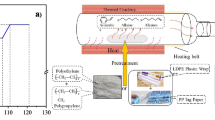
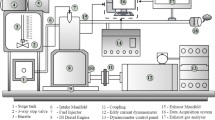
Abstract
This study investigated the effect of input power and process time on microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis of pure plastics (PS, PP, LDPE) and their blends into liquid and gaseous fuels. The microwave power and time were varied to pyrolyze 20 g of each sample in an iron coil. The pure PS underwent maximum conversion into fuels followed by PP and LDPE. Under optimized microwave power (2100–2500 W), PS produced 88.7% oil after 19 min of reaction time, PP produced 54.65% oil at 23 min of reaction time and LDPE produced 30.15% oil after 26 min of reaction time. Pure PS and PP showed high conversion efficiency of 95.40% and 95.10%, respectively, into liquid and gaseous fuels. Pure LDPE showed only 54.30% conversion into fuels by producing large quantity of waxy residue. In blended form, PS-PP blend revealed highest conversion of 65.67% into fuels followed by PS-PP-LDPE blend (57.23%), PS-LDPE blend (46.52%) and PP-LDPE blend (28.08%). Based on mass balance and percentage conversion, PS-PP blend showed maximum conversion of 96.25% whereas PP-LDPE showed minimum conversion of 74.99%. Higher microwave powers within optimal range produced better yield of liquid fuel in shorter time periods. The pyrolytic oils contained some useful aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons (C8–C16).
Graphic Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunwar, B., Cheng, H.N., Chandrashekaran, S.R., Sharma, B.K.: Plastics to fuel: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 54, 421–428 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.015
Aguado, J., Serrano, D.P., Escola, J.M.: Fuels from waste plastics by thermal and catalytic processes: a review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47, 7982–7992 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800393w
Zhang, X., Lei, H., Yadavalli, G., Zhu, L., Wei, Y., Liu, Y.: Gasoline-range hydrocarbons produced from microwave-induced pyrolysis of low-density polyethylene over ZSM-5. Fuel 144, 33–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.013
Hussain, Z., Sardar, A., Khan, K.M., Naz, M.Y., Sulaiman, S.A., Shukrullah, S.: Construction of rechargeable protein battery from mixed-waste processing of fish scales and chicken feathers. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 11, 2129–2135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0535-z
Dayana, S., Sharuddin, A., Abnisa, F., Mohd, W., Wan, A., Anuar Sharuddin, S.D., Abnisa, F., Wan Daud, W.M.A., Aroua, M.K.: A review on pyrolysis of plastic wastes. Energy Convers. Manag. 115, 308–326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.02.037
Sorum, L., Gronli, M.G., Hustad, J.E., Sùrum, L., Grùnli, M.G., Hustad, J.E.: Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of municipal solid wastes. Fuel 80, 1217–1227 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00218-0
Panda, A.K., Singh, R.K., Mishra, D.K.: Thermolysis of waste plastics to liquid fuel. A suitable method for plastic waste management and manufacture of value added products-A world prospective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14, 233–248 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.005
Hussain, Z., Sulaiman, S.A., Khan, A., Khan, K.M., Perveen, S., Naz, M.Y.: Two-step pyrolysis of spirogyra for fuels using cement catalytic. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 7, 1481–1489 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9552-y
Undri, A., Rosi, L., Frediani, M., Frediani, P.: Efficient disposal of waste polyolefins through microwave assisted pyrolysis. Fuel 116, 662–671 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.037
Aishwarya, K.N., Sindhu, N.: Microwave assisted pyrolysis of plastic waste. Procedia Technol. 25, 990–997 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.08.197
Hussain, Z., Khan, K.M., Hussain, K.: Microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis of polystyrene. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 89, 39–43 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2010.05.003
Zheng, X., Chen, C., Ying, Z., Wang, B., Chi, Y.: Py-GC/MS study on tar formation characteristics of MSW key component pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 8, 313–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9596-z
Doucet, J., Laviolette, J.-P., Farag, S., Chaouki, J.: Distributed microwave pyrolysis of domestic waste. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 5, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9216-0
Al-Salem, S.M., Antelava, A., Constantinou, A., Manos, G., Dutta, A.: A review on thermal and catalytic pyrolysis of plastic solid waste (PSW). J. Environ. Manage. 197, 177–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.084
Hussain, Z., Khan, K.M., Basheer, N., Hussain, K.: Co-liquefaction of Makarwal coal and waste polystyrene by microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis in copper coil reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 90, 53–55 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2010.10.002
Suriapparao, D.V., Vinu, R.: Resource recovery from synthetic polymers via microwave pyrolysis using different susceptors. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 113, 701–712 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2015.04.021
Wang, W., Xiqiang, Z.: Review on microwave—metal discharges and their applications in energy and industrial processes. Appl. Energy 175, 141–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.091
Hussain, Z., Khan, K.M., Hussain, K., Perveen, S.: Microwave-metal Interaction pyrolysis of waste polystyrene in a copper coil reactor. Energy Sourc. Part A 36, 1982–1989 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2011.557692
Lee, K.-H., Shin, D.-H., Seo, Y.-H.: Liquid-phase catalytic degradation of mixtures of waste high-density polyethylene and polystyrene over spent FCC catalyst. Effect of mixing proportions of reactants. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 84, 123–127 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2003.09.019
