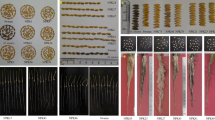
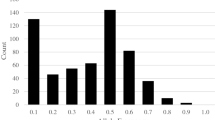
Abstract
Seed traits present important breeding targets for enhancing grain yield and quality in various grain legume crops including pigeonpea. The present study reports significant genetic variation for six seed traits including seed length (SL), seed width (SW), seed thickness (ST), seed weight (SWT), electrical conductivity (EC) and water uptake (WU) among Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh acc. ICPL 20340 and Cajanus scarabaeoides (L.) Thouars acc. ICP 15739 and an F2 population derived from this interspecific cross. Maximum phenotypic values recorded for the F2 population were higher than observed in the parent ICPL 20340 [F2 max vs ICPL 20340: SW (7.05 vs 5.38), ST (4.63 vs 4.51), EC (65.17 vs 9.72), WU (213.17 vs 109.5)], which suggested contribution of positive alleles from the wild parent, ICP 15739. Concurrently, to identify the QTL controlling these seed traits, we assayed two parents and 94 F2 individuals with 113 polymorphic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. In the F2 population, 98 of the 113 SSRs showed Mendelian segregation ratio 1:2:1, whereas significant deviations were observed for 15 SSRs with their χ2 values ranging between 6.26 and 20.62. A partial genetic linkage map comprising 83 SSR loci was constructed. QTL analysis identified 15 marker-trait associations (MTAs) for seed traits on four linkage groups i.e. LG01, LG02, LG04 and LG05. Phenotypic variations (PVs) explained by these QTL ranged from 4.4 (WU) to 19.91% (EC). These genomic regions contributing significantly towards observed variability of seed traits would serve as potential candidates for future research that aims to improve seed traits in pigeonpea.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbo S, Ladizinsky G, Weeden NF (1992) Genetic analysis and linkage studies of seed weight in lentil. Euphytica 58:259–266
Bohra A, Mallikarjuna N, Saxena KB, Upadhyaya H, Vales I, Varshney R (2010) Harnessing the potential of crop wild relatives through genomics tools for pigeonpea improvement. J Plant Biol 37:83–98
Bohra A, Dubey A, Saxena RK, Penmetsa RV, Poornima KN, Kumar N, Farmer AD, Srivani G, Upadhyaya HD, Gothalwal R, Ramesh R, Singh D, Saxena KB, Kavi Kishor PB, Singh NK, Town CD, May GD, Cook DR, Varshney RK (2011) Analysis of BAC-end sequences (BESs) and development of BES-SSR markers for genetic mapping and hybrid purity assessment in pigeonpea. BMC Plant Biol 11:56
Bohra A, Jha UC, Kavi Kishor PB, Pandey S, Singh NP (2014) Genomics and molecular breeding in lesser explored pulse crops: current trends and future opportunities. Biotechnol Adv 32:1410–1428
Bohra A, Jha R, Pandey G, Patil PG, Saxena RK, Singh IP, Singh D, Mishra RK, Mishra A, Singh F, Varshney RK, Singh NP (2017) New Hypervariable SSR markers for diversity analysis, hybrid purity testing and trait mapping in pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh]. Front Plant Sci 8:377
Bohra A, Saxena KB, Varshney RK, Saxena RK (2020) Genomics assisted breeding for pigeonpea improvement. Theor Appl Genet 133:1721–1737
FAOSTAT (2018). https://faostat.fao.org/beta/en/#data/QC/visualize. Accessed 5 Mar 2020
Fedoruk MJ, Vandenberg A, Bett KE (2013) Quantitative trait loci analysis of seed quality characteristics in lentil using single nucleotide polymorphism markers. Plant Genome 6:1–10
Gnanesh BN, Bohra A, Sharma M, Byregowda M, Pande S, Wesley V, Saxena RK, Saxena KB, KaviKishor PB, Varshney RK (2011) Genetic mapping and quantitative trait locus analysis of resistance to sterility mosaic disease in pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.]. Field Crops Res 123:53–61
Han Y, Li D, Zhu D, Li H, Li X, Teng W, Li W (2012) QTL analysis of soybean seed weight across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Theor Appl Genet 125:671–683
Hirota TK, Takahata T, Ogawa M, Iwai IY (2005) Quality of soybean seeds grown in Hyogo prefecture. Bull Hyogo Pre Tech Cent Agric Forest Fish (Agric) 53:6–12
