Abstract
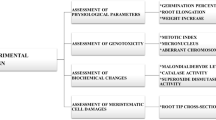
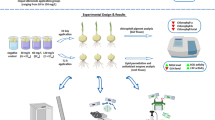
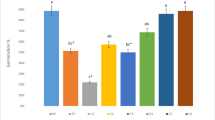
The present study was conducted to investigate the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity induced by abamectin pesticide in Allium cepa L. bulbs. Following 72-h exposure to different doses (0.025 ml/L, 0.050 ml/L, and 0.100 ml/L) of abamectin, growth level, micronuclei abundance, mitotic index, chromosomal aberrations, malondialdehyde content, meristematic cell damages, and total activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase were explored. The results revealed that all concentrations of abamectin were capable of inducing significant and dose-dependent changes in all parameters. Increasing doses of abamectin caused remarkable decreases in germination ratio, weight gain, and root elongation. Due to abamectin-induced genotoxicity, the mitotic index declined, while chromosomal abnormalities listed as micronucleus, fragment, sticky chromosome, unequal distribution of chromatin, bridge, vacuole nucleus, nucleus damage, and multipolar anaphase. Depending on the oxidative stress caused by abamectin administration, the total activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase enzymes increased significantly along with the malondialdehyde content. Indistinct transmission tissue, epidermis cell deformation and flattened cell nucleus were the meristematic cell damages in pesticide-applied groups. Findings of the present study revealed that abamectin is a risky pesticide with a variety of cytotoxic and genotoxic effects in non-targeted organisms. A. cepa is a promising material for biomonitoring the toxicity of abamectin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed FAW (2014) Cytotoxic and genotoxic potency screening of WIDE-SPEC pesticide on Allium cepa L. root meristem cells. J Nat Sci Res 4(24):100–109
Akgündüz MÇ, Çavuşoğlu K, Yalçın E (2020) The potential risk assessment of phenoxyethanol with a versatile model system. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10
Al-Sarar AS, Abobakr Y, Bayoumi AE, Hussein HI (2015) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of abamectin, chlorfenapyr, and imidacloprid on CHO K1 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(21):17041–17052
Ananiev DE, Ananieva K, Abdulova G, Christova N, Videnova E (2002) Effects of abamectin on protein and RNA synthesis in primary leaves of Cucurbita pepo L.(zucchini). Bulg J Plant Physiol 28(1-2):85–91
Atik M, Karagüzel O, Ersoy S (2007) Sıcaklığın Dalbergia sissoo tohumlarının çimlenme özelliklerine etkisi. Akdeniz Univ Ziraat Fak Derg 20(2):203–210
Bai SH, Ogbourne S (2016) Eco-toxicological effects of the avermectin family with a focus on abamectin and ivermectin. Chemosphere 154:204–214
Bianchi J, Fernandes TCC, Marin-Morales MA (2016) Induction of mitotic and chromosomal abnormalities on Allium cepa cells by pesticides imidacloprid and sulfentrazone and the mixture of them. Chemosphere 144:475–483
Blokhina OB, Chirkova TV, Fagerstedt KV (2001) Anoxic stress leads to hydrogen peroxide formation in plant cells. J Exp Bot 52:1179–1190
Boukhrissa A, Ferrag-Siagh F, Rouidi LM, Chemat S, Aït-Amar H (2017) Study of the degradation in aqueous solution of a refractory organic compound: avermectin type used as pesticide in agriculture. Water Sci Technol 76(8):1966–1980
Çavuşoğlu K, Yalçin E, Türkmen Z, Yapar K, Sağir S (2012) Physiological, anatomical, biochemical, and cytogenetic effects of thiamethoxam treatment on Allium cepa (amaryllidaceae) L. Environ Toxicol 27(11):635–643
Çavuşoğlu K, Gür B, Yalçin E, Demirtaş G, Çiçek F (2014) The effect of lambda-cyhalothrin on root tip cytology, pigment contents and antioxidant defense system of Allium cepa. Cytologia 79(1):95–101
de Souza CP, de Andrade Guedes T, Fontanetti CS (2016) Evaluation of herbicides action on plant bioindicators by genetic biomarkers: a review. Environ Monit Assess 188(12):694
