Abstract
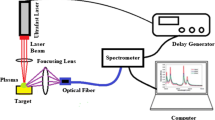
In this paper, we provide the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopic (LIBS) analysis of copper under the action of the ultrafast picosecond Nd:YAG laser and the specifications calculated from the electron temperature of plasma generated by the fundamental (1064 nm), second (532 nm), third (355 nm), and fourth (266 nm) laser harmonics. In this work, a laser pulse energy of 60 mJ±5% with a duration of 170 ps, a beam diameter of ∼0.5±0.1 mm, and a laser intensity 1.79∙1011 W/cm2 ±8% for a single shot was applied. The electron temperature is measured using three spectral lines of neutral copper (Cu I) at 515.3, 521.8, and 522.0 nm, according to the Boltzmann plot model where the local thermodynamic equilibrium (LTE) conditions were assumed. The electron temperature values observed are 13422, 15152, 16605, and 17783K for laser wavelengths of 266, 355, 532, and 1064 nm, respectively. The experimental analysis reveals that the plasma electron temperature rises with the laser wavelength. Variations in the mass ablation rate, inverse Bremsstrahlung absorption, and photoionization with the laser wavelength variation allow us to explore the interaction dynamics. The results obtained allow for variation of the generated plasma electron temperature by guiding the picosecond pulse wavelengths; the later may allow for controlling plasma interactions, which can be applied in plasma spectroscopy of material science.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. S. Eddington, The Internal Constitution of the Stars, Cambridge University Press (1988).
B. R. Adhikari and R. Khanal, Himal. Phys., 4, 60 (2013).
U. Fantz, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 15, S137 (2006).
H. Conrads and M. Schmidt, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 9, 441 (2000).
T. L. Thiem, R. H. Salter, J. A. Gardner, et al., Appl. Spectrosc., 48, 58 (1994).
D. A. Rusak, B. C. Castle, B. W. Smith, et al., “Fundamentals and applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy,” in: Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., Taylor & Francis Group (1997), Vol. 27.
M. A. Gondal and M. A. Dastageer, “Elemental analysis of soils by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy,” in: Springer Ser. Opt. Sci. (2014), Vol. 182, p. 293.
A. Jarota, E. Pastorczak, W. Tawfik, et al., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 21, 192 (2019).
K. C. Phillips, H. H. Gandhi, E. Mazur, et al., Adv. Opt. Photon., 7, 684 (2015).
S. Tan, J. Wu, Y. Zhang, et al., Energies, 11, 3163 (2018).
G. Abdellatif and H. Imam, Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 57, 1155 (2002).
L. Fornarini, V. Spizzichino, F. Colao, et al., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 385, 272 (2006).
S. Messaoud Aberkane, A. Bendib, K. Yahiaoui, et al., Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 113, 147 (2015).
W. Xu, A. Chen, Q. Wang, et al., J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 34, 1018 (2019).
W. A. Farooq, A. S. Al-Johani, M. S. Alsalhi, et al., J. Mol. Struct., 1201, 127152 (2020).
W. A. Farooq, W. Tawfik, F. N. Al-Mutairi, et al., J. Korean Opt. Soc., 17, 548 (2013).
R. Qindeel and W. Tawfik, Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun., 8, 741 (2014).
A. Kramida, Y. Ralchenko, J. Reader, et al., Spectra Database (ver. 5.6.1) NIST At., National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD [http://physics.nist.gov/asd (2019)].
A. B. Gojani, ISRN Spectrosc., 2012, 1 (2012).
W. T. Y. Mohamed, Opt. Appl., 37, 5 (2007).
H. C. Liu, X. L. Mao, J. H. Yoo, et al., Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 54, 1607 (1999).
J. Hoffman, T. Moscicki, and Z. Szymanski, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 104, 815 (2011).
A. E. Hussein, P. K. Diwakar, S. S. Harilal, et al., J. Appl. Phys., 113, 143305 (2013).
A. Bogaerts and Z. Chen, Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 60, 1280 (2005).
L. M. Cabalin and J. J. Laserna, Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 53, 723 (1998).
J. J. Chang and B. E. Warner, Appl. Phys. Lett., 69, 473 (1996).
X. L. Mao, O. V. Borisov, and R. E. Russo, Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 53, 731 (1998).
J. S. Cowpe, R. D. Moorehead, D. Moser, et al., Spectrochim. Acta B: At. Spectrosc., 66, 290 (2011).
K. Afb, N’Mu, and M. Eluille Clark, NASA Technical Note, D-5311 (1969).
X. L. Mao, A. C. Ciocan, O. V. Borisov, et al., Appl. Surf. Sci., 127–129, 262 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fikry, M., Tawfik, W. & Omar, M. Measurement of the Electron Temperature in a Metallic Copper Using Ultrafast Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. J Russ Laser Res 41, 484–490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-020-09901-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-020-09901-w