Abstract
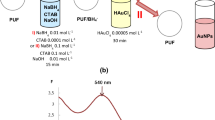
A method for determination of mercury(II) using polyurethane foam modified on the surface with silver triangular nanoplates that have an average edge length of 52 nm and thickness of 4 nm is developed. The method is based on the oxidation of silver nanoplates with mercury(II). This process is accompanied by a decrease in the surface plasmon resonance band of nanoparticles which allows us to consider the nanocomposite material as a solid-phase analytical reagent for the determination of mercury(II). The influence of the reaction time and pH on the sensitivity of mercury determination is studied. The detection limit of mercury under the selected conditions is equal to 50 μg/L; the range of determined contents is 150–1000 μg/L. The increase in the volume of the analyzed solution from 5.0 to 100.0 mL via concentration reduces the detection limit of mercury to 5 μg/L.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. Vilela, M. C. González, and A. Escarpa, “Sensing colorimetric approaches based on gold and silver nanoparticles aggregation: chemical creativity behind the assay. A review,” Anal. Chim. Acta 751, 24 (2012).
A. Liang, Q. Liu, G. Wen, and Z. Jiang, “The surface-plasmon-resonance effect of nanogold/silver and its analytical applications,” Trend. Anal. Chem. 37, 32 (2012).
V. V. Apyari, S. G. Dmitrienko, M. V. Gorbunova, A. A. Furletov, and Yu. A. Zolotov, “Gold and silver nanoparticles in optical molecular absorption spectroscopy,” J. Anal. Chem. 74, 21 (2019).
E. A. Terent’eva, V. V. Apyari, E. V. Kochuk, S. G. Dmitrienko, and Yu. A. Zolotov, “Use of silver nanoparticles in spectrophotometry,” J. Anal. Chem. 72, 1138 (2017).
K. Shrivas, N. Nirmalkar, M. K. Deb, et al., “Application of functionalized silver nanoparticles as a biochemical sensor for selective detection of lysozyme protein in milk sample,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 213, 127 (2019).
M. Rycenga, C. M. Cobley, J. Zeng, et al., “Controlling the synthesis and assembly of silver nanostructures for plasmonic applications,” Chem. Rev. 111, 3669 (2011).
F. A. Kappi, G. Z. Tsogas, D. L. Giokas, et al., “Colorimetric and visual read-out determination of cyanuric acid exploiting the interaction between melamine and silver nanoparticles,” Microchim. Acta 181, 623 (2014).
S. Yousefi and M. Saraji, “Optical aptasensor based on silver nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of adenosine,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 213, 1 (2019).
A. Jinnarak and S. Teerasong, “A novel colorimetric method for detection of gamma-aminobutyric acid based on silver nanoparticles,” Sens. Actuators, B 229, 315 (2016).
M. Gao, L. Li, S. Lu, et al., “Silver nanoparticles for the visual detection of lomefloxacin in the presence of cysteine,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 205, 72 (2018).
V. V. Apyari, P. A. Volkov, and S. G. Dmitrienko, “Synthesis and optical properties of polyurethane foam modified with silver nanoparticles,” Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 3, 015001 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/3/1/015001
E. A. Terenteva, V. V. Apyari, S. G. Dmitrienko, and Yu. A. Zolotov, “Formation of plasmonic silver nanoparticles by flavonoid reduction: a comparative study and application for determination of these substances,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 151, 89 (2015).
E. A. Terenteva, V. V. Arkhipova, V. V. Apyari, et al., “Simple and rapid method for screening of pyrophosphate using 6,6-ionene-stabilized gold and silver nanoparticles,” Sens. Actuators, B 241, 390 (2017).
M. L. Personick, M. R. Langille, J. Zhang, et al., “Plasmon mediated synthesis of silver cubes with unusual twinning structures using short wavelength excitation,” Small 9, 1947 (2013).
