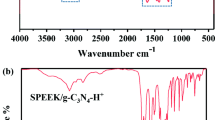
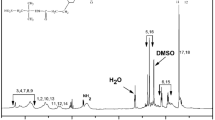
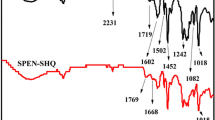
Abstract
Attaining a high performance proton exchange membrane as a suitable replacement for Nafion is one of the research priorities of fuel cell research. In this regard, we synthesized a copolyimide consisting of sulfonic acid substituents filled with different content of GO grafted sulfonated poly (urea-co-urethane) via in situ condensation polymerization. All nanocomposites showed a significant increase in thermal, mechanical properties, ion exchange capacity (IEC), water uptake (WU) and proton conductivity by incorporation of the modified GO nanosheets and the best results were found for membrane containing 1 wt% modified GO loading. The nanocomposite membrane with 1 wt% modified GO nanosheets exhibits 0.73 meq g−1 IEC and 7.3 mS cm−1 proton conductivity at room temperature. A single fuel cell test of this membrane demonstrates a maximum power density of 26.30 mW cm−2 at 0.26 V.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelletier S, Jabali O, Laporte G (2016) Goods distribution with electric vehicles: review and research perspectives. Transp Sci 50:3–22
Frenette G, Forthoffer D (2009) Economic & commercial viability of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles from an automotive manufacturer perspective. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:3578–3588
Sharaf OZ, Orhan MF (2014) An overview of fuel cell technology: fundamentals and applications. Renew. Sust Energ Rev 32:810–853
Wang Y, Chen KS, Mishler J, Chan Cho S, Cordobes Adroher X (2011) A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl Energy 88:981–1007
Zhang H, Shen PK (2012) Recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells. Chem Rev 112:2780–2832
Peighambardoust SJ, Rowshanzamir S, Amjadi M (2010) Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int J Hydrog Energy 75:9349–9384
Kim DJ, Jo MJ, Nam SY (2015) A review of polymer-nanocomposite electrolyte membranes for fuel. J Ind Eng Chem 21:36–52
Ahmadian-Alam L, Kheirmand M, Mahdavi H (2016) Preparation, characterization and properties of PVDF-g-PAMPS/PMMAco-PAMPS/silica nanoparticle as a new proton exchange nanocomposite membrane. Chem Eng J 284:1035–1048
Tayouo R, David G, Ameduri B, Roziere J, Roualdes S (2010) New fluorinated polymers bearing pendant Phosphonic acid groups. Proton conducting membranes for fuel cell. Macromolecules 43:5269–5276
Mauritz KA, Moore RB (2004) State of understanding of Nafion. Chem Rev 104:4535–4585
Jiang Y, Hou M, Hao J, Yi B, Wang Z, Song W, Shao Z (2017) Enhanced durability of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketones)-based polymer electrolyte membranes by a multi-layer composite technology. Solid State Ionics 309:33–40
Perez-Prior MT, Urena N, Tannenberg M, del Rıo C, Levenfeld B (2017) DABCO-functionalized polysulfones as anion-exchange membranes for fuel cell applications: effect of crosslinking. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 55:1326–1336
Molavian MR, Abdolmaleki A, Firouz Tadavani K, Zhiani M (2017) A new sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) hybrid with low humidity dependence for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. J Appl Polym Sci 134:45342
Kim JD, Donnadio A, Jun MS, Di Vona ML (2018) Crosslinked SPES-SPPSU membranes for high temperature PEMFCs. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:1517–1523
Özdemir Y, Üregen N, Devrim Y (2017) Polybenzimidazole based nanocomposite membranes with enhanced proton conductivity for high temperature PEM fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:2648–2657
Kraytsberg A, Ein-Eli Y (2014) A review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Fuel 28:7303–7330
Hickner MA, Pivovar BS (2010) The chemical and structural nature of proton exchange membrane fuel cell properties. Fuel Cells 5:213–229
Martinez-Cisneros CS, Antonelli C, Levenfeld B, Varez A, Sanchez J-Y (2017) Sodium polymer electrolytes composed of sulfonated polysulfone and macromolecular/molecular solvents for Na-batteries. Electrochim Acta 245:807–813
Lee JK, Li W, Manthiram A (2009) Poly (arylene ether sulfone) s containing pendant sulfonic acid groups as membrane materials for direct methanol fuel cells. J Membr Sci 330:73–79
Lee WJ, Lee SH, Bayazit MK, Kim SO, Choi YS (2017) Alkylated Sulfonated poly (arylene sulfone) s for proton exchange membranes. Macromol Res 25:400–407
