Abstract
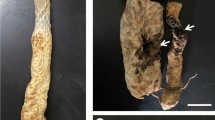
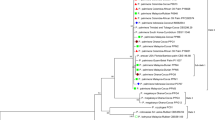
Large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.) is now affected by several diseases caused by both viruses and fungi. At present, leaf blight is considered a major threat to cardamom cultivation in Sikkim. During the past two decades, cultivation of the crop in this region has dropped by almost 60%. Hence, to quantify the severity of leaf blight damage and identification of the causal organism for the disease, a survey was conducted from May to August 2017 in different large cardamom growing regions of Sikkim. During this survey, a typical symptom of leaf blight was observed on cardamom leaves in many locations. The leaves with blights were collected, surface sterilized, and inoculated on potato dextrose agar (PDA). The pathogen was isolated as pure culture, and on the basis of morphological and microscopic characteristics, the fungus was identified species of Curvularia. Molecular characterization of the fungal isolate with ITS-rDNA partial gene amplification using universal primers (ITS4 and ITS5), showed 100% similarity with Curvularia eragrostidis (family: Pleosporaceae). The fungal isolate and nucleotide sequence was deposited in National Fungal Culture Collection of India (NFCCI), Pune and NCBI with accession numbers NFCCI 4541 and MN710527, respectively. This is the first report on the occurrence of C. eragrostidis pathogen causing leaf blight of large cardamom grown in Sikkim.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW and Lipman DJ 1990 A basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215 403–410
Anonymous 2010 Sikkim: A Statistical Profile 2009-10 (Gangtok, Sikkim Directorate of Department of Economics, Statistics, Monitoring & Evaluation, Govt. of Sikkim)
Anonymous 2014 AESA based IPM Package for Large Cardamom (Department of Agriculture and Cooperation Ministry of Agriculture, India)
Bawa GAG, Suprapta DN, Swantara MD, Temaja GRM and Khalimi K 2018 First report of Curvularia specifera the cause of leaf spot disease on rice in Bali, Indonesia. J. Biol. Agric. Health 8 21–26
Benson DA, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J and Sayers EW 2012 GenBank. Nucl. Acid Res. 41 D36–D42
Cagigal EFM and Sanchez AC 2017 Influence of the culture media and the organic matter in the growth of Paxillus ammoniavirescens (Contu & Dessi). Mycobiology 45 172–177
Chung WH and Tsukiboshi T 2005 A new species of Curvularia from Japan. Mycotaxon 91 49–54
Dasgupta S, Saha D and Saha A 2005 Levels of common antigens in determining pathogenicity of Curvularia eragrostidis in different tea varieties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98 1084–1092
Dey D, Saha B, Sircar G, Ghosal K and Bhattacharya SG 2016 Mass spectrometry-based identification of allergens from Curvularia pallescens, a prevalent aerospore in India. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1864 869–879
Fajolu OL, Dee MM, Zale J, Gwinn KD and Ownley BH 2012 First report of leaf spot and necrotic roots on switch grass caused by Curvularia lunata var. aeria in the United States. Plant Dis. 96 1372
Garcia-Aroca T, Doyle V, Singh R, Price T and Collins K 2018 First Report of Curvularia Leaf Spot of Corn, Caused by Curvularia lunata, in the United States. Plant Health Prog. 19 140–142
Gopi R, Kalita H, Avasthe AK, Yadav A, Singh M, Thapa D 2018 Does Pestalotiopsis royenae cause leaf streak of large cardamom? Curr. Sci. 114 2155–2160
Gurung K and Bag N 2018 Occurrence of fungal diseases of large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.) in Sikkim Himalayas; in International conference on climate change, biodiversity and sustainable agriculture 2018 (Assam, India)
Hou JM, Ma BC, Zuo YH, Guo LL, Gao SG, Wang YY and Liu T 2012 Rapid and sensitive detection of Curvularia lunata associated with maize leaf spot based on its Clg2p gene using semi-nested PCR. Lett. Appl. Micro. 56 245–250
Kim YK, Xiao CL and Rogers JD 2005 Influence of culture media and environmental factors on mycelia growth and pycnidial production of Sphaeropsis pyriputrescens. Mycologia 97 25–32
Koch R 1876 Die aetiologie der Milzbrand-Krankheit begründet auf die Entwicklungsgeschichte des Bacillus anthracis (The etiology of anthrax, founded on the course of development of the Bacillus Anthracis). Beiträge zur Biologie der Pflanzen 2 277–310 [English Translation in K. Codell Carter, 15 1987; pp. 1–17]
