Abstract
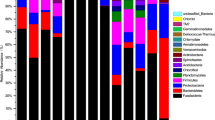
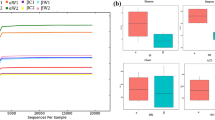
While the fish gut microbiome composition is important to fish health, studies of the gut microbiome of fish lag behind those of terrestrial vertebrates. Whether the microbial communities in an aquatic habitat affect the gut microbiomes of resident fish is unclear. This study investigates and compares the composition of bacterial communities in the gut of crucian carp and humpback and in the water of their habitat using high-throughput sequencing of two hypervariable regions (V3 and V4) of the 16S rRNA gene. We identified 2058 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in the humpback, 2551 OTUs in crucian carp, and 1760 OTUs in their habitat water. 218 OTUs were common to all three bacterial communities. Linear discriminant analysis revealed multiple species that differed significantly in abundance between the communities. This study aims to improve our understanding of the influence of the aquatic habitat on fish–microbe relationships.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari B, Kim SW, Kwon YM (2019) Characterization of microbiota associated with digesta and mucosa in different regions of gastrointestinal tract of nursery pigs. Int J Mol Sci 20(7):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071630
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15718–15723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Beckers B, Beeck MOD, Weyens N, Boerjan W, Vangronsveld J (2017) Structural variability and niche differentiation in the rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiome of field-grown poplar trees. Microbiome 5:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0241-2
Butt RL, Volkoff H (2019) Gut microbiota and energy homeostasis in fish. Front Endocrinol 10:9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00009
Clements KD, Angert ER, Montgomery WL, Choat JH (2014) Intestinal microbiota in fishes: what's known and what's not. Mol Ecol 23:1891–1898. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12699
Eichmiller JJ, Hamilton MJ, Staley C, Sadowsky MJ, Sorensen PW (2016) Environment shapes the fecal microbiome of invasive carp species. Microbiome 4(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-016-0190-1
Feng Q, Chen WD, Wang YD (2018) Gut microbiota: an integral moderator in health and disease. Front Microbiol 9:151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00151
Feng W, Zhang J, Jakovlic I, Xiong F, Wu S, Zou H, Wang G (2019) Gut segments outweigh the diet in shaping the intestinal microbiota composition in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. AMB Express 9:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0770-0
Foysal MJ, Momtaz F, Kawsar AQ, Rahman MM, Gupta S, Tay A (2020) Next-generation sequencing reveals significant variations in bacterial compositions across the gastrointestinal tracts of the Indian major carps, rohu (Labeo rohita), catla (Catla catla) and mrigal (Cirrhinus cirrhosis). Lett Appl Microbiol 70(3):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13256
Gacias M, Sevasti G, Santos P, Sabrina T, Monica A, Fan Z (2016) Microbiota-driven transcriptional changes in prefrontal cortex override genetic differences in social behavior. ELife 5:e13442. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13442
Gilbert JA, Dupont CL (2011) Microbial metagenomics: beyond the genome. Annu Rev Mar Sci 3:347–371. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142811
Larsen AM, Mohammed HH, Arias CR (2014) Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J Appl Microbiol 116:1396–1404. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12475
Lesueur D, Faye A, Sall S, Chotte JL, Sarr A (2015) Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 3:e1029. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1029
Li T, Long M, Gatesoupe F, Zhang Q, Li A, Gong X (2015) Comparative analysis of the intestinal bacterial communities in different species of carp by pyrosequencing. Microb Ecol 69(1):25–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0480-8
Li H, Li T, Tu B, Kou Y, Li X (2017) Host species shapes the co-occurrence patterns rather than diversity of stomach bacterial communities in pikas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:1–11. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.1029
Miyake S, Ngugi DK, Stingl U (2015) Diet strongly influences the gut microbiota of surgeonfishes. Mol Ecol 24(3):656–672. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13050
Morgan XC, Tickle TL, Sokol H, Gevers D, Devaney KL, Ward DV, Huttenhower C (2012) Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol 13(9):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-9-r79
Nelson JS, Grande T, Wilson MVH (1978) Fishes of the world. J Syst Biol 27:136–137. https://doi.org/10.2307/2412830
Qin X (2019) The effect of splenda on gut microbiota of humans could be much more detrimental than in animals and deserves more extensive research. Inflamm Bowel Dis 25(2):e7. https://doi.org/10.1093/ibd/izy181
Rawls JF, Mahowald MA, Ley RE, Gordon JI (2006) Reciprocal gut microbiota transplants from zebrafish and mice to germ-free recipients reveal host habitat selection. Cell 127:423–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.043
Rimoldi S, Gini E, Iannini F, Gasco L, Terova G (2019) The effects of dietary insect meal from Hermetia illucens prepupae on autochthonous gut microbiota of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 9(4):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9040143
Servin AL (2004) Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28(4):405–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2004.01.003
Sian E, Sarah C, Jason W, Catherine S, Paul RR (2018) The gut microbiota of marine fish. Front Microbiol 9:873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00873
Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489:242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11552
Ventura M, Canchaya C, Tauch A, Chandra G, Fitzgerald GF, Chater KF, Van Sinderen D (2007) Genomics of Actinobacteria: tracing the evolutionary history of an ancient phylum. Microbiol Mol Biol R 71(3):495–548. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00005-07
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Williams CL, Ybarra AR, Meredith AN, Durrant BS, Tubbs CW (2019) Gut microbiota and phytoestrogen-associated infertility in southern white rhinoceros. MBio 10:e00311–e00319. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00311-19
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208344
Wu S, Wang G, Angert ER, Wang W, Li W, Zou H (2012) Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine. PLoS One 7:e30440. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030440
Xiong J, Zhu J, Dai W, Dong C, Qiu Q, Li C (2017) Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Envion Microbiol 19:1490–1501. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13701
Ye L, Amberg JJ, Chapman DC, Gaikowski MP, Liu W (2014) Fish gut microbiota analysis differentiates physiology and behavior of invasive Asian carp and indigenous American fish. ISME J 8:541–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.181
Zhang C, Zhang M, Pang X, Zhao Y, Wang L, Zhao L (2012) Structural resilience of the gut microbiota in adult mice under high-fat dietary perturbations. ISME J 6:1848–1857. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.27
Zhang Z, Li D, Refaey MM, Xu W (2017) High spatial and temporal variations of microbial community along the southern catfish gastrointestinal tract: insights into dynamic food digestion. Front Microbiol 8:1531–1531. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01531
Zhang Z, Li D, Refaey MM, Xu W, Tang R, Li L (2018) Host age affects the development of southern catfish gut bacterial community divergent from that in the food and rearing water. Front Microbiol 9:495. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00495
Zhang H, Tang H, Zang Y, Tang X, Wang Y (2019) Microorganism's adaptation of crucian carp may closely relate to its living environments. Microbiol Open 8:e00650. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.650
Zheng X, Yang R, Hu J, Lin S, Gu Z, Ma Z (2019) The gut microbiota community and antioxidant enzymes activity of barramundi reared at seawater and freshwater. Fish Shellfish Immun 89:127–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.03.054
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41476091, U1806213), Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province, China, and the Doctoral scientific fund of Binzhou University (2018Y17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical standards were adhered to in this study and in the production of this manuscript.
Informed consent
No human participants were involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, S., Ren, J., Wang, J. et al. High-throughput sequencing reveals significant diversity in the gut microbiomes of humpback (Chanodichthys dabryi) and crucian carp (Carassius carassius. Biologia 76, 655–662 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00591-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00591-y