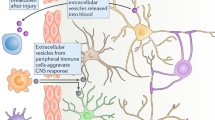
Abstract
Background
The therapeutic potential of stem cells may largely be mediated by paracrine factors contained in exosomes released from intracellular endosomes. A systematic review was performed to identify the effects of stem cell-derived exosomes for their ability to induce restorative effects in animal models of stroke.
Methods
PubMed, Scopus, and ISI Web of Science databases were searched for all available articles testing stem cell-derived exosomes as therapeutic interventions in animal models of stroke until April 2020. The STAIR scale was used to assess the quality of the included studies.
Results
A total of 994 published articles were identified in the systematic search. After screening for eligibility, a total of 16 datasets were included. Type of cerebral ischemia was transient in majority studies and most studies used rat or mice adipose tissue-derived stem cells/bone marrow-derived stem cells. Eight studies indicated improved functional recovery while 8 were able to show reduced infarct volume as a result of exosome therapy. The beneficial effects were mainly attributed to reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, enhanced neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and neurite remodeling. Also, 4 studies demonstrated that exosomes hold great promise as an endogenous drug delivery nano-system.
Conclusion
In preclinical studies, use of stem cell-derived exosomes is strongly associated with improved neurological recovery and reduced brain infarct volume following stroke. Improved preclinical study quality in terms of treatment allocation reporting, randomization and blinding will accelerate needed progress towards clinical trials that should assess feasibility and safety of this therapeutic approach in humans.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10153-7
References
Lackland, D. T., Roccella, E. J., Deutsch, A. F., Fornage, M., George, M. G., Howard, G., Kissela, B. M., Kittner, S. J., Lichtman, J. H., & Lisabeth, L. D. (2014). Factors influencing the decline in stroke mortality: A statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke, 45(1), 315–353.
Lopez, A. D., Mathers, C. D., Ezzati, M., Jamison, D. T., & Murray, C. J. (2006). Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: Systematic analysis of population health data. The Lancet, 367(9524), 1747–1757.
Sarti, C., Rastenyte, D., Cepaitis, Z., & Tuomilehto, J. (2000). International trends in mortality from stroke, 1968 to 1994. Stroke, 31(7), 1588–1601.
Ayala, C., Greenlund, K. J., Croft, J. B., Keenan, N. L., Donehoo, R. S., Giles, W. H., Kittner, S. J., & Marks, J. S. (2001). Racial/ethnic disparities in mortality by stroke subtype in the United States, 1995–1998. American Journal of Epidemiology, 154(11), 1057–1063.
Feigin, V. L., Roth, G. A., Naghavi, M., Parmar, P., Krishnamurthi, R., Chugh, S., Mensah, G. A., Norrving, B., Shiue, I., & Ng, M. (2016). Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. The Lancet Neurology, 15(9), 913–924.
Zhang, Z. G., Buller, B., & Chopp, M. (2019). Exosomes—Beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nature Reviews Neurology, 15(4), 193–203.
Adeoye, O., Hornung, R., Khatri, P., & Kleindorfer, D. (2011). Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator use for ischemic stroke in the United States: A doubling of treatment rates over the course of 5 years. Stroke, 42(7), 1952–1955.
Zivin, J. A. (2009). Acute stroke therapy with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) since it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Annals of Neurology: Official Journal of the American Neurological Association and the Child Neurology Society, 66(1), 6–10.
Campbell, B. C., Mitchell, P. J., Kleinig, T. J., Dewey, H. M., Churilov, L., Yassi, N., Yan, B., Dowling, R. J., Parsons, M. W., & Oxley, T. J. (2015). Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. New England Journal of Medicine, 372(11), 1009–1018.
Lo, E. H., Dalkara, T., & Moskowitz, M. A. (2003). Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4(5), 399–414.
Théry, C., Witwer, K. W., Aikawa, E., Alcaraz, M. J., Anderson, J. D., Andriantsitohaina, R., Antoniou, A., Arab, T., Archer, F., Atkin-Smith, G. K., & Ayre, D. C. (2018). Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 7(1), 1535750.
Otero-Ortega, L., Laso-García, F., Gómez-de Frutos, M., Fuentes, B., Diekhorst, L., Díez-Tejedor, E., & Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. (2019). Role of exosomes as a treatment and potential biomarker for stroke. Translational Stroke Research, 10(3), 241–249.
Otero-Ortega, L., Gutiérrez-Fernández, M., Ramos-Cejudo, J., Rodríguez-Frutos, B., Fuentes, B., Sobrino, T., Hernanz, T. N., Campos, F., López, J. A., & Cerdán, S. (2015). White matter injury restoration after stem cell administration in subcortical ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 6(1), 121.
Zhang, H.-T., Liu, Z.-L., Yao, X.-Q., Yang, Z.-J., & Xu, R.-X. (2012). Neural differentiation ability of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue: A comparative study. Cytotherapy, 14(10), 1203–1214.
