Abstract
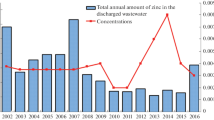
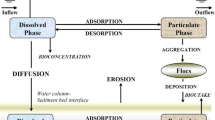
The physically based ECOMAG-HM model, developed to simulate heavy metal cycles in large river basins, was used to study the spatial and temporal regularities in the formation of copper and zinc distributions in water bodies in the basin of the Nizhnekamskoe Reservoir. Maps of the mean annual concentrations of the metals in river network and the mean annual modules of diffuse runoff with its genetic components have been compiled. The contributions of point and diffuse sources to river water pollution by copper and zinc have been evaluated. To specify the estimates of the effect of economic activity on river water pollution, numerical experiments have been carried out to simulate the scenarios of an increase in the amount of metals discharged as wastewater components, wastewater emergency volleys, and complete elimination of anthropogenic impact on a drainage basin.













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abdrakhmanov, R.F., Chalov, Yu.N., and Abdrakhmanova, E.R., Presnye podzemnye vody Bashkortostana (Fresh Groundwater of Bashkortostan), Ufa: Informreklama, 2007.
Atlas Respubliki Bashkortostan (Atlas of the Republic of Bashkortostan), Yaparov, I.M., Ed., Ufa: Kitap, 2005.
Belyaev, S.D., On the issue of taking into account the differentiation of natural environment when planning water protection measures, Geograf. Vestn., 2017, no. 4, vol. 43, pp. 81–96.
Blokov, I.P., Okruzhayushchaya sreda i ee okhrana v Rossii. Izmeneniya za 25 let (Environment and Its Protection in Russia. Changes over 25 Years), Moscow: Sovet Grinpis, 2018.
Gordienko, V.S., Water treatment plants in Ufa today, Vodosnabzh. Sanit. Tekh., 2001, no. 5, pp. 9–11.
Gosudarstvennye doklady o sostoyanii prirodnykh resursov i okruzhayushchei sredy Respubliki Bashkortostan za 2005–2016 gg. (State Reports on the State of Natural Resources and the Environment in the Republic of Bashkortostan over 2005–2016).
Gosudarstvennyi doklad “O sostoyanii i ispol’zovanii vodnykh resursov Rossiiskoi Federatsii v 2016 godu” (State Report “On the State and Use of Water Resources of the Russian Federation in 2016”), Moscow: NIA-Priroda, 2017.
Kachestvo poverkhnostnykh vod Rossiiskoi Federatsii. Informatsiya o naibolee zagryaznennykh vodnykh ob’’ektakh Rossiiskoi Federatsii (Prilozhenie k ezhegodnikam 2011, 2013, 2015, 2016) (Surface Water Quality in the Russian Federation. Information about the Most Heavily Polluted Water Bodies in the Russian Federation (Appendix to Yearbooks of 2011, 2013, 2015, 2016)).
Kirpichnikova, N.V., Major pollution sources in the reservoir, in Ivan’kovskoe vodokhranilishche. Sovremennoe sostoyanie i problemy okhrany (The Ivankovo Reservoir. Current State and Protection Problems), Moscow: Nauka, 2000, pp. 30–62.
Lepikhin, A.P., Bogomolov, A.V., Voznyak, A.A., Lyubimova, T.P., and Parshakova, Ya.N., Diffuse pollution of surface water bodies of Solikamsk–Berezniki Industrial Center: extent, genesis, Gorn.Ekho, 2019, no. 1, vol. 74, pp. 27–31.
Maistrenko, V.N., Khamitov, R.Z., and Budnikov, G.K., Ekologo-analiticheskii monitoring superekotoksikantov (Ecological-Analytical Monitoring of Superecotoxicants), Moscow: Khimiya, 1996.
Mikhailov, S.A., Diffuznoe zagryaznenie diffuznykh ekosistem: metody otsenki i matematicheskie modeli (Diffuse Pollution of Diffuse Ecosystems: Methods of Assessment and Mathematical Models), Barnaul: Den’, 2000.
Moiseenko, T.I. and Gashkina, N.A., Formirovanie khimicheskogo sostava vod ozer v usloviyakh izmeneniya okruzhayushchei sredy (Formation of Water Chemistry in Lakes under Changing Environment), Moscow: Nauka, 2010.
Motovilov, Yu.G., Estimates of anthropogenic pollution of river basins by heavy metals based on ECOMAG model, Sb. Nauch. tr. “Nauchnoe obespechenie realizatsii “Vodnoi strategii Rossiiskoi Federatsii na period do 2020 goda” (Coll. Sci. Pap. “Scientific Support of the Implementation of “The Water Strategy of the Russian Federation for the Period up to 2020”), 2015, vol. 1, pp. 335–343.
Motovilov, Yu.G. and Gel’fan, A.N., Modeli formirovaniya stoka v zadachakh gidrologii rechnykh basseinov (Runoff Formation Models in Problems of River Basin Hydrology), Moscow: Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2018.
