Abstract
In2O3@Cu2MoS4 nanocomposite with superior photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance is used for the first time as a photoactivity material, and a signal-off PEC biosensing platform for miRNA detection has been successfully constructed. Firstly, the Cu2MoS4 nanosheets are synthesized by a hydrothermal method, and then, the homogeneous In2O3 nanoparticles (In2O3 NPs) are synthesized by calcination in the air. The In2O3@Cu2MoS4 nanocomposite is constructed with the Cu2MoS4 nanosheets as matrix and In2O3 NPs as sensitizer through a layer-by-layer assembly strategy. The nanocomposite with a tight interface and the matched band structure restrains the electron-hole pair recombination. Under visible light (400–700 nm), the nanocomposite exhibits a strong initial signal. With the catalyzed hairpin assembly, dozens of PbS quantum dots (QDs) are introduced on the surface of an electrode, significantly reducing the photocurrent of n-type In2O3@Cu2MoS4. Since PbS QDs can compete with the nanocomposite for light energy and electron donors, the signal decreased. Under optimal conditions, the biosensor manifests a broad linear range (1 fM–1 nM) and a low detection limit of about 0.57 fM, at a working potential of 0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). The recovery of spiked human serum is between 94.0 and 102%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) is between 1.3 and 2.7%. Therefore, the as-fabricated biosensor exhibits a potential for the determination of miRNA-21 in practical applications.
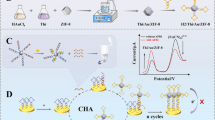
Graphical abstract

The In2O3@Cu2MoS4 nanocomposite owns a strong anode photocurrent signal, which can be used as a photoactive material to construct a “signal-off” biosensor for the detection of miRNA in non-enzymatically catalyzed hairpin assembly (CHA) reaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu SS, Wang S, Zhao JH, Sun J, Yang XR (2017) Fluorescence light-up biosensor for microRNA based on the distance-dependent photoinduced electron transfer. Anal Chem 89:8429–8436. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01900
Lu LP, Wang JX, Miao WJ, Wang XY, Guo GS (2019) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor with a tripod probe for the highly sensitive detection of microRNA. Anal Chem 91:1452–1459. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04271
Ye C, Wang MQ, Luo HQ, Li NB (2017) Label-free photoelectrochemical “off-on” platform coupled with g-wire-enhanced strategy for highly sensitive microRNA sensing in cancer cells. Anal Chem 89:11697–11702. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03150
Zhou MX, Teng XC, Li Y, Deng RJ, Li JH (2019) Cascade transcription amplification of RNA aptamer for ultrasensitive microRNA detection. Anal Chem 91:5295–5302. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00124
Lu J, Wang J, Hu XL, Gyimah E, Yakubu S, Wang K, Wu XY, Zhang Z (2019) Electrochemical biosensor based on tetrahedral DNA nanostructures and g-quadruplex-hemin conformation for the ultrasensitive detection of microRNA-21 in serum. Anal Chem 91:7353–7359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01133
Ling Y, Gao ZF, Zhou Q, Li NB, Luo HQ (2015) Multidimensional optical sensing platform for detection of heparin and reversible molecular logic gate operation based on the phloxine B/polyethyleneimine system. Anal Chem 87:1575–1581. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504023b
Dong HF, Zhang J, Ju HX, Lu HT, Wang SY, Jin S, Hao KH, Du HW, Zhang XJ (2012) Highly sensitive multiple microRNA detection based on fluorescence quenching of graphene oxide and isothermal strand-displacement polymerase reaction. Anal Chem 84:4587–4593. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac300721u
Yang L, Liu CH, Ren W, Li ZP (2012) Graphene surface-anchored fluorescence sensor for sensitive detection of microRNA coupled with enzyme-free signal amplification of hybridization chain reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6450–6453. https://doi.org/10.1021/am302268t
Liu W, Chen AY, Li SK, Peng KF, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2019) Perylene derivative/luminol nanocomposite as a strong electrochemiluminescence emitter for construction of an ultrasensitive microRNA biosensor. Anal Chem 91:1516–1523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04638
Tian L, Qian K, Qi JX, Liu QY, Yao C, Song W, Wang YH (2018) Gold nanoparticles superlattices assembly for electrochemical biosensor detection of microRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron 99:564–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.035
Su S, Cao WF, Liu W, Lu ZW, Zhu D, Chao J, Weng LX, Wang LH, Fan CH, Wang LH (2017) Dual-mode electrochemical analysis of microRNA-21 using gold nanoparticle-decorated MoS2 nanosheet. Biosens Bioelectron 94:552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.040
Mikova B, Dvorak M, Rysava L, Kuban P (2020) Hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction at-line coupled to capillary electrophoresis for direct analysis of human body fluids. Anal Chem 92:7171–7178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00697
Bharti A, Agnihotri N, Prabhakar N (2019) A voltammetric hybridization assay for microRNA-21 using carboxylated graphene oxide decorated with gold-platinum bimetallic nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 186:185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3302-3
Chen ND, Li JY, Feng XZ, Yang YP, Zhu L, Chen XM, Liu X, Li Y, Wang CC, Xia LG (2020) Label-free and self-assembled fluorescent DNA nanopompom for determination of miRNA-21. Mikrochim Acta 187:432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04377-6
