Abstract
Few reports have documented the ability of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE-5-Is) to ameliorate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) mainly by their anti-inflammatory/antioxidant capacities, without unveiling the possible molecular mechanisms involved. Because of the recent role of miR-200 family and Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) trajectory in IPF, we have studied their impact on the anti-fibrotic potential of tadalafil against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Animals were allocated into normal-control, bleomycin-fibrotic control, and bleomycin post-treated with tadalafil or dexamethasone, as the reference drug. On the molecular level, tadalafil has reverted the bleomycin effect on all the assessed parameters. Tadalafil upregulated the gene expression of miR-200a, but decreased the smoothened (SMO) and the transcription factors glioma-associated oncogene homolog (Gli-1, Gli-2), members of SHH pathway. Additionally, tadalafil ebbed transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, its canonical (SMAD-3/alpha smooth muscle actin [α-SMA] and Snail), and non-canonical (p-Akt/p-Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) a) pathways. Besides, a strong negative correlation between miR-200a and the analyzed pathways was proved. The effect of tadalafil was further confirmed by the improved lung structure and the reduced Ashcroft score/collagen deposition. The results were comparable to that of dexamethasone. In conclusion, our study has highlighted the involvement of miR-200a in the anti-fibrotic effect of tadalafil with the inhibition of SHH hub and the pro-fibrotic pathways (TGF-β/ SMAD-3/α-SMA, Snail and p-AKT/p-FOXO3a).
Graphic abstract
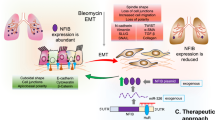
Potential anti-fibrotic effect of tadalafil. Modulation of miR200a/SHH/canonical and non-canonical TGF-β trajectories. → : stimulatory effect; ┴: inhibitory effect







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz RR, Elkashef WF, Said E (2016) Tadalafil reduces airway hyperactivity and protects against lung and respiratory airways dysfunction in a rat model of silicosis. Int Immunopharmacol 40:530–541
Al-Tamari HM, Dabral S, Schmall A, Sarvari P, Ruppert C, Paik J, Depinho RA, Grimminger F, Eickelberg O, Guenther A, Seeger W, Savai R, Pullamsetti SS (2018) FoxO3 an important player in fibrogenesis and therapeutic target for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med 10:276–293
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V (1988) Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol 41:467–470
Attisano L, Wrana JL (2002) Signal transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science 296:1646–1647
Behr J, Nathan SD, Harari S, Wuyts W, Kirchgaessler KU, Bengus M, Gilberg F, Wells AU (2018) Sildenafil added to pirfenidone in patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and risk of pulmonary hypertension: a phase IIb, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study—rationale and study design. Respir Med 138:13–20
Bolanos AL, Milla CM, Lira JC, Ramirez R, Checa M, Barrera L, Garcia-Alvarez J, Carbajal V, Becerril C, Gaxiola M, Pardo A, Selman M (2012) Role of sonic Hedgehog in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 303:L978–L990
Border WA, Noble NA (1994) Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 331:1286–1292
Bringardner BD, Baran CP, Eubank TD, Marsh CB (2008) The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:287–301
Chen L, Wang T, Wang X, Sun BB, Li JQ, Liu DS, Zhang SF, Liu L, Xu D, Chen YJ, Wen FQ (2009) Blockade of advanced glycation end product formation attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Respir Res 10:55
Cigna N, Moshai EF, Brayer S, Marchal-Somme J, Wemeau-Stervinou L, Fabre A, Mal H, Leseche G, Dehoux M, Soler P, Crestani B, Mailleux AA (2012) The hedgehog system machinery controls transforming growth factor-beta-dependent myofibroblastic differentiation in humans: involvement in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 181:2126–2137
Corbin JD, Beasley A, Blount MA, Francis SH (2005) High lung PDE5: a strong basis for treating pulmonary hypertension with PDE5 inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:930–938
Della Latta V, Cecchettini A, Del Ry S, Morales MA (2015) Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: from biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol Res 97:122–130
