Abstract
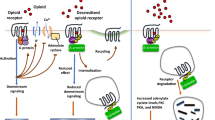
Morphine promotes neuroinflammation after NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) oligomerization in glial cells, but the capacity of other opioids to induce neuroinflammation and its relationship to the development of analgesic tolerance is unknown. We studied the effects of morphine and fentanyl on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in glial and neuronal cells in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), a region involved in pain regulation. Male Wistar rats received i.p. injections of morphine (10 mg/kg) or fentanyl (0.1 mg/kg) 3 × daily for 7 days and were tested for nociception. Two hours after the last (19th) administration, we analyzed NLRP3 oligomerization, caspase-1 activation and gasdermin D-N (GSDMD-N) expression in microglia (CD11b positive cells), astrocytes (GFAP-positive cells) and neurons (NeuN-positive cells). Tolerance developed to both opioids, but only fentanyl produced hyperalgesia. Morphine and fentanyl activated NLRP3 inflammasome in astrocytes and serotonergic (TPH-2-positive) neurons, but fentanyl effects were more pronounced. Both opioids increased GFAP and CD11b immunoreactivity, caspase-1 and GSDMD activation, indicating pyroptotic cell death. The opioid receptor antagonist (−)-naloxone, but not the TLR4 receptor antagonist (+)-naloxone, prevented microglia activation and NLRP3 oligomerization. Only (+)-naloxone prevented astrocytes’ activation. The anti-inflammatory agent minocycline and the NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 delayed tolerance to morphine and fentanyl antinociception and prevented fentanyl-induced hyperalgesia. MCC950 also prevented opioid-induced NLRP3 oligomerization. In conclusion, morphine and fentanyl differentially induce cell-specific activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in the DRN through TLR4 receptors in astrocytes and through opioid receptors in neurons, indicating that neuroinflammation is involved in opioid-induced analgesia and fentanyl-induced hyperalgesia after repeated administrations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams JK, Johnson PL, Hollis JH, Lowry CA (2004) Anatomic and functional topography of the dorsal raphe nucleus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1296.005
Al-Hasani R, Bruchas MR (2011) Molecular mechanisms of opioid receptor-dependent signalling and behaviour. Anesthesiology 115:1363–1381. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238bba6.Molecular
Awad F, Assrawi E, Jumeau C, Georgin-Lavialle S, Cobret L, Duquesnoy P, Piterboth W, Thomas L, Stankovic-Stojanovic K, Louvrier C, Giurgea I, Grateau G, Amselem S, Karabina S-A (2017) Impact of human monocyte and macrophage polarization on NLR expression and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. PLoS ONE 12:e0175336. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175336
Baker KG, Halliday GM, Hornung JP, Geffen LB, Cotton RG, Törk I (1991) Distribution, morphology and number of monoamine-synthesizing and substance P-containing neurons in the human dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuroscience 42:757–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(91)90043-n
Bardin L, Colpaert FC (2004) Role of spinal 5-HT1A receptors in morphine analgesia and tolerance in rats. Eur J Pain 8:253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2003.09.002
Bobeck EN, Haseman RA, Hong D, Ingram SL, Morgan MM (2012) Differential development of antinociceptive tolerance to morphine and fentanyl is not linked to efficacy in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray of the rat. J Pain 13:799–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2012.05.005
Cai Y, Kong H, Pan Y-B, Jiang L, Pan X-X, Hu L, Qian Y-N, Jiang C-Y, Liu W-T (2016) Procyanidins alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. J Neuroinflammation 13:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0520-z
Campion KN, Saville KA, Morgan MM (2016) Relative contribution of the dorsal raphe nucleus and ventrolateral periaqueductal gray to morphine antinociception and tolerance in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 44:2667–2672. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13378
Célèrier E, Rivat C, Jun Y, Laulin JP, Larcher A, Reynier P, Simonnet G (2000) Long-lasting hyperalgesia induced by fentanyl in rats: preventive effect of ketamine. Anesthesiology 92:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200002000-00029
Cesselin F (1995) Opioid and anti-opioid peptides. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 9:409–433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.1995.tb00517.x
