Abstract
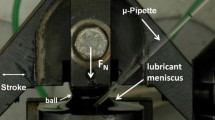
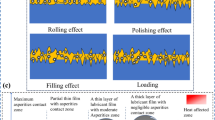
The impact of soot primary nanoparticles affecting metal wear was investigated. The commercial Carbon Black (CB) with different primary particle sizes were mixed with the engine oil for simulating soot contamination. The physical properties of carbon black including density and hardness were calculated using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) image analysis. The metallic wear test was evaluated by using a Four-ball wear tester. After the tests, the ball surfaces were inspected by utilizing High-Resolution Optical Microscope (OM), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis. Based on a Four-ball wear test, the 1 % by weight of carbon black contamination shows a bit higher average wear scar diameter (WSD), but the surface roughness is reduced. SEM micrograph of metallic wear scar for the engine oil without soot shows the area of grooves, plastic deformation and subsurface crack. On the other hand, when carbon black is added to the oil, it can be seen that there are many deep grooves along with the sliding direction. The relationship of calculated oil film thickness, primary nanoparticle size distribution, carbon atom density of soot and hardness is clearly explained metallic wear mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daido, S., Kodama, Y., Inohara, T., Ohyama, N. and Sugiyama, T. (2000). Analysis of soot accumulation inside diesel engines. JSAE Review21, 3, 303–308.
George, S., Balla, S., Gautam, V. and Gautam, M. (2007). Effect of diesel soot on lubricant oil viscosity. Tribology Int.40, 5, 809–818.
Green, D. A. and Lewis, R. (2008). The effects of soot-contaminated engine oil on wear and friction: A review. Proc. Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: J. Automobile Engineering222, 9, 1669–1689.
Hu, E., Hu, X., Lui, T., Fang, L., Deam, K. D. and Xu, H. (2013). The role of soot particles in the tribological behavior of engine lubricating oils. Wear304, 1–2, 152–161.
Jao, T. C., Li, S., Yatsunami, K., Chen, S. J., Csontos, A. A. and Howe, J. M. (2004). Soot characterisation and diesel engine wear. Lubrication Science16, 2, 111–126.
Kamsrisuk, P., Karin, P., Sriprapha, K. and Hanamura, K. (2016). An investigation on particle size distribution in used lubricating. JSAE Paper No. 20165336.
Karin, P., Boonsakda, J., Siricholathum, K., Saenkhumvong, E., Charoenphonphanich, C. and Hanamura, K. (2017a). Morphology and oxidation kinetics of CI engine’s biodiesel particulate matters on cordierite diesel particulate filters using TGA. Int. J. Automotive Technology18, 1, 31–40.
Karin, P., Borhanipour, M., Songsaengchan, Y., Laosuwan, S., Charoenphonphanich, C., Chollacoop, N. and Hanamura, K. (2015). Oxidation kinetics on small CI engine’s biodiesel particulate matter. Int. J. Automotive Technology16, 2, 211–219.
Karin, P., Supanamok, C. and Hanamura, K. (2016). Impact of soot on metal wear characteristics using laser diffraction spectroscopy. J. Research and Applications in Mechanical Engineering4, 2, 126–134.
Karin, P., Watanawongskorn, P., Boonsakda, J., Saenkhumvong, E., Rungsritanapaisan, S., Srivarocha, S., Charoenphonphanich, C., Chollacoop, N. and Hanamura, K. (2017b). Impact of biodiesel on small CI engine combustion behavior and particle emission characteristic. SAE Paper No. 2017-32-0094.
Li, S., Csontos, A. A., Gable, B. M., Passut, C. A. and Jao, T. (2002). Wear in Cummins M-11/EGR test engines. SAE Paper No. 2002-01-1672.
Needelman, W. M. and Madhavan, P. V. (1988). Review of lubricant contamination and diesel engine wear. SAE Paper No. 881827.
Robertson, J. (1911). Structure and electronic properties of diamond-like carbon. Diamond and Diamond-like Films and Coatings, 331–356.
Ryason, P. R., Chan, I. Y. and Gilmore, J. T. (1990). Polishing wear by soot. Wear137, 1, 15–24.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge research financial support from Thailand Research Fund, TRF-RSA6080045.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karin, P., Amornprapa, W., Watanawongskorn, P. et al. Effect of Soot Particle Size on Four Ball Metallic Wear Using Electron Microscopy Image Analysis. Int.J Automot. Technol. 21, 579–589 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-020-0055-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-020-0055-2