El-Wakeel SA, Rahmo RM, El-Abhar HS (2018) Anti-fibrotic impact of Carvedilol in a CCl-4 model of liver fibrosis via serum microRNA-200a/SMAD7 enhancement to bridle TGF-beta1/EMT track. Sci Rep 8:14327
Fitch PM, Howie SE, Wallace WA (2011) Oxidative damage and TGF-beta differentially induce lung epithelial cell sonic hedgehog and tenascin-C expression: implications for the regulation of lung remodelling in idiopathic interstitial lung disease. Int J Exp Pathol 92:8–17
Flanders KC (2004) Smad3 as a mediator of the fibrotic response. Int J Exp Pathol 85:47–64
Franco DL, Mainez J, Vega S, Sancho P, Murillo MM, de Frutos CA, del Castillo G, Lopez-Blau C, Fabregat I, Nieto MA (2010) Snail1 suppresses TGF-beta-induced apoptosis and is sufficient to trigger EMT in hepatocytes. J Cell Sci 123:3467–3477
Fu N, Zhao SX, Kong LB, Du JH, Ren WG, Han F, Zhang QS, Li WC, Cui P, Wang RQ, Zhang YG, Nan YM (2017) LncRNA-ATB/microRNA-200a/beta-catenin regulatory axis involved in the progression of HCV-related hepatic fibrosis. Gene 618:1–7
Greenburg G, Hay ED (1982) Epithelia suspended in collagen gels can lose polarity and express characteristics of migrating mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biol 95:333–339
Harris LG, Samant RS, Shevde LA (2011) Hedgehog signaling: networking to nurture a promalignant tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer Res 9:1165–1174
Kishaba T (2018) Triple kinase inhibitor with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Thorac Dis 10:5974–5978
Koh RY, Lim CL, Uhal BD, Abdullah M, Vidyadaran S, Ho CC, Seow HF (2015) Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta via the activin receptor-like kinase-5 inhibitor attenuates pulmonary fibrosis. Mol Med Rep 11:3808–3813
Kokturk S, Benli E, Ayyildiz A, Cirrik S, Cetinkol Y, Ayyildiz SN, Noyan T (2019) Positive outcomes of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor on histopathologic and biochemical changes induced by ureteral obstruction. Rev Assoc Med Bras 1992(65):388–393
Kolb M, Raghu G, Wells AU, Behr J, Richeldi L, Schinzel B, Quaresma M, Stowasser S, Martinez FJ (2018) Nintedanib plus sildenafil in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 379:1722–1731
Kulkarni AA, Thatcher TH, Olsen KC, Maggirwar SB, Phipps RP, Sime PJ (2011) PPAR-gamma ligands repress TGFbeta-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway: implications for therapy of fibrosis. PLoS ONE 6:e15909
Kyung SY, Kim DY, Yoon JY, Son ES, Kim YJ, Park JW, Jeong SH (2018) Sulforaphane attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 19:13
Lijnen P, Petrov V, Rumilla K, Fagard R (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 promotes contraction of collagen gel by cardiac fibroblasts through their differentiation into myofibroblasts. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 25:79–86
Litingtung Y, Lei L, Westphal H, Chiang C (1998) Sonic hedgehog is essential to foregut development. Nat Genet 20:58–61
Liu Y, Ao X, Ding W, Ponnusamy M, Wu W, Hao X, Yu W, Wang Y, Li P, Wang J (2018a) Critical role of FOXO3a in carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer 17:104
Liu Y, Liu B, Zhang GQ, Zou JF, Zou ML, Cheng ZS (2018b) Calpain inhibition attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via switching the development of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 391:695–704
Li L, Li Q, Wei L, Wang Z, Ma W, Liu F, Shen Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Li H, Qian Y (2019) Dexamethasone combined with berberine is an effective therapy for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Exp Ther Med 18:2385–2392
Lucarini L, Durante M, Lanzi C, Pini A, Boccalini G, Calosi L, Moroni F, Masini E, Mannaioni G (2017) HYDAMTIQ, a selective PARP-1 inhibitor, improves bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by dampening the TGF-beta/SMAD signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 21:324–335
Lu Y, Azad N, Wang L, Iyer AK, Castranova V, Jiang BH, Rojanasakul Y (2010) Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/akt regulates bleomycin-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42:432–441
Mailleux AA, Moshai EF, Crestani B (2013) Sonic Hedgehog signaling in pulmonary fibrosis: a spiky issue? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 304:L391–L393