S. H. Han and J.-S. Lee, “Synthesis of length-controlled polyvalent silver nanowire-DNA conjugates for sensitive and selective detection of DNA targets,” Langmuir 28, 828 (2012).
B. H. Kim and J. S. Lee, “One-pot photochemical synthesis of silver nanodisks using a conventional metal-halide lamp,” Mater. Chem. Phys. 149–150, 678 (2015).
J. Zhang, M. R. Langille, and C. A. Mirkin, “Synthesis of silver nanorods by low energy excitation of spherical plasmonic seeds,” Nano Lett. 11, 2495 (2011).
Q. Zhang, N. Li, J. Goebl, et al., “A systematic study of the synthesis of silver nanoplates: is citrate a ‘magic’ reagent?,” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 18931 (2011).
B. Tang, S. Xu, X. Hou, et al., “Shape evolution of silver nanoplates through heating and photoinduction,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 646 (2013).
V. V. Apyari, M. O. Gorbunova, A. V. Shevchenko, et al., “Towards highly selective detection using metal nanoparticles: a case of silver triangular nanoplates and chlorine,” Talanta 176, 406 (2018).
M. O. Gorbunova, A. A. Baulina, M. S. Kulyaginova, et al., “Dynamic gas extraction of iodine in combination with a silver triangular nanoplate-modified paper strip for colorimetric determination of iodine and of iodine-interacting compounds,” Microchim. Acta 186, 188 (2019).
M. O. Gorbunova, A. V. Shevchenko, V. V. Apyari, et al., “Selective determination of chloride ions using silver triangular nanoplates and dynamic gas extraction,” Sens. Actuators, B 256, 699 (2018).
X. C. Jiang and A. C. Yu, “Silver nanoplates: a highly sensitive material toward inorganic anions,” Langmuir 24, 4300 (2008).
X.-H. Yang, J. Ling, J. Peng, et al., “A colorimetric method for highly sensitive and accurate detection of iodide by finding the critical color in a color change process using silver triangular nanoplates,” Anal. Chim. Acta 798, 74 (2013).
S. Cheng, X. Y. Hou, J. Tang, and Y. F. Long, “Silver nanoplates-based colorimetric iodide recognition and sensing using sodium thiosulfate as a sensitizer,” Anal. Chim. Acta 825, 57 (2014).
G.-L. Wang, X.-Y. Zhu, Y.-M. Dong, et al., “The pH-dependent interaction of silver nanoparticles and hydrogen peroxide: a new platform for visual detection of iodide with ultra-sensitivity,” Talanta 107, 146 (2013).
M. O. Gorbunova, A. A. Baulina, M. S. Kulyaginova, et al., “Determination of iodide based on dynamic gas extraction and colorimetric detection by paper modified with silver triangular nanoplates,” Microchem. J. 145, 729 (2018).
T. Kiatkumjorn, P. Rattanarat, W. Siangproh, et al., “Glutathione and L-cysteine modified silver nanoplates-based colorimetricassay for a simple, fast, sensitive and selective determination of nickel,” Talanta 128, 215 (2014).
S. Chaiyo, W. Siangproh, A. Apilux, and O. Chailapakul, “Highly selective and sensitive paper-based colorimetric sensor using thiosulfate catalytic etching of silver nanoplates for trace determination of copper ions,” Anal. Chim. Acta 866, 75 (2015).
X.-D. Xia, T.-L. Wang, and X.-Y. Yuan, “Tuning plasmon absorption of unmodified silver nanoplates for sensitive and selective detection of copper ions by introduction of ascorbate,” Chin. Chem. Lett. 25, 1403 (2014).
X. Y. Hou, S. Chen, J. Tang, and Y. F. Long, “Visual determination of trace cysteine based on promoted corrosion of silver triangular nanoplates by sodium thiosulfate,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 125, 285 (2014).
Y. Li, Z. Li, Y. Gao, et al., “‘Red-to-blue’ colorimetric detection of cysteine via anti-etching of silver nanoprisms,” Nanoscale 6, 10631 (2014).
