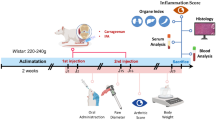
Abstract
Background
Bothrops moojeni snake venom (VBm) has toxins that cause pronounced tissue damage and exacerbated inflammatory reaction. Cannabis sativa L. is a plant species that produces an oil (CSO) rich in unsaturated fatty acids. Nano-emulsions have several advantages, such as better stability and higher penetrating power in membranes. Therefore, this study evaluated the effect of a nano-emulsion based on this herbal derivative (NCS) against VBm-induced inflammation in Wistar rats.
Methods
The CSO and NCS were submitted to physicochemical characterization. The inflammatory process was induced by the VBm (0.10 mg/kg) as follows: rat paw edema, peritonitis, analysis of leukocyte infiltrate in gastrocnemius muscle of rats and formation of granulomatous tissue.
Results
No significant changes were observed when the NCS was submitted to the centrifugation and thermal stress tests. There was no phase separation, changes in density (0.978 ± 0.01 g/cm3) and viscosity (0.889 ± 0.15). The droplet diameter ranged from 119.7 ± 065 to 129.3 ± 0.15 nm and the polydispersity index ranged from 0.22 ± 0.008 to 0.23 ± 0.011. The results showed that treatments with CSO (200 and 400 mg/kg) and NCS (100 mg/kg) were able to decrease significantly (p < 0.001) the formation of edema and granulomatous tissue. The CSO and NCS groups significantly attenuated (p < 0.001) the recruitment of inflammatory cells in the tests for peritonitis and leukocyte infiltrate. The histopathological analysis of the gastrocnemius muscle showed a reduction in tissue damage caused by VBm.
Conclusion
The results obtained in this study showed anti-inflammatory activity of the CSO which may be due to a high UFA content. The nanosizing, as evidenced by the incorporation of the CSO in the NCS improved the effect and opens the perspective for the obtainment of a nanomedicine in which a kinetic stable phytotherapic can be used at low doses.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area on the curve
- CK:
-
Creatine kinase
- CS:
-
Cannabis sativa L.
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry
- HLDs:
-
Hyaluronidases
- i.m:
-
Intramuscular
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- LTB4 :
-
Leukotriene B4
- MNs:
-
Leukocytes mononuclear
- NCS:
-
Nanoemulsion from fixed oil from Cannabis sativa L.
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- CSO:
-
Fixed oil from Cannabis sativa L.
- PGE2 :
-
Prostaglandin E2
- PGI2 :
-
Prostacyclin
- PLA2 :
-
Phospholipase A2
- PMNs:
-
Polymorphonuclear
- po:
-
Per os
- PPARs:
-
Receptors activated by peroxisome proliferators
- SVMPs:
-
Metalloproteinases
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TXA2 :
-
Thromboxane A2
- UFA:
-
Unsaturated fatty acids
- VBm:
-
Bothrops moojeni Snake venom
References
Assis LM, Zavareze ER, Prentice-Hernández C, Souza-Soares LA (2012) Characteristics of nanoparticles and their potential applications in foods. Braz J Food Technol 15:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1981-67232012005000004
Barbosa AM, Do Amaral RO, Teixeira CF, Hyslop S, Cogo JC (2003) Pharmacological characterization of mouse hind paw oedema induced by Bothrops insularis (jararaca ilhoa) snake venom. Toxicon 42:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0041-0101(03)00230-7
Batista EKF, Trindade HI, Lira SRS, Muller JBBS, Silva LLB, Batista MCS (2016) Atividades antinociceptiva e antiinflamatória do extrato etanólico de Luehea divaricata. Rev Bras Plantas Med 8(2):433–441. https://doi.org/10.9771/cmbio.v14i1.12559
Bernardi DS, Pereira TA, Maciel NR, Bortoloto J, Viera GS, Oliveira GC, Rocha-Filho PA (2011) Formation and stability of oil-in-water nanoemulsions containing rice bran oil: in vitro and in vivo assessments. J Nanobiotechnol 9:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-9-44
Bertoli A, Tozzi S, Pistelli L, Angelini LG (2010) Fiber hemp inflorescences: from crop-residues to essential oil production. Ind Crops Prod 32:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.05.012
Borges RS, Lima ES, Keita H, Ferreira IM, Fernandes CP, Cruz RAS, Duarte JL, Moyado JV, Ortiz BLS, Castro AN, Ferreira JV, Hage-Melim LIS, Carvalho JCT (2017) Anti-inflammatory and antialgic actions of a nanoemulsion of Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil and a molecular docking study of its major chemical constituents. Inflammopharmacology 26(1):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0374-8
Calder PC (2013) n-3 Fatty acids, inflammation and immunity: new mechanisms to explain old actions. Proc Nutr Soc 72:326–336. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665113001031
Calder PC (2017) Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man. Biochem Soc Trans 45(5):1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160474