Meng L, Zhang X, Wang H, Dong H, Gu X, Yu X, Liu Y, Yiqi Y (2019) Mixture ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through inhibiting TGF-beta1/Smad pathway and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019:2710509
Mercer PF, Woodcock HV, Eley JD, Plate M, Sulikowski MG, Durrenberger PF, Franklin L, Nanthakumar CB, Man Y, Genovese F, McAnulty RJ, Yang S, Maher TM, Nicholson AG, Blanchard AD, Marshall RP, Lukey PT, Chambers RC (2016) Exploration of a potent PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor as a novel anti-fibrotic agent in IPF. Thorax 71:701–711
Moshai EF, Wemeau-Stervinou L, Cigna N, Brayer S, Somme JM, Crestani B, Mailleux AA (2014) Targeting the hedgehog-glioma-associated oncogene homolog pathway inhibits bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:11–25
Newton AC, Trotman LC (2014) Turning off AKT: PHLPP as a drug target. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 54:537–558
Nho RS (2015) Alteration of aging-dependent MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Drug Dev Res 76:343–353
Nie Y, Sun L, Wu Y, Yang Y, Wang J, He H, Hu Y, Chang Y, Liang Q, Zhu J, Ye RD, Christman JW, Qian F (2017) AKT2 regulates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via modulating macrophage activation. J Immunol 198:4470–4480
Norambuena-Soto I, Nunez-Soto C, Sanhueza-Olivares F, Cancino-Arenas N, Mondaca-Ruff D, Vivar R, Diaz-Araya G, Mellado R, Chiong M (2017) Transforming growth factor-beta and forkhead box O transcription factors as cardiac fibroblast regulators. Biosci Trends 11:154–162
Pecot CV, Rupaimoole R, Yang D, Akbani R, Ivan C, Lu C, Wu S, Han HD, Shah MY, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Bottsford-Miller J, Liu Y, Kim SB, Unruh A, Gonzalez-Villasana V, Huang L, Zand B, Moreno-Smith M, Mangala LS, Taylor M, Dalton HJ, Sehgal V, Wen Y, Kang Y, Baggerly KA, Lee JS, Ram PT, Ravoori MK, Kundra V, Zhang X, Ali-Fehmi R, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Massion PP, Calin GA, Lopez-Berestein G, Zhang W, Sood AK (2013) Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat Commun 4:2427
Peng R, Sridhar S, Tyagi G, Phillips JE, Garrido R, Harris P, Burns L, Renteria L, Woods J, Chen L, Allard J, Ravindran P, Bitter H, Liang Z, Hogaboam CM, Kitson C, Budd DC, Fine JS, Bauer CM, Stevenson CS (2013) Bleomycin induces molecular changes directly relevant to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a model for “active” disease. PLoS ONE 8:e59348
Pepicelli CV, Lewis PM, McMahon AP (1998) Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian lung. Curr Biol 8:1083–1086
Pu J, Zhang Y, Zhou J (2016) Effect of Huai Qi Huang on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells through miR-200a. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:8612190
Rajasekaran S, Rajaguru P, Sudhakar PSG (2015) MicroRNAs as potential targets for progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol 6:254
Ren L, Yang C, Dou Y, Zhan R, Sun Y, Yu Y (2017) MiR-541-5p regulates lung fibrosis by targeting cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A. Exp Lung Res 43:249–258
Ricupero DA, Poliks CF, Rishikof DC, Cuttle KA, Kuang PP, Goldstein RH (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent stabilization of alpha1(I) collagen mRNA in human lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C99–C105
Riobo NA, Manning DR (2007) Pathways of signal transduction employed by vertebrate Hedgehogs. Biochem J 403:369–379
Sebkhi A, Strange JW, Phillips SC, Wharton J, Wilkins MR (2003) Phosphodiesterase type 5 as a target for the treatment of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 107:3230–3235
Selman M, Pardo A, Kaminski N (2008) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: aberrant recapitulation of developmental programs? PLoS Med 5:e62
Stefani G, Slack FJ (2008) Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:219–230
Sun X, He Y, Ma TT, Huang C, Zhang L, Li J (2014) Participation of miR-200a in TGF-beta1-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation. Mol Cell Biochem 388:11–23
Todd NW, Luzina IG, Atamas SP (2012) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5:11
Tsukioka T, Takemura S, Minamiyama Y, Mizuguchi S, Toda M, Okada S (2017) Attenuation of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats with S-allyl cysteine. Molecules 22:543