Doganlar ZB, Doganlar O, Tozkir H, Gokalp FD, Dogan A, Yamac F, Askin OO, Aktas UE (2018) Nonoccupational exposure of agricultural area residents to pesticides: pesticide accumulation and evaluation of genotoxicity. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 75:530–544
Dutta J, Ahmad A, Singh J (2018) Study of industrial effluents induced genotoxicity on Allium cepa L. Caryologia 71(2):139–145
El-Gendy KS, Radwan MA, Gad AF, Khamis AE, Eshra EH (2019) Use of multiple endpoints to investigate the ecotoxicological effects of abamectin and thiamethoxam on Theba pisana snails. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:242–249
European Food Safety Authority (2008) Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of active substance. Abamectin. EFSA Sci Rep 147:1–106
Fatma F, Verma S, Kamal A, Srivastava A (2018) Phytotoxicity of pesticides mancozeb and chlorpyrifos: correlation with the antioxidative defence system in Allium cepa. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24(1):115–123
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN Project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res Gen Tox En 534:65–75
Feretti D, Zerbini I, Zani C, Ceretti E, Moretti M, Monarca S (2007) Allium cepa chromosome aberration and micronucleus tests applied to study genotoxicity of extracts from pesticide-treated vegetables and grapes. Food Addit Contam 24(6):561–572
Fisher MH, Mrozik M (1989) Ivermectin and abamectin. Springer Verlag, New York, pp 1–23
He B, Wang X, Yang C, Zhu J, Jin Y, Fu Z (2020) The regulation of autophagy in the pesticide-induced toxicity: angel or demon. Chemosphere 242:125138
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: II. Role of electron transfer. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(3):850–857
Khallef M, Benouareth DE, Konuk M, Liman R, Bouchelaghem S, Hazzem S, Kerdouci K (2019) The effect of silver nanoparticles on the mutagenic and the genotoxic properties of the urban wastewater liquid sludges. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(18):18403–18410
Kolar L, Eržen NK, Hogerwerf L, van Gestel CA (2008) Toxicity of abamectin and doramectin to soil invertebrates. Environ Pollut 151(1):182–189
Kuchy AH, Wani AA, Kamili AN (2016) Cytogenetic effects of three commercially formulated pesticides on somatic and germ cells of Allium cepa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(7):6895–6906
Lepage CC, Thompson LL, Larson B, McManus KJ (2020) An automated, single cell quantitative imaging microscopy approach to assess micronucleus formation, genotoxicity and chromosome instability. Cells 9(2):344
Liu DH, Jiang WS, Li M (1992) Effects of trivalent and hexavalent chromium on root growth and cell division of Allium cepa. Hereditas 117:23–29
Macar O, Kalefetoğlu Macar T, Çavuşoğlu K, Yalçın E (2020) Protective effects of anthocyanin-rich bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) extract against copper (II) chloride toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2):1428–1435
Magdy BW, Mohamed FE, Amin AS, Rana SS (2016) Ameliorative effect of antioxidants (vitamins C and E) against abamectin toxicity in liver, kidney and testis of male albino rats. J Basic Appl Zool 77:69–82
Mahabali S, Spanoghe P (2015) Risk assessment of pesticide usage by farmers in Commewijne, Suriname, South America: a pilot study for the Alkmaar and Tamanredjo regions. Environ Monit Assess 187:153
Maluszynska J, Juchimiuk J (2005) Plant genotoxicity: a molecular cytogenetic approach in plant bioassays. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 56:177–184
Mishra K (1993) Cytotoxic effects of distillary waste on Allium cepa L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50(2):199–204
Mishra K, Sanwal E, Tandon PK, Gupta K (2015) Influence of pesticide effluent on Allium cepa L.(onion) plants. Int J Environ 4(2):95–105