Chang L, Ye F, Luo Q, Tao Y, Shu H (2018) Increased hyperalgesia and proinflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion after surgery and/or fentanyl administration in rats. Anesth Analg 126:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002601
Chen S-P, Zhou Y-Q, Wang X-M, Sun J, Cao F, HaiSam S, Ye D-W, Tian Y-K (2019) Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome as a potential target for cancer-induced bone pain. Pharmacol Res 147:104339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104339
Chen W, Foo S-S, Zaid A, Teng T-S, Herrero LJ, Wolf S, Tharmarajah K, Vu LD, van Vreden C, Taylor A, Freitas JR, Li RW, Woodruff TM, Gordon R, Ojcius DM, Nakaya HI, Kanneganti T-D, O’Neill LAJ, Robertson AAB, King NJ, Suhrbier A, Cooper MA, Ng LFP, Mahalingam S (2017) Specific inhibition of NLRP3 in chikungunya disease reveals a role for inflammasomes in alphavirus-induced inflammation. Nat Microbiol 2:1435–1445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0015-4
Chen YL, Law P-Y, Loh HH (2006) Nuclear factor κB signaling in opioid functions and receptor gene expression. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-006-9028-0
Coll RC, Hill JR, Day CJ, Zamoshnikova A, Boucher D, Massey NL, Chitty JL, Fraser JA, Jennings MP, Robertson AAB, Schroder K (2019) MCC950 directly targets the NLRP3 ATP-hydrolysis motif for inflammasome inhibition. Nat Chem Biol 15:556–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0277-7
Colovic M, Caccia S (2003) Liquid chromatographic determination of minocycline in brain-to-plasma distribution studies in the rat. J Chromatogr B 791:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-0232(03)00247-2
Compton P, Griffis C, Breen EC, Torrington M, Sadakane R, Tefera E, Irwin MR (2015) Opioid treatment of experimental pain activates nuclear factor-KB. J Opioid Manag 11:115–125. https://doi.org/10.5055/jom.2015.0261
Craft RM, Stratmann JA, Bartok RE, Walpole TI, King SJ (1999) Sex differences in development of morphine tolerance and dependence in the rat. Psychopharmacology 143:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050911
Debye B, Schmülling L, Zhou L, Rune G, Beyer C, Johann S (2018) Neurodegeneration and NLRP3 inflammasome expression in the anterior thalamus of SOD1(G93A) ALS mice. Brain Pathol 28:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12467
Dempsey C, Rubio Araiz A, Bryson KJ, Finucane O, Larkin C, Mills EL, Robertson AAB, Cooper MA, O’Neill LAJ, Lynch MA (2017) Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 promotes non-phlogistic clearance of amyloid-β and cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav Immun 61:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.014
Den Haan JMM, Kraal G (2012) Innate immune functions of macrophage subpopulations in the spleen. J Innate Immun 4:437–445. https://doi.org/10.1159/000335216
Doyle HH, Eidson LN, Sinkiewicz DM, Murphy AZ (2017) Sex differences in microglia activity within the periaqueductal gray of the rat: a potential mechanism driving the dimorphic effects of morphine. J Neurosci 37:3202–3214. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2906-16.2017
Doyle HH, Murphy AZ (2017) Sex differences in innate immunity and its impact on opioid pharmacology. J Neurosci Res 95:487–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23852
Ellis A, Grace PM, Wieseler J, Favret J, Springer K, Skarda B, Ayala M, Hutchinson MR, Falci S, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2016) Morphine amplifies mechanical allodynia via TLR4 in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Behav Immun 58:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.08.004
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, Samokhvalov IM, Merad M (2010) Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 330:841–845. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1194637
Ginhoux F, Lim S, Hoeffel G, Low D, Huber T (2013) Origin and differentiation of microglia. Front Cell Neurosci 7:45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00045
Gordon R, Albornoz EA, Christie DC, Langley MR, Kumar V, Mantovani S, Robertson AAB, Butler MS, Rowe DB, O’Neill LA, Kanthasamy AG, Schroder K, Cooper MA, Woodruff TM (2018) Inflammasome inhibition prevents α-synuclein pathology and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aah4066
Grace PM, Strand KA, Galer EL, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2018) Protraction of neuropathic pain by morphine is mediated by spinal damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in male rats. Brain Behav Immun 72:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.018
Grace PM, Strand KA, Galer EL, Urban DJ, Wang X, Baratta MV, Fabisiak TJ, Anderson ND, Cheng K, Greene LI, Berkelhammer D, Zhang Y, Ellis AL, Yin HH, Campeau S, Rice KC, Roth BL, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2016) Morphine paradoxically prolongs neuropathic pain in rats by amplifying spinal NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:E3441–E3450. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602070113
