental case study of seismically induced loess liquefaction and landslide. Eng Geol 223:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.016
Price AB, DeJong JT, Boulanger RW (2017) Cyclic loading response of silt with multiple loading events. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001759
Rong MS, Wang ZM, Woolery E, Lyu YJ, Li XJ, Li SY (2016) Nonlinear site response from the strong ground-motion recordings in western China. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 82:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.12.001
Rouholamin M, Bhattacharya S, Orense RP (2017) Effect of initial relative density on the post-liquefaction behaviour of sand. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 97:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.02.007
Seed HB, Idriss IM (1971) Simplified procedure for evaluating soil liquefaction potential. J Soil Mech Found Division 97(9):1249–1273
Seed HB, Idriss IM, Arango I (1983) Evaluation of liquefaction potential using field performance data. J Geotech Eng 109(3):458–482. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1983)109:3(458)
Song BH, Tsinaris A, Anastasiadis A, Pitilakis K, Chen WW (2017) Small-strain stiffness and damping of Lanzhou loess. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 95:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.01.041
Tasiopoulou P, Giannakou A, Chacko J, Wit S (2019) Liquefaction triggering and post-liquefaction deformation of laminated deposits. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 124:330–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.04.044
Toyota H, Takada S (2016) Variation of liquefaction strength induced by monotonic and cyclic loading histories. J Geotechn Geoenviron Eng 143(4):04016120. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001634
Tsukamoto Y, Kawabe S, Matsumoto J, Hagiwara S (2014) Cyclic resistance of two unsaturated silty sands against soil liquefaction. Soils Found 54(6):1094–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.11.005
Wang LM (2003) Loess dynamics. Earthquake Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Wang YL (2017) Liquefaction characteristics of gravelly soil under cyclic loading with constant strain amplitude by experimental and numerical investigations. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 92:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.10.029
Wang G, Wei J (2016) Microstructure evolution of granular soils in cyclic mobility and post-liquefaction process. Granular Matter 18(3):51–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0621-5
Wang J, Shi YC, Wang JM, Wang Q, Zhong XM (2011) Comparative analysis of characters of loess subsidence under different seismic load. Chin J Geotechn Eng 33(sup 1):102–105 (in Chinese)
Wang Q, Wang LM, Wang J, Ma HP, Zhong XM, Wang N, Wang J (2012a) Laboratory study on the liquefaction properties of the saturation structural loess. Appl Mech Mater 170(173):1339–1343. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.170-173.1339
Wang ZJ, Luo YS, Guo H, Tian H (2012b) Effects of initial deviatoric stress ratios on dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of undisturbed loess in China. Eng Geol 143–144:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.06.009
Wang SY, Luna R, Yang JS (2013) Post cyclic behavior of low-plasticity silt with limited liquefaction. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 54:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7083-9_6
Wang GH, Zhang DX, Furuya G, Yang J (2014) Pore-pressure generation and fluidization in a loess landslide triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake, China: a case study. Eng Geol 174:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.006
Wang P, Wang Q, Wang J, Wang Q, Chai SF (2015a) Discussion on the influencing factors and test results of loess saturation under back pressure and saturated conditions. Chin J Undergr Sp Eng 11(supp 2):408–412 (in Chinese)
Wang SY, Luna R, Onyejekwe S (2015b) Post liquefaction behavior of low-plasticity silt at various degrees of reconsolidation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 75:259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.04.014
Wang SY, Luna R, Zhao HH (2015c) Cyclic and post-cyclic shear behavior of low-plasticity silt with varying clay content. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 75:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.03.015
Wang SY, Luna R, Onyejekwe S (2016) Effect of initial consolidation condition on post-liquefaction undrained monotonic shear behavior of Mississippi river valley silt. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 142(2):04015075. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001401
