Abstract
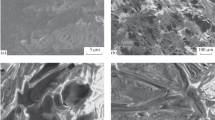
The methods of atomic-force- and scanning-electron microscopy are used to study the surface morphology of polymeric microfiltration membranes. Commercial membranes of the MFFK (on the basis of a hydrophobic fluoroplastic composite membrane, pore size of 0.45 μm) and MPS (polyethersulfone membrane, pore size of 0.45 μm) brands produced by OOO NPP Tekhnofil’tr (Vladimir, Russia) are used as the objects of study. A mature molasses brew produced by OAO Biokhim (Rasskazovo, Tambov Oblast) is used as the technological fluid for the working samples of MFFK and MPS membranes in the microfiltration process. An analysis of the surface morphology of the microfiltration membranes makes it possible to determine the regions of the location of pores, yeast, and polysaccharides, and the interpore connecting regions. By analyzing microscopic images, the flow lines of the solution to be separated are revealed in the profile hollows on the surface of the working microfiltration membranes. The initial MFFK and MPS membranes are found to have slit pores (0.4–0.6 μm in length and width), and the working membranes are contaminated (clogged) by yeast, polysaccharides, and their fragments, which is associated with residual dynamic membrane formation. The surface-roughness parameters of the working MFFK and MPS membranes are shown to be different: the Ra and Rz values differ by factors of 1.69 and 1.87, respectively; and the Rmax values in the case of oblique and frontal sections differ by factors of 1.67 and 1.05, respectively. This is explained by the specific features accompanying the process of the microfiltration separation of solutions containing yeast, polysaccharides, and their fragments (the presence of an adsorption layer on the membrane surface and cracks in the residual layer of the dynamic membrane, i.e., the clogged layer).








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. V. Shishkina, E. A. Zhelonkina, and B. A. Ananchenko, Adv. Sci. Khim. Nauki, No. 2, 1 (2017).
V. I. Vasil’eva, N. A. Kranina, M. D. Malykhin, E. M. Akberova, and A. V. Zhiltsova, J. Surf. Invest.: X‑ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 7, 144 (2013).
V. E. Sitnikova, Candidate’s Dissertation in Chemistry (Tver, 2015).
V. V. Kalinin, A. N. Filippov, and D. Yu. Khanukaeva, Tr. RGU Nefti i gaza (NIU) im. I.M. Gubkina. Avtomatizatsiya, modelirovanie i energoobespechenie, No. 1 (266), 129 (2012).
V. V. Kotov, M. V. Grechkina, O. V. Peregonchaya, and A. N. Zyablov, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy 16 (1), 118 (2016).
N. A. Zaichenko, V. I. Vasil’eva, O. V. Grigorchuk, A. N. Zyablov, and M. V. Grechkina, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy 10 (5), 745 (2010).
L. C. Powell, N. Hilal, and C. J. Wright, Desalination 404, 313 (2017).
S. P. Rudobashta and S. Yu. Makhmud, Khim. Khim. Tekhnol. 53 (1), 108 (2010).
A. V. Krasikov, V. N. Naraev, and V. L. Krasikov, Izv. S.-Peterb. Gos. Tekhnol. In-ta (Tekhn. Univ.), No. 13, 33 (2012).
V. O. Gritsenko and N. S. Orlov, Membrany, No. 16, 10 (2002).
S. D. Bazhenov, I. L. Borisov, D. S. Bakhtin, A. N. Rybakova, V. S. Khotimskiy, S. P. Molchanov, and V. V. Volkov, Green Energy Environment 1 (3), 235 (2016).
M.A. Trusov, Nanoindustriya, No. 4, 8 (2011).
D. Gudilin, Nanoindustriya, No. 4, 28 (2014).
D. Yu. Khanukaeva and A. N. Filippov, Membr. Membran. Tekhnol. 3 (3), 210 (2013).
N. V. Loza, I. V. Falina, D. S. Popova, and N. A. Kononenko, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy 16 (5), 663 (2016).
N. G. Tsirkunova, V. E. Borisenko, L. V. Kukharenko, M. V. Gol’tsev, and S. A. Chizhik, J. Surf. Invest.: X‑ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 3, 730 (2009).
Y. Chen, J. Cai, M. Liu, G. Zeng, Q. Feng, and Z. Chen, Scanning 26 (4), 155 (2004).
O. A. Kovaleva, S. I. Lazarev, and S. V. Kovalev, Pet. Chem. 57 (11), 974 (2017).
O. A. Kovaleva and S. V. Kovalev, Pet. Chem. 57 (6), 542 (2017).
A. V. Stovpyaga and I. N. Lobova, Nauch.-Tekh. Vestn. S.-Peterb. Gos. Univ. Inform. Tekhnol., Mekh. Opt., No. 6 (70), 94 (2010).
V. L. Mironov, Fundamentals of Scanning Probe Microscopy. A Study Guide (In-t fiziki mikrostruktur RAN, Nizhnii Novgorod, 2004) [in Russian].
http://www.vladipor.ru/catalog/show/&cid=015&id=1 (Accessed September 21, 2018).
www.technofilter.ru/prod/filtry_i_oborudovanie_dlya_ laboratornoj_filtracii/filtr_disc/ membrana_ poliefirsulfonovaya_marki_mps/ (Accessed September 21, 2018).
NanoEducator Scanning Probe Microscope. User’s Guide (NT-MDT, Zelenograd, 2008) [in Russian].
E. V. Krisilova, T. V. Eliseeva, and M. V. Grechkina, Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy 10 (1), 103 (2010).
V. V. Litvyak, S. M. Butrim, A. V. Kanarskii, and Z. A. Kanarskaya, Vestn. Tekhnol. Univ. 21 (3), 64 (2018).
R. Marzban, F. Saberi, and M. M. A. Shirazi, Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 33 (4), 783 (2016).
O. A. Konovalova, M. E. Sibgatullin, A. N. Montach, N. V. Kolacheva, D. Z. Galimullin, and M. Kh. Salakhov, Uch. Zap. Kazan. Univ., Ser. Fiz.-Mat. Nauki, No. 3, 99 (2010).
M. Ulbricht, W. Ansorge, I. Danielzik, M. Konig, and O. Schuster, Sep. Purif. Technol. 68 (3), 335 (2009).
Y. Fang and S. J. Duranceau, Membranes 3 (3), 196 (2013).
D. Saeki, H. Karkhanechi, H. Matsuura, and H. Matsuyama, Desalination 378, 74 (2016).
O. Akin and F. Temelli, Desalination 278 (1–3), 387 (2011).
Funding
This study was carried out within the framework of a State assignment under financial support from the Ministry of Education and Science of Russian Federation (project no. 10.4798.2017/BCh).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Kadkin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovalev, S.V., Lazarev, S.I. & Kovaleva, O.A. A Study of the Surface Morphology of Microfiltration Membranes of the MFFK and MPS Brands by Atomic-Force- and Scanning-Electron Microscopy. J. Surf. Investig. 14, 696–705 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451020040126
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451020040126