Nasr HM, El-Demerdash FM, El-Nagar WA (2016) Neuro and renal toxicity induced by chlorpyrifos and abamectin in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1852–1859
Rank J, Nielsen MH (1994) Evaluation of Allium anaphase–telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutat Res 312:17–24
Samanta A (2019) Study of some cytotoxic chemicals on onion (Allium cepa L.) and grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). BPAS - Botany 38(2):68–73
Sharma A, Kumar V, Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Sidhu GPS, Handa N, Kohli SK, Yadav P, Bali AS, Parihar RD, Dar OI, Singh K, Jasroita S, Bakshi P, Kumar S, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK (2019) Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl Sci 1(11):1446
Sheikh N, Patowary H, Laskar RA (2020) Screening of cytotoxic and genotoxic potency of two pesticides (malathion and cypermethrin) on Allium cepa L. Mol Cell Toxicol 16:291–299
Siddique S, Syed Q, Adnan A, Nadeem M, Irfan M, Qureshi FA (2013) Production of avermectin B1b from Streptomyces avermitilis 41445 by batch submerged fermentation. Jundishapur J Microbiol 6(8):e7198
Silveira MAD, Ribeiro DL, dos Santos TA, Vieira GM, Cechinato CN, Kazanovski M, d’Arce LPG (2016) Mutagenicity of two herbicides widely used on soybean crops by the Allium cepa test. Cytotechnology 68(4):1215–1222
Singh D, Roy BK (2017) Evaluation of malathion-induced cytogenetical effects and oxidative stress in plants using Allium test. Acta Physiol Plant 39(4):92–102
Siqueira HAA, Guedes RNC, Fragoso DDB, Magalhaes LC (2001) Abamectin resistance and synergism in Brazilian populations of Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Int J Pest Manage 47(4):247–251
Staykova TA, Ivanova EN, Velcheva IG (2005) Cytogenetic effect of heavy metal and cyanide in contamined waters from the region of southwest Bulgaria. J Cell Mol Biol 4(1):41–46
Stumpf N, Nauen R (2002) Biochemical markers linked to abamectin resistance in Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 72(2):111–121
Sutan NA, Popescu A, Mihaescu C, Soare LC, Marinescu MV (2014) Evaluation of cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of the fungicide Ridomil in Allium cepa L. An Stiint Univ Al I Cuza Iasi 60(1):5–12
Tišler T, Eržen NK (2006) Abamectin in the aquatic environment. Ecotoxicology 15(6):495–502
Tütüncü E, Yalçin E, Acar A, Yapar K, Çavuşoğlu K (2019) Investigation of the toxic effects of a carbamate insecticide methiocarb in Allium cepa L. Cytologia 84(2):113–117
Yalçın E, Çavuşoğlu K, Acar A, Yapar K (2020) In vivo protective effects of Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract against hydrogen peroxide toxicity: cytogenetic and biochemical evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(3):3156–3164
Yi H, Meng Z (2003) Genotoxicity of hydrated sulfur dioxide on root tips of Allium sativum and Vicia faba. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 537(1):109–114
Yildiztekin M, Ozler MA, Nadeem S, Tuna AL (2019) Investigations on the effects of commonly used pesticides on tomato plant growth. Fresenius Environ Bull 28:376–382
Zhang ZL, Zhai WQ (2003) The experimental guide for plant physiology, 3rd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Zhang HY, Jiang YN, He ZY, Ma M (2005) Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum). J Plant Physiol 162:977–984
Zou KH, Tuncali K, Silverman SG (2003) Correlation and simple linear regression. Radiology 227(3):617–628
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalefetoğlu Macar, T. Investigation of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of abamectin pesticide in Allium cepa L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 2391–2399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10708-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10708-0