Ikegame, Y., Yamashita, K., Hayashi, S.-I., Mizuno, H., Tawada, M., You, F., Yamada, K., Tanaka, Y., Egashira, Y., & Nakashima, S. (2011). Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow for ischemic stroke therapy. Cytotherapy, 13(6), 675–685.
György, B., Hung, M. E., Breakefield, X. O., & Leonard, J. N. (2015). Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles: Clinical promise and open questions. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 55, 439–464.
Lai, C. P.-K., & Breakefield, X. O. (2012). Role of exosomes/microvesicles in the nervous system and use in emerging therapies. Frontiers in Physiology, 3, 228.
Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2009). Neurorestorative therapies for stroke: Underlying mechanisms and translation to the clinic. The Lancet Neurology, 8(5), 491–500.
Li, Y., Liu, Z., Xin, H., & Chopp, M. (2014). The role of astrocytes in mediating exogenous cell-based restorative therapy for stroke. Glia, 62(1), 1–16.
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Reviews, 4(1), 1.
Chen, L., Zhang, G., Gu, Y., & Guo, X. (2016). Meta-analysis and systematic review of neural stem cells therapy for experimental ischemia stroke in preclinical studies. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–8.
Jiang, M., Wang, H., Jin, M., Yang, X., Ji, H., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Wu, F., Wu, G., & Lai, X. (2018). Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs reverse acute ischemic stroke-induced, autophagy-mediated brain injury by promoting M2 microglial/macrophage polarization. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 47(2), 864–878.
Gutierrez-Fernandez, M., Laso-Garcia, F., Gomez-de Frutos, M. C., Otero-Ortega, L., Lopez, E. A., Arroyo, A. M., Diekhorst, L., Gonzalo, M. A., Fuentes, B., & Tejedor, E. D. (2018). Exosomes role in brain repair and recovery in stroke. A dose response study. Stroke, 49.
Yang, Y. J., Cai, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., & Xu, Z. Q. (2018). Exosomes secreted by adipose-derived stem cells contribute to angiogenesis of brain microvascular endothelial cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro through MicroRNA-181b/TRPM7 Axis. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 65(1), 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1071-9.
Deng, Y. M., Chen, D. D., Gao, F., Lv, H., Zhang, G. J., Sun, X., Liu, L., Mo, D. P., Ma, N., Song, L. G., Huo, X. C., Yan, T. Y., Zhang, J. B., & Miao, Z. R. (2019). Exosomes derived from microRNA-138-5p-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells confer neuroprotection to astrocytes following ischemic stroke via inhibition of LCN2. Journal of Biological Engineering, 13(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-019-0193-0.
Geng, W. J., Tang, H. L., Luo, S., Lv, Y., Liang, D. D., Kang, X. H., & Hong, W. D. (2019). Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified ADSCs promotes functional recovery after stroke in rats by improving neurogenesis and suppressing microglia activation. American Journal of Translational Research, 11(2), 780–792.
Jiang, M., Wang, H., Jin, M., Yang, X., Ji, H., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Wu, F., Wu, G., Lai, X., Cai, L., Hu, R., Xu, L., & Li, L. (2018). Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs reverse acute ischemic stroke-induced, autophagy-mediated brain injury by promoting M2 microglial/macrophage polarization. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry : International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology, 47(2), 864–878. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490078.
Liu, Y., Fu, N. S., Su, J. L., Wang, X. M., & Li, X. H. (2019). Rapid Enkephalin delivery using Exosomes to promote neurons recovery in ischemic stroke by inhibiting neuronal p53/Caspase-3. BioMed Research International, 2019, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4273290.
Safakheil, M., & Safakheil, H. (2020). The effect of Exosomes derived from bone marrow stem cells in combination with Rosuvastatin on functional recovery and Neuroprotection in rats after ischemic stroke. Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN, 70, 724–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01483-1.
Tian, T., Zhang, H. X., He, C. P., Fan, S., Zhu, Y. L., Qi, C., Huang, N. P., Xiao, Z. D., Lu, Z. H., Tannous, B. A., & Gao, J. (2018). Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials, 150, 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.012.
Xin, H., Li, Y., Buller, B., Katakowski, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Shang, X., Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2012). Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio), 30(7), 1556–1564. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1129.
Xin, H., Li, Y., Cui, Y., Yang, J. J., Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2013). Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism : Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(11), 1711–1715. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.152.
Xin, H., Wang, F., Li, Y., Lu, Q. E., Cheung, W. L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2017). Secondary release of Exosomes from astrocytes contributes to the increase in neural plasticity and improvement of functional recovery after stroke in rats treated with Exosomes harvested from MicroRNA 133b-overexpressing multipotent Mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Transplantation, 26(2), 243–257. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368916x693031.