Capeletti E, Mendes M, Biondo D, Oliveira MMD (2016) Procedência de serpentes dos gêneros Bothrops e Crotalus (Viperidae) catalogadas no Serpentário do Jardim Zoológico da Universidade de Caxias do Sul (UCS). Biota Amazon 6(3):45–51. https://doi.org/10.18561/2179-5746/biotaamazonia.v6n3p45-51
Carvalho HO, Santos IVF, Rocha CF, Barros ASA, Souza BSF, Ferreira IM, Bezerra RM, Lima CS, Castro AN, Carvalho JCT (2018a) Effect of the treatment of Copaifera duckei oleoresin (copaiba) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Rev bras Farmacogn 28(6):724–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2018.09.004
Carvalho JCT, Keita H, Santana GR, Souza GC, Dos Santos IVF, Amado JRR, Kourouma A, Prada AL, Carvalho HO, Silva ML (2018b) Effects of Bothrops alternatus venom in zebrafish: a histopathological study. Inflammopharmacology 26(1):273–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0362-z
Favacho HAS, Oliveira BR, Santos KC, Medeiros BJL, Sousa PJC, Perazzo FF, Carvalho JCT (2011) Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Euterpe oleracea oil. Rev Bras Farmacogn 21(1):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2011005000007
Félix-Silva J, Gomes JAS, Xavier-Santos JB, Passos JGR, Silva-Junior AA, Tambourgi DV, Fernandes-Pedrosa MF (2017) Inhibition of local effects induced by Bothrops erythromelas snake venom: assessment of the effectiveness of Brazilian polyvalent bothropic antivenom and aqueous leaf extract of Jatropha gossypiifolia. Toxicon 125:74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.11.260
Fiorini D, Molle A, Nabissi M, Santini G, Benelli G, Maggi F (2019) Valorizing industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products: cannabidiol enrichment in the inflorescence essential oil optimizing sample pre-treatment prior to distillation. Ind Crop Prod 128:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.10.045
González-Mañán D, D'Espessailles A, Dossi CG, Martín MS, Mancilla RA, Tapia GS (2017) Rosa mosqueta oil prevents oxidative stress and inflammation through the upregulation of PPAR-α and NRF2 in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr 147(4):579–588. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.116.243261
Gumiero VC, Rocha-Filho PA (2012) Babassu nanoemulsions have physical and chemical stability. J Disp Sci Technol 33:1569–1573. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2011.625219
Gutiérrez JM, Ownby CL (2003) Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 42(8):915–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.005
Gutiérrez JM, Rucavado A, Chaves F, Díaz C, Escalante T (2009) Experimental pathology of local tissue damage induced by Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 54:958–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.01.038
Irache JM, Esparza I, Gamazo C, Agüeros M, Espuelas S (2011) Nanomedicine: novel approaches in human and veterinary therapeutics. Vet Parasitol 180:47–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.05.028
James MJ, Gibson RA, Cleland LG (2000) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory mediator production. Am J Clin Nutr 71:343–348. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/71.1.343s
Jonsson F, Mancardi DA, Albanesi M, Bruhns P (2013) Neutrophils in local and systemic antibody-dependent inflammatory and anaphylactic reactions. J Leukoc Biol 94:643–656. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1212623
Karthik P, Ezhilarasi PN, Anandharamakrishnan C (2017) Challenges associated in stability of food grade nanoemulsions. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:1435–1450. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1006767
Kremer JM (2007) ω-3 fatty acid supplements in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Clin Nutr 71(1):349–351. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/71.1.349s
Marchionni AMT, Pagnoncelli RM, Reis SRA (2006) Influência do meloxicam e da dexametasona no processo inflamatório e no reparo tecidual. Revista Odonto Ciência 21(51):22–29
Mehmood T (2015) Optimization of the canola oil-based vitamin e nanoemulsions stabilized by food grade mixed surfactants using response surface methodology. Food Chem 183:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.021
Menaldo DL, Bernardes CP, Zoccal KF, Jacob-Ferreira AL, Costa TR, Del Lama MPFM, Naal RMZG, Frantz FG, Faccioli LH, Sampaio SV (2017) Immune cells and mediators involved in the inflammatory responses induced by a P-I metalloprotease and a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops atrox venom. Mol Immunol 85:238–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.03.008