Ge L, Li HN, Du XJ, Zhu MY, Chen W, Shi TY, Hao N, Liu Q, Wang K (2018) Facile one-pot synthesis of visible light-responsive BiPO4/nitrogen doped graphene hydrogel for fabricating label-free photoelectrochemical tetracycline aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron 111:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.008
Wang FX, Ye C, Mo S, Liao LL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2019) A novel photoelectrochemical sensing platform based on Fe2O3@Bi2S3 heterojunction for an enzymatic process and enzyme activity inhibition reaction. Sensors Actuators B Chem 288:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.02.121
Yan K, Liu Y, Yang YH, Zhang JD (2015) A cathodic “signal-off” photoelectrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of oxytetracycline. Anal Chem 87:12215–12220. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03139
Han QZ, Wang RY, Xing B, Zhang T, Khan MS, Wu D, Wei Q (2018) Label-free photoelectrochemical immunoassay for CEA detection based on CdS sensitized WO3@BiOI heterostructure nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 99:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.034
Liu C, Zhao L, Liang DX, Zhang XR, Song WL (2019) An CuInS2 photocathode for the sensitive photoelectrochemical determination of microRNA-21 based on DNA-protein interaction and exonuclease III assisted target recycling amplification. Mikrochim Acta 186:692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3804-z
Chen WX, Chen HP, Zhu HT, Gao QQ, Luo J, Wang Y, Zhang S, Zhang K, Wang CM, Xiong YJ, Wu YF, Zheng XS, Chu WS, Song L, Wu ZY (2014) Solvothermal synthesis of ternary Cu2MoS4 nanosheets: structural characterization at the atomic level. Small 10:4637–4644. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201400752
Ma N, Wei B, Cao WL, Gao H, Xu LL (2017) Carbon dots/Cu2MoS4 nanosheets hybrids with efficient photoelectrochemical performance. Mater Lett 197:79–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.03.101
Chi HT, Han QZ, Chi TH, Xing B, Ma N, Wu D, Wei Q (2019) Manganese doped CdS sensitized graphene/Cu2MoS4 composite for the photoelectrochemical immunoassay of cardiac troponin I. Biosens Bioelectron 132:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.048
Feng YX, Yan T, Wu TT, Zhang N, Yang QQ, Sun M, Yan LG, Du B, Wei Q (2019) A label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensing platform base on plasmon Au coupling with MOF-derived In2O3@g-C3N4 nanoarchitectures for tetracycline detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 298:126817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126817
Li MJ, Zheng YN, Liang WB, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2017) Using p-type PbS quantum dots to quench photocurrent of fullerene-Au NP@MoS2 composite structure for ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical detection of ATP. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:42111–42120. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13894
Dai WX, Zhang L, Zhao WW, Yu XD, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2017) Hybrid PbS quantum dot/nanoporous NiO film nanostructure: preparation, characterization, and application for a self-powered cathodic photoelectrochemical biosensor. Anal Chem 89:8070–8078. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01557
Liao YH, Huang R, Ma ZK, Wu YX, Zhou XM, Xing D (2014) Target-triggered enzyme-free amplification strategy for sensitive detection of microRNA in tumor cells and tissues. Anal Chem 86:4596–4604. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5007427
Sun MF, Liu JL, Chai YQ, Zhang J, Tang Y, Yuan R (2019) Three-dimensional cadmium telluride quantum dots-DNA nanoreticulation as a highly efficient electrochemiluminescent emitter for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA from cancer cells. Anal Chem 91:7765–7773. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01185
Duan RX, Zuo XL, Wang ST, Quan XY, Chen DL, Chen ZF, Jiang L, Fan CH, Xia F (2013) Lab in a tube: ultrasensitive detection of microRNAs at the single-cell level and in breast cancer patients using quadratic isothermal amplification. J Am Chem Soc 135:4604–4607. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja311313b
Lin MH, Wen YL, Li LY, Pei H, Liu G, Song HY, Zuo XL, Fan CH, Huang Q (2014) Target-responsive, DNA nanostructure-based E-DNA sensor for microRNA analysis. Anal Chem 86:2285–2288. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500251t
Labib M, Khan N, Ghobadloo SM, Cheng J, Pezacki JP, Berezovski MV (2013) Three-mode electrochemical sensing of ultralow microRNA levels. J Am Chem Soc 135:3027–3038. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja308216z
Su S, Hao Q, Yan ZY, Dong RM, Yang R, Zhu D, Chao J, Zhou Y, Wang LH (2019) A molybdenum disulfide@methylene blue nanohybrid for electrochemical determination of microRNA-21, dopamine and uric acid. Mikrochim Acta 186:607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3678-0
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675131) and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTC-2015jcyjB50001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.18 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L.D., Wen, Y.X., Zhang, X.Y. et al. Signal-off photoelectrochemical determination of miRNA-21 using aptamer-modified In2O3@Cu2MoS4 nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 187, 561 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04540-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04540-z