Vaughan MB, Howard EW, Tomasek JJ (2000) Transforming growth factor-beta1 promotes the morphological and functional differentiation of the myofibroblast. Exp Cell Res 257:180–189
Wang B, Koh P, Winbanks C, Coughlan MT, McClelland A, Watson A, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Burns WC, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P (2011) miR-200a Prevents renal fibrogenesis through repression of TGF-beta2 expression. Diabetes 60:280–287
White ES, Atrasz RG, Hu B, Phan SH, Stambolic V, Mak TW, Hogaboam CM, Flaherty KR, Martinez FJ, Kontos CD, Toews GB (2006) Negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:112–121
Williamson JD, Sadofsky LR, Hart SP (2015) The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res 41:57–73
Wygrecka M, Zakrzewicz D, Taborski B, Didiasova M, Kwapiszewska G, Preissner KT, Markart P (2012) TGF-beta1 induces tissue factor expression in human lung fibroblasts in a PI3K/JNK/Akt-dependent and AP-1-dependent manner. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47:614–627
Yang S, Banerjee S, de Freitas A, Sanders YY, Ding Q, Matalon S, Thannickal VJ, Abraham E, Liu G (2012) Participation of miR-200 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 180:484–493
Yang JJ, Tao H, Liu LP, Hu W, Deng ZY, Li J (2017) miR-200a controls hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrosis via SIRT1/Notch1 signal pathway. Inflamm Res 66:341–352
Yildirim A, Ersoy Y, Ercan F, Atukeren P, Gumustas K, Uslu U, Alican I (2010) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition by sildenafil citrate in a rat model of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 23:215–221
Yu F, Zheng Y, Hong W, Chen B, Dong P, Zheng J (2015) MicroRNA200a suppresses epithelialtomesenchymal transition in rat hepatic stellate cells via GLI family zinc finger 2. Mol Med Rep 12:8121–8128
Zaringhalam J, Akhtari Z, Eidi A, Ruhani AH, Tekieh E (2014) Relationship between serum IL10 level and p38MAPK enzyme activity on behavioral and cellular aspects of variation of hyperalgesia during different stages of arthritis in rats. Inflammopharmacology 22:37–44
Zhang L, Li Y, Liang C, Yang W (2014) CCN5 overexpression inhibits profibrotic phenotypes via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in an in vivo model of lung fibrosis. Int J Mol Med 33:478–486
Zhang H, Hu J, Liu L (2017) MiR-200a modulates TGF-beta1-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal shift via suppression of GRB2 in HAECs. Biomed Pharmacother 95:215–222
Zhang J, Liu H, Song C, Wang Y, Lv C, Song X (2018) Astilbin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via blockade of Hedgehog signaling pathway. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 50:19–27
Zhang LM, Zhang Y, Fei C, Zhang J, Wang L, Yi ZW, Gao G (2019) Neutralization of IL-18 by IL-18 binding protein ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:660–666
Zhao J, Shi W, Wang YL, Chen H, Bringas P Jr, Datto MB, Frederick JP, Wang XF, Warburton D (2002) Smad3 deficiency attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L585–L593
Zhu Y, Tan J, Xie H, Wang J, Meng X, Wang R (2016) HIF-1alpha regulates EMT via the Snail and beta-catenin pathways in paraquat poisoning-induced early pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med 20:688–697
Zidar N, Bostjancic E, Jerala M, Kojc N, Drobne D, Stabuc B, Glavac D (2016) Down-regulation of microRNAs of the miR-200 family and up-regulation of inflammatory bowel diseases—hallmark of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Mol Med 20:1813–1820
Zisman DA, Keane MP, Belperio JA, Strieter RM, Lynch JP III (2005) Pulmonary fibrosis. Methods Mol Med 117:3–44
Acknowledgements
We kindly thank Dr. Mohamed Abdelraziq (Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University) for performing the histopathological studies. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. All authors have self-funded the current work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansour, S.M., El-Abhar, H.S. & Soubh, A.A. MiR-200a inversely correlates with Hedgehog and TGF-β canonical/non-canonical trajectories to orchestrate the anti-fibrotic effect of Tadalafil in a bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model. Inflammopharmacol 29, 167–182 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00748-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00748-w