Mesquita TR, Souza AA, Constantino E, Pelógia NCC, Posso IP, Pires OC (2011) Efeito anti-inflamatório da suplementação dietética com ácidos graxos ômega-3, em ratos. Rev Dor 12(4):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1806-00132011000400010
Mikulcova V, Kašparkova V, Humpoliček P, Buňkova L (2017) Formulation, characterization and properties of hemp seed oil and its emulsions. Molecules 22(5):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050700
Moraes IMM, Albuquerque CFG, Kurz ARM, Oliveira FMJ, Abreu VHP, Torres RC, Carvalho VF, Estato V, Bozza PT, Sperandio M, Faria-Neto HCC, SilvaAR, (2018) Omega-9 oleic acid, the main compound of olive oil, mitigates inflammation during experimental sepsis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6053492
Moreira V, Dos-Santos MC, Nascimento NG, Silva HB, Fernandes CM, D'Imperio-Lima MR, Teixeira C (2012) Local inflammatory events induced by Bothrops atrox snake venom and the release of distinct classes of inflammatory mediators. Toxicon 60:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.03.004
Moreira V, Teixeira C, Borges da Silva H, D’Império Lima MR, Dos-Santos MC (2016) The role of TLR2 in the acute inflammatory response induced by Bothrops atrox snake venom. Toxicon 118:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.04.042
MurakamiK BH, Unoki H, Saito Y (2007) Effect of PPARα activation ofmacrophages on the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in cultured adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 561(1):206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.037
Nascimento NG, Sampaio MC, Olivo RA, Teixeira C (2010) Contribution of mast cells to the oedema induced by Bothrops moojeni snake venom and a pharmacological assessment of the inflammatory mediators involved. Toxicon 55:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.08.009
Oca-Ávalos JMM, Candal RJ, Herrera ML (2017) Nanoemulsions: stability and physical properties. Curr Opin Food Sci 16:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2017.06.003
Pereira CB, Marin A, Dalmora SL, Necchi RMM, Moresco RN, Manfro MP (2013) Atividade anti-inflamatória e Avaliação da Toxicidade do Extrato Hidroetanólico de Morus alba (Moraceae). Rev Ciênc Farm Básica Apl 34(1):43–46
Picanço LCS, Bittencourt JAHM, Henriques SVC, Silva JS, Oliveira JMS, Ribeiro JR, Sanjay AB, Carvalho JCT, Stien D, Silva JO (2016) Pharmacological activity of Costus spicatus in experimental Bothrops atrox envenomation. Pharm Biol 54:2103–2110. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2016.1145703
Porto C, Decorti D, Tubaro F (2012) Fatty acid composition and oxidationstability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil extracted by supercriticalcarbon dioxide. Ind Crops Prod 36(1):401–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.09.015
Queiroz MR, Mamede CC, Fonseca KC, Canabrava LCMN, França LV, Silva MC, Stanziola L, Beletti ME, Canabrava HAN, Oliveira F (2011) Biological characterization of a myotoxin phosphoplipase A2 homologue purified from the venom of the snake Bothrops moojeni. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis 17(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1678-91992011000100007
Rai U, Rawal A, Singh S (2017) Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effect of an anti-platelet agent crinumin on carrageenan-induced paw oedema and granuloma tissue formation in rats. Inflammopharmacology 26(3):769–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0411-7
Rao J, McClements DJ (2012) Lemon oil solubilization in mixed surfactant solutions: rationalizing microemulsion and nanoemulsion formation. Food Hydrocoll 26:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.06.002
Rehman MSU, Rashid N, Saif A, Mahmood T, Han J-I (2013) Potential of bioenergy production from industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa): Pakistan perspective. Renew Sust Energ Rev 18:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.10.019
Rodrigues LCC, Meyer TN, Pereira JBB, Silva GR (2015) Avaliação da atividade anti-inflamatória do extrato hidroalcoólico do caroço de abacate sobre a peritonite induzida pela carragenina em ratos. Revista da Universidade Vale do Rio Verde 13(2):367–376. https://doi.org/10.5892/ruvrd.v13i2.2305
Rosset IG, Cavalheiro MCHT, Assaf EM, Porto ALM (2013) Enzymatic esterification of oleic acid with aliphatic alcohols for the biodiesel production by Candida antarctica lipase. Catal Lett 43:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-013-1044-0
Shah KK, Pritt BS, Alexander P (2017) Histopathologic review of granulomatous inflammation. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jctube.2017.02.001
Silva EO, Pardal PPO (2018) Envenenamento por serpente Bothrops no município de Afuá, Ilha de Marajó, estado do Pará. Brasil Rev Pan-Amaz Saude 9(3):57–62. https://doi.org/10.5123/s2176-62232018000300007
