Abstract
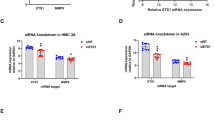
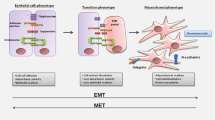
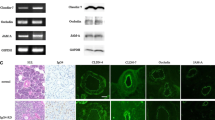
To determine the role of IL-6 in bringing about the EMT, in SGEC obtained from healthy subjects. Human salivary gland (SGs) epithelial cells (SGEC) from primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) are able to synthesize interleukin (IL)-6, which is a critical mediator of the SGs modifications in response to chronic inflammation. Recently, a hypothetical link between epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-dependent salivary gland fibrosis and chronic inflammatory conditions has been suggested for pSS; the present study was conducted to evaluate this link. Primary cultures of human SGEC from salivary mucoceles were stimulated with increasing concentrations of IL-6 for 24–72 h. Microscopy, RT-PCR, Real-time PCR, immunoblotting and flow cytometry were used to detect morphological changes, mRNA and protein expression of the EMT markers E-Cadherin, Vimentin and Collagen type I following IL-6 stimulation. The data collected demonstrate that IL-6 can induce SGEC to undergo a morphological and phenotypical transition to a mesenchymal phenotype, in a dose-dependent manner. Decreased mRNA levels of E-Cadherin accompanied by higher mRNA levels of Vimentin and Collagen type I were observed in the IL-6-treated cells compared to control cells (all p < 0.05). This was confirmed at the protein level, demonstrating the decreased E-Cadherin expression, while Vimentin and Collagen type I expression was increased in IL-6-treated SGEC compared to controls (all p < 0.05). The results obtained corroborate the hypothesis that dysregulated cytokines IL-6 may contribute to the EMT-dependent fibrosis, offering a more complete understanding of the role of the EMT during SGs fibrosis in pSS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boumba D, Skopouli FN, Moutsopoulos HM (1995) Cytokine mRNA expression in the labial salivary gland tissues from patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome. Br J Rheumatol 34:326–333
Drosos AA, Andonopoulos AP, Costopoulos JS et al (1988a) Sjögren's syndrome in progressive systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 15:965–968
Drosos AA, Andonopoulos AP, Costopoulos JS et al (1988b) Prevalence of primary Sjögren's syndrome in an elderly population. Br J Rheumatol 27:123–127
Fisher DT, Appenheimer MM, Evans SS (2014) The two faces of IL-6 in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Immunol 26:38–47
Hirano T (2010) Interleukin 6 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: a personal memoir. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 86:717–730
Humphreys-Beher MG, Peck AB (1999) New concepts for the development of autoimmune exocrinopathy derived from studies with the NOD mouse model. Arch Oral Biol 44(Suppl 1):S21–S25
Jiang GX, Cao LP, Kang PC et al (2016) Interleukin-6 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep 13:1563–1569
Kapsogeorgou EK, Dimitriou ID, Abu-Helu RF et al (2001) Activation of epithelial and myoepithelial cells in the salivary glands of patients with Sjögren's syndrome: high expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM.1) in biopsy specimens and cultured cells. Clin Exp Immunol 124:126–133
Kishimoto T (2006) Interleukin-6: discovery of a pleiotropic cytokine. Arthritis Res Ther 8(Suppl 2):S2
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:178–196
Lisi S, Sisto M, Lofrumento DD et al (2010) Pro-inflammatory role of Anti-Ro/SSA autoantibodies through the activation of Furin-TACE-amphiregulin axis. J Autoimmun 35:160–170
Lisi S, Sisto M, Lofrumento DD et al (2012) Sjögren's syndrome autoantibodies provoke changes in gene expression profiles of inflammatory cytokines triggering a pathway involving TACE/NFκB. Lab Invest 92:615–624
López-Novoa JM, Nieto MA (2009) Inflammation and EMT: an alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression. EMBO Mol Med 1:303–314
Masjedi A, Hashemi V, Hojjat-Farsangi M et al (2018) The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 108:1415–1424
Mihara M, Hashizume M, Yoshida H et al (2012) IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci 122:143–159
Moutsopoulos HM, Chused TM, Mann DL et al (1980) Sjogren’s syndrome (Sicca syndrome): current issues. Ann Intern Med 92:212–226
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA et al (2016) EMT: 2016. Cell 166:21–45
Nishimoto N, Kanakura Y, Aozasa K et al (2005) Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease. Blood 106:2627–2632
Ogura H, Murakami M, Okuyama Y et al (2008) Interleukin-17 promotes autoimmunity by triggering a positive-feedback loop via interleukin-6 induction. Immunity 29:628–636
Radisky DC, Kenny PA, Bissell MJ (2007) Fibrosis and cancer: do myofibroblasts come also from epithelialcells via EMT? J Cell Biochem 101:830–839
Ramos-Casals M, Tzioufas AG, Font J (2005) Primary Sjögren's syndrome: new clinical and therapeutic concepts. Ann Rheum Dis 64:347–354
Roescher N, Tak PP, Illei GG (2009) Cytokines in Sjögren's syndrome. Oral Dis 15:519–526
Sens DA, Hintz DS, Rudisill MT et al (1985) Explant culture of human submandibular gland epithelial cells: evidence for ductal origin. Lab Invest 52:559–567
Sisto M, Lisi S, Lofrumento DD et al (2010) Expression of pro-inflammatory TACE-TNF-α-amphiregulin axis in Sjögren's syndrome salivary glands. Histochem Cell Biol 134:345–353
Sisto M, Lisi S, Ribatti D (2018a) The role of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in diseases of the salivary glands. Histochem Cell Biol 150:133–147
Sisto M, Lorusso L, Ingravallo G et al (2018b) The TGF-β1 signaling pathway as an attractive target in the fibrosis pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2018:1965935
Sisto M, Lorusso L, Tamma R et al (2019) Interleukin-17 and -22 synergy linking inflammation and EMT-dependent fibrosis in Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 198:261–272
Sisto M, Lorusso L, Ingravallo G et al (2020) TGFβ1-Smad canonical and - Erk non canonical pathways participate in interleukin-17-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Sjögren's syndrome. Lab Invest 100:824–836
Suarez-Carmona M, Lesage J, Cataldo D et al (2017) EMT and inflammation: inseparable actors of cancer progression. Mol Oncol 11:805–823
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE et al (2009) Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28:2940–2947
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY et al (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139:871–890
Trikha M, Corringham R, Klein B et al (2003) Targeted anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for cancer: a review of the rationale and clinical evidence. Clin Cancer Res 9:4653–4665
Wolf J, Rose-John S, Garbers C (2014) Interleukin-6 and its receptors: a highly regulated and dynamic system. Cytokine 70:11–20
Wynn TA, Ramalingam TR (2012) Mechanisms of fibrosis: therapeutic translation for fibroticdisease. Nat Med 18:1028–1040
Xie G, Yao Q, Liu Y et al (2012) IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes the generation of breast cancer stem-like cells analogous to mammosphere cultures. Int J Oncol 40:1171–1179
Zheng X, Lu G, Yao Y et al (2019) An autocrine IL-6/IGF-1R loop mediates emt and promotes tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Sci 15:1882–1891
Zhou J, Zhang C, Pan J et al (2017) Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma cells and promotes tumor cell migration. Mol Med Rep 15:4123–4131
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to M.V.C. Pragnell, B.A., a professional scientific text editor, for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All the authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Sisto, M., Tamma, R., Ribatti, D. et al. IL-6 Contributes to the TGF-β1-Mediated Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Human Salivary Gland Epithelial Cells. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 68, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-020-00591-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-020-00591-5