Guo H, Callaway JB, Ting JPY (2015) Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med 21:677–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3893
Gustafson-Vickers SL, Van Lu B, Lai AY, Todd KG, Ballanyi K, Smith PA (2008) Long-term actions of interleukin-1β on delay and tonic firing neurons in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to central sensitization. J Mol Pain. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-63
Haleem DJ (2018) Serotonin-1A receptor dependent modulation of pain and reward for improving therapy of chronic pain. Pharmacol Res 134:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.030
Harada S, Nakamoto K, Tokuyama S (2013) The involvement of midbrain astrocyte in the development of morphine tolerance. Life Sci 93:573–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2013.08.009
Hayhurst CJ, Durieux ME (2016) Differential opioid tolerance and opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a clinical reality. Anesthesiology 124:483–488. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000963
Ho MKC, Su Y, Yeung WWS, Wong YH (2009) Regulation of transcription factors by heterotrimeric G proteins. Curr Mol Pharmacol 2:19–31. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874467210902010019
Hornung J-P (2012) Raphe nuclei. In: The human nervous system. Elsevier, pp. 401–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374236-0.10011-2
Hu S, Chao CC, Hegg CC, Thayer S, Peterson PK (2000) Morphine inhibits human microglial cell production of, and migration towards RANTES. J Psychopharmacol 14:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/026988110001400307
Hutchinson MR, Shavit Y, Grace PM, Rice KC, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2011) Exploring the neuroimmunopharmacology of opioids: an integrative review of mechanisms of central immune signaling and their implications for opioid analgesia. Pharmacol Rev 63:772–810. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.004135
Hutchinson MR, Zhang Y, Shridhar M, Evans JH, Buchanan MM, Zhao TX, Slivka PF, Coats BD, Rezvani N, Wieseler J, Hughes TS, Landgraf KE, Chan S, Fong S, Phipps S, Falke JJ, Leinwand LA, Maier SF, Yin H, Rice KC, Watkins LR (2010) Evidence that opioids may have toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 effects. Brain Behav Immun 24:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.08.004
Jacobs BL, Azmitia EC (1992) Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiol Rev 72:165–230. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1992.72.1.165
Kaneto H, Yamazaki A, Kihara T (1985) Evidence for the dissociation of morphine analgesia, tolerance and dependence. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:507–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb03054.x
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8:e1000412. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000412
Kim JK, Jin HS, Suh H-W, Jo E-K (2017) Negative regulators and their mechanisms in NLRP3 inflammasome activation and signaling. Immunol Cell Biol 95:584–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2017.23
Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM (2010) Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 8:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2010.06.007
Lewanowitsch T, Irvine RJ (2003) Naloxone and its quaternary derivative, naloxone methiodide, have differing affinities for μ, δ, and κ opioid receptors in mouse brain homogenates. Brain Res 964:302–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(02)04117-3
Lin C-P, Lu D-H (2018) Role of neuroinflammation in opioid tolerance: translational evidence from human-to-rodent studies. In: Advances in experimental medicine and biology. pp. 125–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1756-9_11
Lin H-Y, Chang Y-Y, Kao M-C, Huang C-J (2017) Naloxone inhibits nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome. J Surg Res 219:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2017.05.119
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun S-C (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Liu Z, Wang C, Rathkey JK, Yang J, Dubyak GR, Abbott DW, Xiao TS (2018) Structures of the gasdermin D C-terminal domains reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition. Structure 26:778–784.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.03.002
Lueptow LM, Fakira AK, Bobeck EN (2018) The Contribution of the Descending pain modulatory pathway in opioid tolerance. Front Neurosci 12:886. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00886