A. A. Furletov, V. V. Apyari, A. V. Garshev, et al., “Silver triangular nanoplates as a colorimetric probe for sensing thiols: characterization in the interaction with structurally related thiols of different functionality,” Microchem. J. 147, 979 (2019).
D. Wu, H.-F. Lu, H. Xie, et al., “Uricase-stimulated etching of silver nanoprisms for highly selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of uric acid in human serum,” Sens. Actuators, B 221, 1433 (2015).
K. Tan, G. Yang, H. Chen, et al., “Facet dependent binding and etching: ultra-sensitive colorimetric visualization of blood uric acid by unmodified silver nanoprisms,” Biosens. Bioelectron. 59, 227 (2014).
Y. Xia, J. Ye, K. Tan, et al., “Colorimetric visualization of glucose at the submicromole level in serum by a homogenous silver nanoprism-glucoseoxidase system,” Anal. Chem. 85, 6241 (2013).
G. S. Metraux and C. A. Mirkin, “Rapid thermal synthesis of silver nanoprisms with chemically tailorable thickness,” Adv. Mater. 17, 412 (2005).
V. V. Apyari, S. G. Dmitrienko, and Yu. A. Zolotov, “Unusual application of common digital devices: potentialities of eye-one pro mini-spectrophotometer—a monitor calibrator for registration of surface plasmon resonance bands of silver and gold nanoparticles in solid matrices,” Sens. Actuators, B 188, 1109 (2013).
J. E. Millstone, S. J. Hurst, G. S. Metraux, et al., “Colloidal gold and silver triangular nanoprisms,” Small 5, 646 (2009).
A. A. Furletov, V. V. Apyari, A. V. Garshev, S. G. Dmitrienko, and Yu. A. Zolotov, “Silver triangular nanoplates as a spectrophotometric reagent for the determination of mercury(II),” J. Anal. Chem. 72, 1203 (2017).
L. K. Svetlov and T. N. Kutekhov, Methods of Analysis of Wastewater of Chemical Industries in the USSR and Abroad (NIITEKhIM, Moscow, 1975), p. 7 [in Russian].
M. Nidya, M. Umadevi, and B. J. M. Rajkumar, “Structural, morphological and optical studies of l-cysteine modified silver nanoparticles and its application as a probe for the selective colorimetric detection of Hg2+,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 133, 265 (2014).
K. Farhadi, M. Forough, R. Molaei, et al., “Highly selective Hg2+ colorimetric sensor using green synthesized and unmodified silver nanoparticles,” Sens. Actuators, B 161, 880 (2012).
A. Apilux, W. Siangproh, N. Praphairaksit, and O. Chailapakul, “Simple and rapid colorimetric detection of Hg(II) by a paper-based device using silver nanoplates,” Talanta 97, 388 (2012).
P. Jarujamrus, M. Amatatongchai, A. Thima, et al., “Selective colorimetric sensors based on the monitoring of an unmodified silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) reduction for a simple and rapid determination of mercury,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 142, 86 (2015).
J.-L. Chen, P.-C. Yang, T. Wu, and Y.-W. Lin, “Determination of mercury (II) ions based on silver-nanoparticles-assisted growth of gold nanostructures: UV–Vis and surface enhanced Raman scattering approaches,” Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 199, 301 (2018).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 18-73-10001. Separate studies were performed using equipment purchased with funds from the Moscow University Development Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by V. Kudrinskaya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furletov, A.A., Apyari, V.V., Garshev, A.V. et al. NEW NANOCOMPOSITE MATERIAL BASED ON POLYURETHANE FOAM MODIFIED WITH SILVER TRIANGULAR NANOPLATES AS A SOLID-PHASE ANALYTICAL REAGENT FOR DETERMINATION OF MERCURY(II). Nanotechnol Russia 14, 91–97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S199507801902006X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S199507801902006X