Wang LM, Wu ZJ, Xia K (2017) Effects of site conditions on earthquake ground motion and their applications in seismic design in loess region. J Mt Sci 14(6):1185–1193
Wang JD, Li P, Ma Y, Vanapalli SK (2019a) Evolution of pore-size distribution of intact loess and remolded loess due to consolidation. J Soils Sediments 19(3):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2136-7
Wang Q, Wang LM, Zhong XM, Guo P, Wang J, Ma HP, Gao ZN, Wang HJ (2019b) Dynamic behaviour and constitutive relationship of saturated fly ash-modified loess. Eur J Environ Civil Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2019.1577181
Wei YN, Fan W, Yu B, Deng LS, Wei TT (2020) Characterization and evolution of three-dimensional microstructure of Malan loess. CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104585
Wen BP, Yan YJ (2014) Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou, China. Eng Geol 168:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.023
Wu ZJ, Wang LM, Wang P, Chen T, Shi H, Yang XP (2013) Influence of site conditions on ground motion at far field loess sites during strong earthquake. J Central South Univ 20(8):2333–2341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1741-2
Xie X, Qi S, Zhao F, Wang D (2018) Creep behavior and the microstructural evolution of loess-like soil from Xi’an area, China. Eng Geol 236:43–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5006-2
Xu L, Dai FC, Tham LG, Zhou YF, Wu CX (2012) Investigating landslide-related cracks along the edge of two loess platforms in northwest China. Earth Surf Proc Land 37:1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3214
Xu L, Coop MR, Zhang M, Wang GL (2018) The mechanics of a saturated silty loess and implications for landslides. Eng Geol 236:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.021
Yasuda S, Tohno I (1988) Sites of reliquefaction caused by the 1983 Nihonkai-Chubu earthquake. Soils Found 28(2):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(89)90016-8
Yasuda S, Harada K, Ishikawa K, Kanemaru Y (2012) Characteristics of liquefaction in Tokyo Bay area by the 2011 Great East Japan earthquake. Soils Found 52(5):793–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2012.11.004
Yoshimi Y, Yanaka K, Tokimatsu K (1989) Liquefaction resistance of partially saturated sand. Soils Found 29(2):157–162. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.29.3_157
Zeng RQ, Meng XM, Zhang FY, Wang SY, Cui ZJ, Zhang MS, Zhang Y, Chen G (2016) Characterizing hydrological processes on loess slopes using electrical resistivity tomography-a case study of the Heifangtai Terrace, Northwest China. J Hydrol 541:742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.07.033
Zhang Z, Wang L (1995) Geological disasters in loess areas during the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake, China. Geojournal 36(2–3):269–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00813183
Zhang DX, Wang GH (2007) Study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake-induced landslides in loess (China). Eng Geol 94:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.07.007
Zhang XZ, Lu YD, Li X, Lu YC, Pan WS (2019) Microscopic structure changes of Malan loess after humidification in South Jingyang Plateau, China. Environ Earth Sci 78(10):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8290-4
Zhao CG, Yang ZM, Zhang YN, Gao FP (2005) Influential factors of loess liquefaction and pore pressure development. Acta Mech Sin 21(2):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-005-0021-2
Zhou YF, Tham LG, Yan WM, Dai FC, Xu L (2014) Laboratory study on soil behavior in loess slope subjected to infiltration. Eng Geol 183:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.09.010
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Xu He (Lanzhou University) and Wang Jun (China Earthquake Administration) for help in sampling and tests. This work was supported by (Natural Science Foundation of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region) under Grant (2020BS04003); (The Project of High-Level Talent Research in Inner Mongolia University) under Grant (12000-15031942); (National Key Basic Research Development Program of China) under Grant (2014CB744701); and (National Natural Science Foundation of China) under Grant (51778590).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Wang, Q., Lin, G. et al. Effect of pre-dynamic loading on dynamic liquefaction of undisturbed loess. Bull Earthquake Eng 18, 5779–5806 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-020-00917-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-020-00917-w