Mao J, Price DD, Mayer DJ (1995) Mechanisms of hyperalgesian and morphine tolerance: a current view of their possible interactions. Pain 62:259–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(95)00073-2
Mao X, Sarkar S, Chang SL (2013) Involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the modulation of an LPS-induced inflammatory response during morphine tolerance. Drug Alcohol Depend 132:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.12.022
Martyn JAJ, Mao J, Bittner EA (2019) Opioid tolerance in critical illness. N Engl J Med 380:365–378. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1800222
Masters SL (2013) Specific inflammasomes in complex diseases. Clin Immunol 147:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2012.12.006
Mayer DJ, Mao J (1999) Mechanisms of opioid tolerance. Pain Forum 8:14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1082-3174(99)70014-0
Mélik Parsadaniantz S, Rivat C, Rostène W, Réaux-Le Goazigo A (2015) Opioid and chemokine receptor crosstalk: a promising target for pain therapy? Nat Rev Neurosci 16:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3858
Mika J, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Osikowicz M, Makuch W, Przewlocka B (2009) Attenuation of morphine tolerance by minocycline and pentoxifylline in naive and neuropathic mice. Brain Behav Immun 23:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.07.005
Miller FD, Gauthier AS (2007) Timing is everything: making neurons versus glia in the developing cortex. Neuron 54:357–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.04.019
Molina-Martínez LM, González-Espinosa C, Cruz SL (2014) Dissociation of immunosuppressive and nociceptive effects of fentanyl, but not morphine, after repeated administration in mice: Fentanyl-induced sensitization to LPS. Brain Behav Immun 42:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2014.06.011
Nicotra L, Loram LC, Watkins LR, Hutchinson MR (2012) Toll-like receptors in chronic pain. Exp Neurol 234:316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.09.038
NIH (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. In: Eighth Edi. (ed.). National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C. https://doi.org/10.17226/12910
Nikodemova M, Duncan ID, Watters JJ (2006) Minocycline exerts inhibitory effects on multiple mitogen-activated protein kinases and IκBα degradation in a stimulus-specific manner in microglia. J Neurochem 96:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03520.x
Nyström S, Antoine DJ, Lundbäck P, Lock JG, Nita AF, Högstrand K, Grandien A, Erlandsson-Harris H, Andersson U, Applequist SE (2013) TLR activation regulates damage-associated molecular pattern isoforms released during pyroptosis. EMBO J 32:86–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.328
Oka T, Aou S, Hori T (1993) Intracerebroventricular injection of interleukin-1β induces hyperalgesia in rats. Brain Res 624:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(93)90060-Z
Paxinos G, Watson C (2009) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier/Academic, San Diego
Posillico CK, Terasaki LS, Bilbo SD, Schwarz JM (2015) Examination of sex and minocycline treatment on acute morphine-induced analgesia and inflammatory gene expression along the pain pathway in Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol Sex Differ 6:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-015-0049-3
Qing-Ping W, Nakai Y (1994) The dorsal raphe: an important nucleus in pain modulation. Brain Res Bull 34:575–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-9230(94)90143-0
Qu J, Tao X-Y, Teng P, Zhang Y, Guo C-L, Hu L, Qian Y-N, Jiang C-Y, Liu W-T (2017) Blocking ATP-sensitive potassium channel alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting HSP70-TLR4-NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 14:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0997-0
Raghavendra V, Rutkowski MD, Deleo JA (2002) The role of spinal neuroimmune activation in morphine tolerance/hyperalgesia in neuropathic and sham-operated rats. J Neurosci 22:9980–9989. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-22-09980.2002
Rathinam VAK, Zhao Y, Shao F (2019) Innate immunity to intracellular LPS. Nat Immunol 20:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0368-3
Reeve AJ, Patel S, Fox A, Walker K, Urban L (2000) Intrathecally administered endotoxin or cytokines produce allodynia, hyperalgesia and changes in spinal cord neuronal responses to nociceptive stimuli in the rat. Eur J Pain 4:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1053/eujp.2000.0177
Schaefer CP, Tome ME, Davis TP (2017) The opioid epidemic: a central role for the blood brain barrier in opioid analgesia and abuse. Fluids Barriers CNS 14:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12987-017-0080-3