Kim K, Kim SK, Park JO, Choi SW, Kim KH, Ko T, Pak C, Lee JC (2017) Highly reinforced pore-filling membranes based on sulfonated poly (arylene ether sulfone) s for high-temperature/low-humidity polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J Membr Sci 537:11–21
Wang XQ, Lin CX, Zhang QG, Zhu AM, Liu QL (2017) Anion exchange membranes from hydroxyl-bearing poly (ether sulfone) s with flexible spacers via ring-opening grafting for fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:19044–19055
Zarrin H, Higgins D, Jun Y, Chen Z, Fowler M (2011) Functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane for low humidity and high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J Phys Chem C 115:20774–20781
Kowsari E, Zare A, Ansari V (2015) Phosphoric acid-doped ionic liquid-functionalized graphene oxide/sulfonated polyimide composites as proton exchange membrane. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:13964–13978
Pandey RP, Shukla G, Manohar M, Shahi VK (2017) Graphene oxide based nanohybrid proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications: an overview. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 240:15–30
Pandey RP, Shahi VK (2015) Sulphonated imidized graphene oxide (SIGO) based polymer electrolyte membrane for improved water retention, stability and proton conductivity. J Power Sources 299:104–113
Yao H, Shi K, Song N, Zhang N, Huo P, Zhu S, Zhang Y, Guan S (2016) Polymer electrolyte membranes based on cross-linked highly sulfonated copolyimides. Polymer 103:171–179
Chen JC, Wu JA, Lee CY, Tsai MC, Chen KH (2015) Novel polyimides containing benzimidazole substituents for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J Membr Sci 483:144–154
Park J, Enomoto K, Yamashita T, Takagi Y, Todaka K, Maekawa Y (2013) Polymerization mechanism for radiation-induced grafting of styrene into alicyclic polyimide films for preparation of polymer electrolyte membranes. J Membr Sci 438:1–7
Pandey RP, Shahi VK (2013) Aliphatic-aromatic sulphonated polyimide and acid functionalized polysilsesquioxane composite membranes for fuel cell applications. J Mater Chem A 1:14375–14383
Li W, Guo X, Aili D, Martin S, Li Q, Fang J (2015) Sulfonated copolyimide membranes derived from a novel diamine monomer with pendant benzimidazole groups for fuel cells. J Membr Sci 481:44–53
Pan H, Chen S, Zhang Y, Jin M, Chang Z, Pu H (2015) Preparation and properties of the cross-linked sulfonated polyimide containing benzimidazole as electrolyte membranes in fuel cells. J Membr Sci 476:87–94
Ahmadian-Alam L, Teymoori M, Mahdavi H (2018) Graphene oxide-anchored reactive sulfonated copolymer via simple one pot condensation polymerization: proton-conducting solid electrolytes. J Polym Res 25:13–21
Chang WY, Chen SH, Yang CH, Chuang CN, Wang CK, Hsieh KH (2015) Preparation and characterization of aromatic polyimides derived from 4,4′-oxydiphthalic anhydride and 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane with different alkyl substituents. J Polym Res 22:38–64
Einsla BR, Hong YT, Kim YS, Wang F, Gunduz N, Mcgrath JE (2004) Sulfonated naphthalene dianhydride based polyimide copolymers for proton-exchange-membrane fuel cells. I. Monomer and Copolymer Synthesis. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 42:862–874
Ahmadian-Alam L, Haddadi-Asl V, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Hatami L, Salami-Kalajahi M (2012) Use of clay-anchored reactive modifier for the synthesis of poly (styrene-co-butyl acrylate)/clay nanocomposite via in situ AGET ATRP. J Polym Res 19:9773–9784
Salarizadeh P, Javanbakht M, Pourmahdian S (2015) Fabrication and physico-chemical properties of iron titanate nanoparticles based sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membrane forproton exchange membrane fuel cell application. Solid State Ionics 281:12–20
Ryu T, Sutradhar SC, Ahmed F, Choi K, Yang H, Yoon S, Lee S, Kim W (2017) Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated mutiphenyl conjugated polyimide for PEMFC. J Ind Eng Chem 49:99–104
Mandal AK, Bera D, Banerjee S (2016) Sulfonated polyimides containing triphenylphosphine oxide for proton exchange membranes. Mater Chem Phys 181:265–276
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for the grants provided for them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadian-Alam, L., Teymoori, M. & Mahdavi, H. Polymer grafted GO/sulfonated copolyimide proton exchange nanocomposite membrane: as a polymer electrolyte membranes fuel cell. J Polym Res 27, 302 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02049-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02049-w