Silva JO, Fernandes RS, Ticli FK, Oliveira CZ, Mazzi MV, Franco JJ, Giuliatti S, Pereira PS, Soares AM, Sampaio SV (2007) Triterpenoid saponins, new metalloprotease snake venom inhibitors isolated from Pentaclethra macroloba. Toxicon 50:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.03.024
Sousa EA, Bittencourt JAHM, Oliveira NKS, Henriques SVC, Picanço LCS, Lobato CP, Ribeiro JR, Pereira WLA, Carvalho JCT, Silva JO (2012) Influence of a low-level semiconductor gallium arsenate laser in experimental envenomation induced by Bothrops atrox snake venom. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 7(4):141–148. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajptsp.2012.141.148
Sousa EA, Bittencourt JAHM, Oliveira NKS, Henriques SVC, Picanço LCS, Lobato CP, Ribeiro JR, Pereira WLA, Carvalho JCT, Silva JO (2013) Effects of a low-level semiconductor gallium arsenide laser on local pathological alterations induced by Bothrops moojeni snake venom. Photochem Photobiol Sci 12:1895–1902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3PP50036E
Souza BSF, Carvalho HO, Taglialegna T, Barros ASA, Cunha EL, Ferreira IM, Keita H, Navarrete A, Carvalho JCT (2017) Effect of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (AÇAÍ) oil on dyslipidemia caused by Cocos nucifera L. saturated fat in wistar rats. J Med Food 20(9):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.0027
Strauch MA, Tomaz MA, Machado MM, Ricardo HD, Cons BL, Fernandes FFA, El-Kik CZ, Azevedo MS, Melo PA (2013) Antiophidic activity of the extract of the Amazon plant Humirianthera ampla and constituents. J Ethnopharmacol 145:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.033
Sunitha K, Hemshekhar M, Thushara RM, Sundaram MS, Santhosh MS, Kemparaju K, Girish KS (2015) Inflammation and oxidative stress in viper bite: an insight within and beyond. Toxicon 98:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.02.014
Teh SS, Birch J (2013) Physicochemical and quality characteristics of cold-pressed hemp, flax and canola seed oils. J Food Compos Anal 30:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2013.01.004
Teixeira C, Cury Y, Moreira V, Picolo G, Chaves F (2009) Inflammation induced by Bothrops asper venom. Toxicon 54:988–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.05.026
Vonapartis E, Aubin MP, Seguin P, Mustafa AF, Charron JB (2015) Seed composition of ten industrial hemp cultivars approved for production in Canada. J Food Compos Anal 39:8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2014.11.004
Wang P, Ke Z, YiJ LX, Hao L, Kang Q, Lu J (2019) Effects of β-cyclodextrin on the enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp seed oil by lipase Candida sp. 99–125. Ind Crop Prod 129:688–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.046
Xavier WKS, Medeiros BJ, Lima CS, Favacho HA, Andrade EHA, Araújo RNM, Santos LS, Carvalho JCT (2011) Topical anti-inflammatory action of Caryocar villosum oil (Aubl) Pers. J Appl Pharm Sci 1(03):62–67
Yu Y, Correll PH, Vanden-Heuvel JP (2002) Conjugated linoleic acid decreases production of pro-inflammatory products in macrophages: evidence for a PPAR gamma-dependent mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1581(3):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-1981(02)00126-9
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the CAPES (1723/2018-00 PROCAD-AMAZONIA), CNPq (Proc.402332/2013-0), and INCT North-Northeast Network of Phytoproducts—CNPq.
Funding
CAPES (1723/2018-00 PROCAD-AMAZONIA), CNPq (Proc.402332/2013-0), and INCT North-Northeast Network of Phytoproducts—CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HOC, DESG, KRTP, and AVTLTS, realized the analytics experiments and pharmacological assays. HOC supervised the pharmacologic tests. ML was responsible for the collected venom snack. CPF and IMF supervised the analytics experiments. XH, reviewed the results and final text and JCTC, study General Coordinator. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing for financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
The authors followed the guidelines of the legislation for animal experimentation established by the National Council for Animal Experimentation of Brazil (CONCEA). The project was approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (CEUA) of the Federal University of Amapá-UNIFAP under protocol number 015/2018.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira Carvalho, H., Gonçalves, D.E.S., Picanço, K.R.T. et al. Actions of Cannabis sativa L. fixed oil and nano-emulsion on venom-induced inflammation of Bothrops moojeni snake in rats. Inflammopharmacol 29, 123–135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00754-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00754-y