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C and Tamura K 2018 MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Bio. Evol. 35 1547–1549
Lee SB, Milgroom MG and Taylor JW 1988 A rapid, high yield mini-prep method for isolation of total genomic DNA from fungi. Fungal Genet. Newslett. 35 23–24
Manamgoda DS, Rossman AY, Castlebury LA, Chukeatirote E and Hyde KD 2015 A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-appraisal of the genus Curvularia (Pleosporaceae): human and plant pathogens. Phytotaxa 212 175–198
Pandey Aand Palni LMS 1998 Isolation of Pseudomonas corrugata from Sikkim Himalaya. World J. Micro. Biotech. 14 411–413
Partap U, Sharma G, Gurung MB, Chettri N and Sharma E 2014 Large cardamom farming in changing climatic and socioeconomic conditions in the Sikkim Himalayas. ICIMOD Working Paper 2014/2 (International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development, Kathmandu, Nepal)
Peterson MT, Jo Y, Vines PL and Hoffmann FG 2016 Curvularia malina sp. nov. incites a new disease of warm-season turf- grasses in the southeastern United States. Mycologia 108 915–924
Saha A, Mandal P, Dasgupta S and Saha D 2008 Influence of culture media and environmental factors on mycelial growth and sporulation of Lasiodiplodia theobromae (Pat.) Griffon Maubl. J. Environ. Biol. 29 407–410
Saju KA, Deka TN, Gupta U, Biswas AK, Sudharshan MR, Vijayan AK and Thomas J 2013 Identity of Colletotrichum infections in large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.). J. Spices Aromatic Crops 22 101–103
Saju KA, Deka TN, Sudharshan MR, Gupta U and Biswas AK 2011 Incidence of Phoma leaf spot disease of large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.) and in vitro evaluation of fungicides against the pathogen. J. Spices Aromatic Crops 20 86–88
Sarkar T, Chakraborty P, Das S, Saha D and Saha A 2018 Curvularia leaf spot of pointed gourd in India. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 40 594–600
Seephueak P, Preecha C and Seephueak W 2019 The diversity of fungi associated with rice (Oryza sativa L.) from Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thai. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 15 485–500
Sharma E, Sharma R, Singh KK and Sharma G 2000 A boon for mountain populations: Large cardamom farming in the Sikkim Himalaya. Mount. Res. Dev. 20 108–111
Sharma G and Rai LK 2012 Climate change and sustainability of agrodiversity in traditional farming of the Sikkim Himalaya; In: Climate Change in Sikkim: Patterns, Impacts, Initiatives (eds.) ML Arawatia and S Tambe (Information and Public Relations Department, Gangtok) pp. 193–218
Snedecor GW and Cochran WG 1968 Statistical methods (Oxford and IBH, New Delhi, India)
Srivastava LS and Verma RN 1989 Leaf streak (C.O. Pestalotiopsis royenae—a new disease of large cardamom from Sikkim. Curr. Sci. 58 682–683
White TM, Bruns T, Lee S and Taylor J 1990 Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA for phylogenetics; in PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications (Eds.) Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ and White TJ (Academic Press, San Diego, CA) pp 315–321
Zhang M, Zhang TY and Wu WP 2004 A new name and a new variety in Curvularia. Mycosystema 23 177–178
Acknowledgements
Financial support received from G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment and Sustainable Development, Kosi-Katarmal, Almora, under the research grant ‘Integrated Eco-development Research Programme (IERP)’ is gratefully acknowledged. Agharkar Research Institute Fungus Culture Collection (ARIFCC), Pune, India, is also acknowledged for identification of the pathogen. The authors are thankful to the reviewers for valuable comments to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Manchikatla Venkat Rajam
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurung, K., Dasila, K., Pandey, A. et al. Curvularia eragrostidis, a new threat to large cardamom (Amomum subulatum Roxb.) causing leaf blight in Sikkim. J Biosci 45, 113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00086-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00086-7