Motovilov, Yu.G. and Fashchevskaya, T.B., Spatially distributed model of heavy metal runoff in a river basin, Voda: Khim. Ekol., 2018, nos. 1–3, pp. 18–31.
Nauchno-populyarnaya internet-entsiklopediya “Voda Rossii” (Popular-Science Internet-Encyclopedia “Water of Russia”).
Nikanorov, A.M., Minina, L.I., Lobchenko, E.E., Emel’yanova, V.P., Nichiporova, I.P., Lyampert, N.A., Pervysheva, O.A., and Lavrenko, N.Yu., Dinamika kachestva poverkhnostnykh vod krupnykh rechnykh basseinov Rossiiskoi Federatsii (Dynamics of Surface Water Quality in Large River Basins in the Russian Federation), Minina, L.I, Ed., Rostov-on-Don: Gidrokhim. Inst., 2015.
Selezneva, A.V., Anthropogenic load on rivers from point pollution sources, Izv. Samar. Nauh. Ts. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2003, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 268–277.
SN 435-72. Ukazaniya po opredeleniyu raschetnykh gidrologicheskikh kharakteristik (Guides for Estimating Hydrological Characteristics), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1972.
Tendentsii i dinamika sostoyaniya i zagryazneniya okruzhayushchei sredy v Rossiiskoi Federatsii po dannym mnogoletnego monitoringa za poslednie 10 let. Analiticheskii obzor (Trends and Dynamics of the State and Pollution of the Environment over the Past 10 Years. An Analytical Review), Chernogaev, G.M., Ed., Moscow: Rosgidromet, 2017.
Fashchevskaya, T.B., Krasnogorskaya, N.N., and Rogozina, T.A., On the effect of “Ufavodokanal” plant on water quality in the Belaya river, Materialy mezhdunarod. nauch. konf. “Ekologicheskie i gidrometeorologicheskie problemy bol’shikh gorodov i promyshlennykh zon” (Mater. Intern. Sci. Conf. “Ecological and Hydrometeorological Problems and Industrial Zones”), St. Petersb.: Izd. Ros. Gos. Gidromet. Univ., 2006, pp. 80–82.
Fashchevskaya, T.B., Motovilov, Yu.G., and Shadiyanova, N.B., Natural and anthropogenic variations of the concentrations of iron, copper, and zinc in water streams of the Republic of Bashkortostan, Water Resour., 2018, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 873–887.
Khublaryan, M.G. and Moiseenko, T.I., Water quality, Herald Russ. Acad. Sci., 2009, vol. 79, no. 5, pp. 230–236.
Chernogaeva, G.M., Kuz’mich, V.N., and Berdnikov, S.V., Problem of standardization of chemical runoff from a drainage area, Meteorol. Gidrol., 2003, no. 3, pp. 75–86.
Shul’kin, V.M., Heavy metals in river and coastal marine ecosystems, Extended Abstract of Doctoral (Geogr.) Dissertation, Pacific Geograph. Inst., Far-Eastern Branch, Russ. Acad. Sci., Vladivostok, 2007, 38 p.
Shcherbakov, B.Ya., Chilikin, A.Ya., and Izhevskii, V.S., Valley discharges of production wastewaters and their effects, Ekol. Prom-st. Ross., 2002, no. 6, pp. 39–41.
EPA-State Approach to Instream Monitoring for NWQI.EPA, 2013. Electronic Resource. www.epa. gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/nwqi-monitoringapproach-2013-state-april30.pdf.
Fashchevskaya, T.B., Polianin, V.O., and Fedosova, L.V., Structural analysis of water quality formation in an urban watercourse: point, non-point, transit, and natural, Water Resour., 2018, vol. 45, suppl. 1, pp. S67–S78.
Moriasi, D.N., Arnold, J.G., Van Liew, M.W., Bingner, R.L., Harmel, R.D., and Veith, T.L., Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations, Trans. ASABE, 2007, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 885–900.
Motovilov, Yu.G. and Fashchevskaya, T.B., Simulation of spatially-distributed copper pollution in a large river basin using the ECOMAG-HM model, Hydrol. Sci. J., 2019, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 739–756.
Sauve, S., Manna, S., Turmel, M.-C., Roy, A.G., and Courchesne, F., Solid-solution partitioning of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in the organic horizons of a forest soil, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, no. 37, vol. 22, pp. 5191–5196.
Vink, R. and Peters, S., Modelling point and diffuse heavy metal emissions and loads in the Elbe basin, Hydrol. processes, 2003, vol. 17, pp. 1307–1328.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 17-7730006 and carried out under Governmental Assignment to the Water Problems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, subject 0147-2019-0001, State Registration no. АААА-А18-118022090056-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by G. Krichevets
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fashchevskaya, T.B., Motovilov, Y.G. Simulation of Heavy Metal Pollution of Watercourses in the Basin of the Nizhnekamskoe Reservoir. Water Resour 47, 794–809 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807820050085
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807820050085