Zhang, H. X., Wu, J., Wu, J. H., Fan, Q., Zhou, J. C., Wu, J. W., Liu, S. C., Zang, J., Ye, J. H., Xiao, M., Tian, T., & Gao, J. (2019). Exosome-mediated targeted delivery of miR-210 for angiogenic therapy after cerebral ischemia in mice. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 17, 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0461-7.
Ling, X. Z., Zhang, G. W., Xia, Y. G., Zhu, Q. W., Zhang, J. T., Li, Q., Niu, X., Hu, G. W., Yang, Y. L., Wang, Y., & Deng, Z. F. (2020). Exosomes from human urine-derived stem cells enhanced neurogenesis via miR-26a/HDAC6 axis after ischaemic stroke. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(1), 640–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14774.
Nalamolu, K. R., Venkatesh, I., Mohandass, A., Klopfenstein, J. D., Pinson, D. M., Wang, D. Z., Kunamneni, A., & Veeravalli, K. K. (2019). Exosomes secreted by the cocultures of normal and oxygen–glucose-deprived stem cells improve post-stroke outcome. Neuromolecular Medicine, 21(4), 529–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08540-y.
Nalamolu, K. R., Venkatesh, I., Mohandass, A., Klopfenstein, J. D., Pinson, D. M., Wang, D. Z., & Veeravalli, K. K. (2019). Exosomes treatment mitigates ischemic brain damage but does not improve post-stroke neurological outcome. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry : International Journal of Experimental Cellular Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology, 52(6), 1280–1291. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000090.
Sun, X., Jung, J. H., Arvola, O., Santoso, M. R., Giffard, R. G., Yang, P. C., & Stary, C. M. (2019). Stem cell-derived Exosomes protect astrocyte cultures from in vitro ischemia and decrease injury as post-stroke intravenous therapy. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 13, 394. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00394.
Chen, K. H., Chen, C. H., Wallace, C. G., Yuen, C. M., Kao, G. S., Chen, Y. L., Shao, P. L., Chen, Y. L., Chai, H. T., Lin, K. C., Liu, C. F., Chang, H. W., Lee, M. S., & Yip, H. K. (2016). Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget, 7(46), 74537–74556. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12902.
Otero-Ortega, L., Laso-García, F., del Carmen Gómez-de Frutos, M., Rodríguez-Frutos, B., Pascual-Guerra, J., Fuentes, B., Díez-Tejedor, E., & Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. (2017). White matter repair after extracellular vesicles administration in an experimental animal model of subcortical stroke. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–11.
Xin. (2017). MicroRNA-17-92 cluster in exosomes enhance neuroplasticity and functional recovery after stroke in rats (vol 48, pg 747, 2017). Stroke, 48(5), E137–E137. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0000000000000130.
Chen, K.-H., Chen, C.-H., Wallace, C. G., Yuen, C.-M., Kao, G.-S., Chen, Y.-L., Shao, P.-L., Chen, Y.-L., Chai, H.-T., & Lin, K.-C. (2016). Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget, 7(46), 74537–74556.
Xin, H. Q., Li, Y., Cui, Y. S., Yang, J. J., Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2013). Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(11), 1711–1715. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.152.
Pathipati, P., LeCuyer, M., Faustino, J., Strivelli, J., Phinney, D. G., & Vexler, Z. (2019). Interaction of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes with microglia isolated after acute neonatal stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 39, 634–634.
Raposo, G., & Stoorvogel, W. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. Journal of Cell Biology, 200(4), 373–383.
Kalra, H., Drummen, G. P., & Mathivanan, S. (2016). Focus on extracellular vesicles: Introducing the next small big thing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(2), 170.
Doeppner, T. R., Herz, J., Görgens, A., Schlechter, J., Ludwig, A.-K., Radtke, S., de Miroschedji, K., Horn, P. A., Giebel, B., & Hermann, D. M. (2015). Extracellular vesicles improve post-stroke neuroregeneration and prevent postischemic immunosuppression. Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 4(10), 1131–1143.
Xin, H., Li, Y., Cui, Y., Yang, J. J., Zhang, Z. G., & Chopp, M. (2013). Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 33(11), 1711–1715.
Acknowledgements
This study is related to the project NO. 1398/9887 from Student Research Committee, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. We also appreciate the “Student Research Committee” and “Research & Technology Chancellor” in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for their financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The paper is a systematic review and do not involve human or animal.
The consent form is not needed.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection Special Issue on Exosomes and Microvesicles: from Stem Cell Biology to Translation in Human Diseases
Guest Editor: Giovanni Camussi
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: One of the affiliations was incorrect.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dehghani, L., Hashemi, S., Saadatnia, M. et al. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Treatment for Stroke: a Systematic Review. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 17, 428–438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10024-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10024-7