Miandad, R., Barakat, M.A., Aburiazaiza, A.S., Rehan, M., Nizami, A.S.: Catalytic pyrolysis of plastic waste: a review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 102, 822–838 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.06.022
Hussain, Z., Khan, K.M., Perveen, S., Hussain, K., Voelter, W.: The conversion of waste polystyrene into useful hydrocarbons by microwave-metal interaction pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 94, 145–150 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.10.009
Lee, K.-H.: Effects of the types of zeolites on catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis wax oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 94, 209–214 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.12.015
Serrano, D.P., Aguado, J., Escola, J.M., Garagorri, E.: Performance of a continuous screw kiln reactor for the thermal and catalytic conversion of polyethylene–lubricating oil base mixtures. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 44, 95–105 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00024-9
Seth, D., Sarkar, A.: Thermal pyrolysis of polypropylene: effect of reflux-condenser on the molecular weight distribution of products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 59, 2433–2445 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.03.008
Scheirs, J., Kaminsky, W.: Feedstock recycling and pyrolysis of waste plastics. Wiley, New York (2006)
Demirbas, A.: Pyrolysis of municipal plastic wastes for recovery of gasoline-range hydrocarbons. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 72, 97–102 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2004.03.001
Garforth, A.A., Lin, Y.-H., Sharratt, P.N., Dwyer, J.: Production of hydrocarbons by catalytic degradation of high density polyethylene in a laboratory fluidised-bed reactor. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 169, 331–342 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(98)00022-2
Mastral, F.J., Esperanza, E., Garcı́a, P., Juste, M.: Pyrolysis of high-density polyethylene in a fluidised bed reactor Influence of the temperature and residence time. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 63, 1–15 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(01)00137-1
Ding, W., Liang, J., Anderson, L.L.: Thermal and catalytic degradation of high density polyethylene and commingled post-consumer plastic waste. Fuel Process. Technol. 51, 47–62 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(96)01080-6
Park, D.W., Hwang, E.Y., Kim, J.R., Choi, J.K., Kim, Y.A., Woo, H.C.: Catalytic degradation of polyethylene over solid acid catalysts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 65, 193–198 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(99)00004-X
Pinto, F., Costa, P., Gulyurtlu, I., Cabrita, I.: Pyrolysis of plastic wastes. 1. Effect of plastic waste composition on product yield. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 51, 39–55 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(99)00007-8
Ahmad, I., Khan, M.I., Khan, H., Ishaq, M., Tariq, R., Gul, K., Ahmad, W.: Pyrolysis study of polypropylene and polyethylene into premium oil products. Int. J. Green Energy. 12, 663–671 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2014.880146
Desai, S.B.: Production and analysis of pyrolysis oil from waste plastic in kolhapur city method. Int. J. Eng. Res. Gen. Sci. 3, 590–595 (2015)
Watanabe, M., Nakata, C., Wu, W., Kawamoto, K., Noma, Y.: Characterization of semi-volatile organic compounds emitted during heating of nitrogen-containing plastics at low temperature. Chemosphere 68, 2063–2072 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.022
Kwon, D., Ko, M.S., Yang, J.S., Kwon, M.J., Lee, S.W., Lee, S.: Identification of refined petroleum products in contaminated soils using an identification index for GC chromatograms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 12029–12034 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4465-z
Marcilla, A., García-Quesada, J.C., Sánchez, S., Ruiz, R.: Study of the catalytic pyrolysis behaviour of polyethylene–polypropylene mixtures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 74, 387–392 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2004.10.005
Lin, Y.-H., Yang, M.-H.: Catalytic reactions of post-consumer polymer waste over fluidised cracking catalysts for producing hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 231, 113–122 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.01.003
Bhaskar, T., Kaneko, J., Muto, A., Sakata, Y., Jakab, E., Matsui, T., Uddin, M.A.: Pyrolysis studies of PP/PE/PS/PVC/HIPS-Br plastics mixed with PET and dehalogenation (Br, Cl) of the liquid products. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 72, 27–33 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2004.01.005
Donaj, P.J., Kaminsky, W., Buzeto, F., Yang, W.: Pyrolysis of polyolefins for increasing the yield of monomers’ recovery. Waste Manag. 32, 840–846 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.10.009
Kim, J.-R., Yoon, J.-H., Park, D.-W.: Catalytic recycling of the mixture of polypropylene and polystyrene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 76, 61–67 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(01)00266-X
Wong, H.-W., Broadbelt, L.J.: Tertiary resource recovery from waste polymers via pyrolysis: neat and binary mixture reactions of polypropylene and polystyrene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40, 4716–4723 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie010171s
Faravelli, T., Bozzano, G., Colombo, M., Ranzi, E., Dente, M.: Kinetic modeling of the thermal degradation of polyethylene and polystyrene mixtures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 70, 761–777 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00058-5
Acknowledgement
The work is supported by Yayasan Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS Grant No. 015 3AA- E06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arshad, H., Sulaiman, S.A., Hussain, Z. et al. Effect of Input Power and Process Time on Conversion of Pure and Mixed Plastics into Fuels Through Microwave-Metal Interaction Pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valor 12, 3443–3457 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01225-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01225-9