Jha R, Bohra A, Jha UC, Rana M, Chahota RK, Kumar S, Sharma TR (2017) Analysis of an intraspecific RIL population uncovers genomic segments harbouring multiple QTL for seed relevant traits in lentil (Lens culinaris L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:675–684
Kassa MT, Penmetsa RV, Carrasquilla-Garcia N, Sarma BK, Datta S, Upadhyaya HD, Varshney RK, Von Wettberg EJB, Cook DR (2012) Genetic patterns of domestication in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L,) Millsp.) and wild Cajanus relatives. PLoS ONE 7:e39563
Khazaei H, Fedoruk M, Caron CT, Vandenber A, Bett KE (2018) Single nucleotide polymorphism markers associated with seed quality characteristics of cultivated lentil. Plant Genome 11:170051
Khoury CK, Castaeda-Alvarez NP, Achicanoy HA, Sosa CC, Bernau V, Kassa MT, Norton SL, von der Maesen LJG, Upadhyaya HD, Ramirez-Villegas J, Jarvis A, Struik PC (2015) Crop wild relatives of pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.]: distributions, ex situ conservation status, and potential genetic resources for abiotic stress tolerance. Biol Conserv 184:259–270
Lamichaney A, Katiyar PK, Natarajan S, Sripathy KV (2016) Relationship among some seed characters, laboratory germination and field emergence in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genotypes differing in testa colour. J Food Legume 29(1):29–32
Lamichaney A, Kudekallu S, Kamble U, Sarangapany N, Katiyar PK, Bohra A (2017) Differences in seed vigour traits between desi (pigmented) and kabuli (non-pigmented) ecotypes of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and its association with field emergence. J Environ Biol 38:735–742
Li J, Zhao J, Li Y, Gao Y, Hua S, Nadeem M, Sun G, Zhang W, Hou J, Wang X (2019) Identification of a novel seed size associated locus SW9-1 in soybean. Crop J 7:548–559
Liang HZ, Li WD, Wang H, Fang XJ (2005) Genetic effects on seed traits in soybean. Acta Genet Sin 32:1199–1204
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127:1019–1037
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acid Res 8:4321–4326
Niu Y, Xu Y, Liu XF, Yang SX, Wei SP, Xie FT, Zhang YM (2013) Association mapping for seed size and shape traits in soybean cultivars. Mol Breed 31:785–794
Obala J, Saxena RK, Singh VK et al (2019) Development of sequence-based markers for seed protein content in pigeonpea. Mol Genet Genom 294:57–68
Obala J, Saxena RK, Singh VK et al (2020) Seed protein content and its relationships with agronomic traits in pigeonpea is controlled by both main and epistatic effects QTLs. Sci Rep 10:214
Peksen E (2007) Relationships among electrical conductivity of seed leakage, germination, field emergence percentage and some seed traits in faba bean (Vicia faba). Asian J Chem 19:3178–3184
Peksen A, Peksen E, Bozoglu H (2004) Relationships among some seed traits, laboratory germination and field emergence in cowpea genotypes. Pak J Bot 36:311–320
Pérez-Vega E, Pañeda A, Rodríguez-Suárez C et al (2010) Mapping of QTLs for morpho-agronomic and seed quality traits in a RIL population of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:1367–1380
Porch TG, Beaver JS, Debouck DG, Jackson SA, Kelly JD, Dempewolf H (2013) Use of wild relatives and closely related species to adapt common bean to climate change. Agronomy 3:433–461
Qi L, Sun Y, Li J, Su L, Zheng XM, Wang XN et al (2017) Identify QTLs for grain size and weight in common wild rice using chromosome segment substitution lines across six environments. Breed Sci 67:472–482
Saeidi G (2008) Genetic variation and heritability for germination, seed vigour and field emergence in brown and yellow-seeded genotypes of flax. Int J Plant Prod 2:15–22
Sharma D, Green JM (1980) Pigeonpea. In: Fehr WR, Hadley HH (eds) Hybridization of crop plants. American Society of Agronomy Crop Science. Society of America, Wisconsin, pp 471–481
Singh RK, Raipuria RK, Bhatia VS, Rani A, Husain SM, Satyavathi CT, Chauhan GS, Mohapatra T (2008) Identification of SSR markers associated with seed coat permeability and electrolyte leaching in soybean. Physiol Mol Biol Plant 14:173–177
