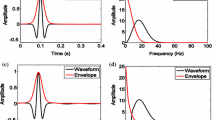
Abstract
The full-waveform inversion method is a high-precision inversion method based on the minimization of the misfit between the synthetic seismograms and the observed data. However, this method suffers from cycle skipping in the time domain or phase wrapping in the frequency because of the inaccurate initial velocity or the lack of low-frequency information. furthermore, the object scale of inversion is affected by the observation system and wavelet bandwidth, the inversion for large-scale structures is a strongly nonlinear problem that is considerably difficult to solve. In this study, we modify the unwrapping algorithm to obtain accurate unwrapped instantaneous phase, then using this phase conducts the inversion for reducing the strong nonlinearity. The normal instantaneous phases are measured as modulo 2π, leading the loss of true phase information. The path integral algorithm can be used to unwrap the instantaneous phase of the seismograms having time series and one-dimensional (1D) signal characteristics. However, the unwrapped phase is easily affected by the numerical simulation and phase calculations, resulting in the low resolution of inversion parameters. To increase the noise resistance and ensure the inversion accuracy, we present an improved unwrapping method by adding an envelope into the path integral unwrapping algorithm for restricting the phase mutation points, getting accurate instantaneous phase. The objective function constructed by unwrapping instantaneous phase is less affected by the local minimum, thereby making it suitable for full-waveform inversion. Further, the corresponding instantaneous phase inversion formulas are provided. Using the improved algorithm, we can invert the low-wavenumber components of the underneath structure and ensure the accuracy of the inverted velocity. Finally, the numerical tests of the 2D Marmousi model and 3D SEG/EAGE salt model prove the accuracy of the proposed algorithm and the ability to restore large-scale low-wavenumber structures, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Theyab, A., and Schuster, G., 2015, Reflection full-waveform inversion for inaccurate starting models: 2015 SEG Workshop: Depth Model Building, Expanded Abstracts,18–22.
Bunks, C., Saleck, F., Zaleski, S., and Chavent, G., 1995, Multiscale seismic waveform inversion: Geophysics, 60(5), 1457–1473.
Bozdag, E., Trampert, J., and Tromp, J., 2011, Misfit functions for full waveform inversion based on instantaneous phase and envelope measurements: Geophysical Journal International, 185(2), 845–870.
Chi, B., Dong, L., and Liu, Y., 2013, Full waveform inversion based on envelope objective function: 75th EAGE Annual Meeting, Expanded Abstracts, 348–351.
Chi, B., Dong, L., and Liu, Y., 2014, Full waveform inversion method using envelope objective function without low frequency data: Journal of Applied Geophysics, 109, 36–46.
Choi, Y., and Alkhalifah, T., 2011, Frequency-domain waveform inversion using the unwrapped phase: 81st Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 2576–2580.
Choi, Y., and Alkhalifah, T., 2015, Unwrapped phase inversion with an exponential damping: Geophysics, 80(5), R251–R264.
Collaro A., Franceschetti G., Palmieri F., and Ferreiro M. S., 1997, Phase unwrapping by means of genetic algorithms: Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 15(2), 407–418.
Fornaro, G., Franceschetti, G., and Lanari, R., 1996, Interferometric SAR phase unwrapping using Green’s formulation: IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens, 34, 720–727.
Fornaro G., Franceschetti G., Lanari R., and Sansoti E., 1996, Robust phase unwrapping techniques: a comparison: Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 13(12), 2355–2366.
Fu, L., Guo, B., Sun, Y., and Schuster, G. T., 2018, Multiscale phase inversion of seismic data: Geophysics, 83(2), R159–R71.
Goldstein, R. M., Zebker, H. A., and Werner, C., 1988, Satellite radar interferometry: two-dimensional phase unwrapping: Radio Sci, 23, 713–720.
Ghiglia, D. C., and Romero, L. A., 1994, Robust two-dimensional weighted and unweighted phase unwrapping that uses fast transforms and iterative methods: J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11, 107–117.
Hu, W., 2014, FWI without low frequency data - beat tone inversion: 84th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 1116–1120.
Luo, Y., and Schuster, G., 1991, Wave-equation traveltime inversion: Geophysics, 56(5), 645–653.
Li, Y. E., and Demanet, L., 2016, Full-waveform inversion with extrapolated low frequency data: Geophysics, 81(6), R339–R348.
Lei, F., and Symes, W. W., 2017, A Robust Approach for Extended Waveform Inversion without Low-Frequency Data: 2017 SEG Workshop: Full-Waveform Inversion and Beyond, Expanded Abstracts, 38–42.
Ma, Y., and Hale, D., 2013, Wave-equation reflection traveltime inversion with dynamic warping and full waveform inversion: Geophysics, 78(6), R223–R233.
Pritt, M. D., and Shipman, J. S., 1994, Least-squares two dimensional phase unwrapping using FFT’s: IEEE Trans: Geosci. Remote Sens, 32, 706–708.
Pritt M. D., 1996, Phase unwrapping by means of multigrid techniques for interferometric SAR: IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 34, 728–738.
Pratt, R. G., and Shipp, R. M., 1999, Seismic waveform inversion in the frequency domain. Part 2: Fault delineation in sediments using crosshole data: Geophysics, 64, 902–914.
Plessix, R. E., 2006, A review of the adjoint-state method for computing the gradient of a functional with geophysical applications: Geophysical Journal International, 167(2), 495–503.
Sun, Y., and Schuster, G. T., 1993, Time-domain phase inversion: 63rd Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 684–687.
Symes, W. W., and Carazzone, J. J., 1991, Velocity inversion by differential semblance optimization: Geophysics, 56(5), 654–663.
Symes, W. W., 2008, Migration velocity analysis and waveform inversion: Geophysical Prospecting, 56(6), 765–790.
Tarantola, A., 1984, Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation: Geophysics, 49, 1259–1266.
Virieux, J., and Operto, S., 2009, An overview of full-waveform inversion in exploration geophysics: Geophysics, 74(6), WCC1–WCC26.
Yu, H. W., Li, Z. F, and Bao, Z., 2011, Residues cluster-based segmentation and outlier-detection method for large-scale phase unwrapping: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 20(10), 2865–2875.
Zebker, H. A., and Lu Y., 1998, Phase unwrapping algorithms for radar interferometry: residue-cut, least-squares, and synthesis algorithms: Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 15(15), 586–598.
Acknowledgments
We thank the remaining members of the China University of Petroleum (East China) Seismic Wave Propagation and Imaging Laboratory (SWPI) for their suggestions and assistance. We would also like to thank the three reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on this article. We express sincere thanks to Editor Weicun Fan for her considerable and patiently work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by the National Science and Technology major projects of China (No. 2017ZX05032-003-002), Shandong Key Research and Development Plan Project (No. 2018GHY115016), and China University of Petroleum (East China) Independent Innovation Research Project (No. 18CX06023A).
Lin Yu-Zhao received his Geophysics bachelor’s degree from China University of Petroleum (East China) in 2015; From 2015 to present, he has been in the successive postgraduate and doctoral program in Geological Resources and Geological Engineering of China University of Petroleum (East China). He is mainly engaged in seismic wave inversion and imaging.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YZ., Li, ZC., Zhang, K. et al. Instantaneous phase inversion based on an unwrapping algorithm. Appl. Geophys. 17, 124–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-019-0794-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-019-0794-x