Shavit Y, Wolf G, Goshen I, Livshits D, Yirmiya R (2005) Interleukin-1 antagonizes morphine analgesia and underlies morphine tolerance. Pain 115:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.02.003
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F, Shao F (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526:660–665. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15514
Suzuki J, El-Haddad S (2017) A review: fentanyl and non-pharmaceutical fentanyls. Drug Alcohol Depend 171:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.11.033
Taylor DA, Fleming WW (2001) Unifying perspectives of the mechanisms underlying the development of tolerance and physical dependence to opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:11–18
Tortorici V, Robbins CS, Morgan MM (1999) Tolerance to the antinociceptive effect of morphine microinjections into the ventral but not lateral-dorsal periaqueductal gray of the rat. Behav Neurosci 113:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.113.4.833
Vardanyan RS, Hruby VJ (2014) Fentanyl-related compounds and derivatives: current status and future prospects for pharmaceutical applications. Future Med Chem 6:385–412. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.215
von Herrmann KM, Salas LA, Martinez EM, Young AL, Howard JM, Feldman MS, Christensen BC, Wilkins OM, Lee SL, Hickey WF, Havrda MC (2018) NLRP3 expression in mesencephalic neurons and characterization of a rare NLRP3 polymorphism associated with decreased risk of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park Dis 4:24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-018-0061-5
Wang X, Loram LC, Ramos K, De Jesus AJ, Thomas J, Cheng K, Reddy A, Somogyi AA, Hutchinson MR, Watkins LR, Yin H (2012) Morphine activates neuroinflammation in a manner parallel to endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:6325–6330. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200130109
Wang X, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Hutchinson MR, Rice KC, Yin H, Watkins LR (2016) Pharmacological characterization of the opioid inactive isomers (+)-naltrexone and (+)-naloxone as antagonists of toll-like receptor 4. Br J Pharmacol 173:856–869. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13394
Xu E, Liu J, Wang X, Xiong H (2017) Inflammasome in drug abuse. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 9:165–177
Xu X, Yin D, Ren H, Gao W, Li F, Sun D, Wu Y, Zhou S, Lyu L, Yang M, Xiong J, Han L, Jiang R, Zhang J (2018) Selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor reduces neuroinflammation and improves long-term neurological outcomes in a murine model of traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis 117:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.05.016
Yu L, Wang L, Chen S (2010) Endogenous toll-like receptor ligands and their biological significance. J Cell Mol Med 14:2592–2603. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01127.x
Zhang H, Li F, Li W-W, Stary C, Clark JD, Xu S, Xiong X (2016) The inflammasome as a target for pain therapy. Br J Anaesth 117:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aew376
Zhang X, Wang J, Yu T, Du D, Jiang W (2015) Minocycline can delay the development of morphine tolerance, but cannot reverse existing tolerance in the maintenance period of neuropathic pain in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12316
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to thank Mr. Abraham Contreras for animal care and technical assistance. This work is derived from César J. Carranza-Aguilar PhD dissertation.
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from Grant 101 SEP-Cinvestav (SLC and CJCA) and scholarship 338376 (CJCA) from the National Council of Science and Technology (Conacyt, México).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors SLC, CGE and CJCA designed the study. Authors CJCA and AHM carried out the antinociceptive test, immunofluorescence, imaging and the analysis of data set. Authors AHM and CMA were involved in immunofluorescence experiments and images acquisition. Author KCR synthetized (+)-naloxone. Authors SLC, CGE and MM provided drugs, reagents, equipment and, contributed to interpretation of results. The draft manuscript was written by CJCA. All authors contributed to and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carranza-Aguilar, C.J., Hernández-Mendoza, A., Mejias-Aponte, C. et al. Morphine and Fentanyl Repeated Administration Induces Different Levels of NLRP3-Dependent Pyroptosis in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus of Male Rats via Cell-Specific Activation of TLR4 and Opioid Receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 677–694 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00957-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00957-5