Singh NK, Gupta DK, Jayaswal PK, Mahato AK, Dutta S, Singh S, Bhutani S, Dogra V, Singh BP, Kumawat G, Pal JK, Pandit A, Singh A, Rawal H, Kumar A, Rama Prashat G, Khare A, Yadav R, Raje RS, Singh MN, Datta S, Fakrudin B, Wanjari KB, Kansal R, Dash PK, Jain PK, Bhattacharya R, Gaikwad K, Mohapatra T, Srinivasan R, Sharma TR (2012) The first draft of the pigeonpea genome sequence. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 21:98–112
Smykal P, Vernoud V, Blair MW, Soukup A, Thompson RD (2014) The role of the testa during development and in establishment of dormancy of the legume seed. Front Plant Sci 5:351
Smýkal P, Coyne CJ, Ambrose MJ et al (2015) Legume crops phylogeny and genetic diversity for science and breeding. Crit Rev Plant Sci 34:43–104
Teng WL, Sui MN, Li W, Wu DP, Zhao X, Li HY, Han YP, Li WB (2018) Identification of quantitative trait loci underlying seed shape in soybean across multiple environments. J Agric Sci 156:3–12
Varshney RK, Chen W, Li Y, Bharti AK, Saxena RK, Schlueter JA, Donoghue MTA, Azam S, Fan G, Whaley AM, Farmer AD, Sheridan J, Iwata A, Tuteja R, Penmetsa RV, Wu W, Upadhyaya HD, Yang SP, Shah T, Saxena KB, Michael T, McCombie WR, Yang B, Zhang G, Yang H, Wang J, Spillane C, Cook DR, May GD, Xu X, Jackson SA (2012) Draft genome sequence of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan), an orphan legume crop of resource-poor farmers. Nat Biotechnol 30:83–89
Verma P, Goyal R, Chahota RK, Sharma TR, Abdin MZ, Bhatia S (2015) Construction of a genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs for seed weight and seed size traits in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.). PLoS ONE 10:e0139666
Williams K, Sorrells ME (2014) Three-dimensional seed size and shape QTL in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) populations. Crop Sci 54:98–110
Xu Y, Li HN, Li GJ, Wang X, Cheng LG, Zhang YM (2011) Mapping quantitative trait loci for seed size traits in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor Appl Genet 122:581–594
Yadav P, Saxena KB, Hingane A, Kumar CS, Kandalkar VS, Varshney RK, Saxena RK (2019) An “Axiom Cajanus SNP Array” based high density genetic map and QTL mapping for high-selfing flower and seed quality traits in pigeonpea. BMC Genomics 20:35
Yang S, Ash G, Harper J, Varling J, Wenzl P et al (2006) Low level of genetic diversity in cultivated pigeonpea compared to its wild relatives is revealed by diversity arrays technology. Theor Appl Genet 113:585–595
Yuste-Lisbona FJ, González AM, Capel C et al (2014) Genetic variation underlying pod size and color traits of common bean depends on quantitative trait loci with epistatic effects. Mol Breed 33:939–952
Zavinon F, Adoukonou-Sagbadja H, Bossikponnon A, Dossa H, Ahanhanzo C (2019) Phenotypic diversity for agro-morphological traits in pigeon pea landraces [(Cajanus cajan L.) Millsp.] cultivated in southern Benin. Open Agric 4:487–549
Zhang S, Hu X, Miao H, Chu Y, Cui F, Yang W, Wang C, Shen Y, Xu T, Zhao L, Zhang J, Chen J (2019) QTL identification for seed weight and size based on a high-density SLAF-seq genetic map in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol 3:19
Acknowledgements
Financial support from Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged. Dr C.V. Sameer Kumar is highly acknowledged for providing seeds of ICPL 20340 and ICP 15739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB conceived the idea, planned experiments and wrote manuscript with RJ, UCJ and NPS. RJ, AT performed genotyping experiments. RJ performed QTL analysis. AL along with AKM, VY recorded measurements related to seed traits. AB, RJ, DS analyzed the data. FS, IPS and DD helped in developing mapping population and interpretation of results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohra, A., Jha, R., Lamichaney, A. et al. Mapping QTL for important seed traits in an interspecific F2 population of pigeonpea. 3 Biotech 10, 434 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02423-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02423-x