Abstract
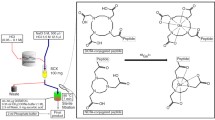
Dendrimer nanoparticles (DNPs), which have been studied extensively as drug delivery systems, can be synthesized easily with zirconium without chelators. A UV/Vis spectrophotometer and a Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) analysis were used to confirm the synthesis and the particle size of the composite. Compound B synthesized using a chelator compound was found to be more complex than compound A, and natZr was found to bind at a low yield through Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer (SEM-EDS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS). In PBS (1×), The binding was confirmed to be strong and stable at 99% stability or more. The stability to human serum was very good with a value of about 98%. The stability of the bound 89 Zr was confirmed to be stable for 160 minutes through the evaluation of serum stability. Using CT-26 and MDA-MB-231, We also were able to confirm the difference in the cell uptake of 89Zr-DNPs. After 24 hours, a high cell uptake of close to 40% was observed. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images were observed, it was confirmed that no accumulation of 89 Zr-DNPs in the bones and its stability in the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. C. Farokhzad and R. Langer, ACS Nano 3, 16 (2009).
M. Ferrari, Cancer Nanotechnol. 5, 161 (2005).
R. Langer, Nature 392, 5 (1998).
R. Gref et al., Science 263, 1600 (1994).
S. M. Moghimi, A. C. Hunter and J. C. Murray, Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 283 (2001).
I. Brigger, C. Dubernet and P. Couvreur, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 54, 631 (2002).
K. Kim et al., J. Am. Chem.Soc. 128, 3490 (2006).
X. Montet, R. Weissleder and L. Josephson, Bioconjug. Chem. 7, 905 (2006).
N. Nasongkla et al., Nano Lett. 6, 2427 (2006).
S. K. Murthy, Int. J. Nanomed. 2, 129 (2017).
I. C. Radu et al., Front. Pharmacol. 8, 508 (2017).
D. A. Tomalia, A. M. Naylor and W. A. Goddard III, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 29, 138 (1990).
G. Hay, M. E. Mackay and C. J. Hawker, J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 39, 1766 (2001).
M. Seiler, Chem. Eng. Technol. 25, 237 (2002).
P. Hodgem, Nature 365, 18 (1993).
M. J. Turk et al., Arthritis Rheumatol. 46, 1947c (2002).
S. Anderson et al., Nature 290, 457 (1981).
N. Bertrand et al., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 66, 2 (2014).
F. Danhier, J. Control. Release 244, 108 (2016).
S. Yan et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 138 (2014).
A. Zhu, D. M. Marcus, H. K. G. Shu and H. Shim, Radiat. Res. 177, 436 (2012).
P. Zanzonico, Radiat. Res. 177, 349 (2012).
I. Kelesidis and M.n I. Travin, J. Nucl. Cardiol. 19, 142 (2012).
K. Ozker, Curr. Pharm. Des. 6, 1123 (2000).
C. Y. Shiue and M. J. Welch, Radiol. Clin. North Am. 42, 1033 (2004).
K. Wechalekar, B. Sharma and G. Cook, Clin. Radiol. 60, 1143 (2005).
C. J. Anderson et al., J. Nucl. Med. 51, 3S (2010).
M. P. Dunphy and J. S. Lewis, J. Nucl. Med. 50, 106S (2009).
C. Xu et al., J. Nanotechnol. 22, 494001(17pp) (2011).
S. S. Gambhir, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 683 (2002).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Dongguk University Research Fund of 2020 and by a National Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (2017R1D1A1B03035589).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kim, G.G., Kim, S.W. et al. Zr-89 Labeled PAMAM Dendrimers 5G without a Chelator for a Cancer Diagnostic Agent. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 77, 409–413 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.409
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.77.409