Abstract
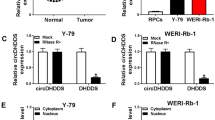
Retinoblastoma (RB) is an intraocular malignancy that mainly occurs in infants and young children under 5 years of age. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000034 (circ_0000034) was reported to be upregulated in RB tissues. Nevertheless, the function and mechanism of circ_0000034 in RB are unclear. Expression of circ_0000034, microRNA-361-3p (miR-361-3p), and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 19 (ADAM19) was examined via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were determined though Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), transwell, or flow cytometry assays. Caspase-3 activity was detected using a caspase-3 activity assay kit. Some protein levels were examined using Western blot analysis. Dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, or RNA pull-down assay were performed to verify the relationship between circ_0000034 or ADAM19 and miR-361-3p. The function of circ_0000034 in vivo was confirmed via animal experiment. We verified that circ_0000034 expression was elevated in RB tissues and cells. Circ_0000034 silencing reduced RB growth in vivo, repressed viability, migration, invasion, and EMT, and induced apoptosis of RB cells in vitro. Circ_0000034 acted as a sponge for miR-361-3p, which targeted ADAM19 in RB cells. Furthermore, the inhibition of miR-361-3p restored circ_0000034 knockdown-mediated impacts on viability, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and EMT of RB cells. Moreover, ADAM19 overexpression abolished the influence of miR-361-3p mimic on viability, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and EMT of RB cells. Circ_0000034 expedited RB progression through upregulating ADAM19 via sponging miR-361-3p, which indicated that circ_0000034 might a target for RB therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 January 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04311-1
References
de Jong MC, Kors WA, de Graaf P, Castelijns JA, Kivela T, Moll AC (2014) Trilateral retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 15:1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70336-5
Pritchard EM, Dyer MA, Guy RK (2016) Progress in small molecule therapeutics for the treatment of retinoblastoma. Mini Rev Med Chem 16:430–454. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150722100610
Errico A (2014) Cancer therapy: retinoblastoma–chemotherapy increases the risk of secondary cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11:623. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.155
Fabian ID, Onadim Z, Karaa E, Duncan C, Chowdhury T, Scheimberg I, Ohnuma SI, Reddy MA, Sagoo MS (2018) The management of retinoblastoma. Oncogene 37:1551–1560. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0050-x
Gao J, Zeng J, Guo B, He W, Chen J, Lu F, Chen D (2016) Clinical presentation and treatment outcome of retinoblastoma in children of South Western China. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e5204. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000005204
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, Sun W, Dou K, Li H (2015) Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett 365:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2017) Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol 14:1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1271524
Zhao ZJ, Shen J (2017) Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol 14:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1122162
Xing L, Zhang L, Feng Y, Cui Z, Ding L (2018) Downregulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 indicates poor prognosis for retinoblastoma and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis via AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 105:326–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.141
Lyu J, Wang Y, Zheng Q, Hua P, Zhu X, Li J, Li J, Ji X, Zhao P (2019) Reduction of circular RNA expression associated with human retinoblastoma. Exp Eye Res 184:278–285
Du S, Wang S, Zhang F, Lv Y (2019) SKP2, positively regulated by circ_ODC1/miR-422a axis, promotes the proliferation of retinoblastoma. J Cell Biochem 121:322
Hammond SM (2015) An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.001
Kabekkodu SP, Shukla V, Varghese VK, D'Souza J, Chakrabarty S, Satyamoorthy K (2018) Clustered miRNAs and their role in biological functions and diseases. Biol Rev 93:1955–1986. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12428
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02871
Hu J, Li L, Chen H, Zhang G, Liu H, Kong R, Chen H, Wang Y, Li Y, Tian F, Lv X, Li G, Sun B (2018) MiR-361-3p regulates ERK1/2-induced EMT via DUSP2 mRNA degradation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9:807. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0839-8
Chen L, Nan A, Zhang N, Jia Y, Li X, Ling Y, Dai J, Zhang S, Yang Q, Yi Y, Jiang Y (2019) Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 18:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0943-0
Zhao D, Cui Z (2019) MicroRNA-361-3p regulates retinoblastoma cell proliferation and stemness by targeting hedgehog signaling. Exp Ther Med 17:1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.7062
Reiss K, Saftig P (2009) The "a disintegrin and metalloprotease" (ADAM) family of sheddases: physiological and cellular functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.11.002
Takeda S (2016) ADAM and ADAMTS family proteins and snake venom metalloproteinases: a structural overview. Toxins (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050155
Melenhorst WB, van den Heuvel MC, Timmer A, Huitema S, Bulthuis M, Timens W, van Goor H (2006) ADAM19 expression in human nephrogenesis and renal disease: associations with clinical and structural deterioration. Kidney Int 70:1269–1278. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5001753
Qi B, Newcomer RG, Sang Q-XA (2009) ADAM19/adamalysin 19 structure, function, and role as a putative target in tumors and inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des 15:2336–2348
Sun Z, Zhang A, Jiang T, Du Z, Che C, Wang F (2015) MiR-145 suppressed human retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ADAM19. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:14521–14527
Wang F, Li Y, Zhang Z, Wang J, Wang J (2019) SHCBP1 regulates apoptosis in lung cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog. Oncol Lett 18:1888–1894
Jabbour P, Chalouhi N, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Dumont AS, Chitale R, Rosenwasser R, Bianciotto CG, Shields C (2012) Pearls and pitfalls of intraarterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:175–181. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.peds1277
Zhang Y, Liang W, Zhang P, Chen J, Qian H, Zhang X, Xu W (2017) Circular RNAs: emerging cancer biomarkers and targets. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0624-z
Wang R, Zhang S, Chen X, Li N, Li J, Jia R, Pan Y, Liang H (2018) CircNT5E acts as a sponge of miR-422a to promote glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 78:4812–4825. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-0532
Li XN, Wang ZJ, Ye CX, Zhao BC, Li ZL, Yang Y (2018) RNA sequencing reveals the expression profiles of circRNA and indicates that circDDX17 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-1006-x
Tang YY, Zhao P, Zou TN, Duan JJ, Zhi R, Yang SY, Yang DC, Wang XL (2017) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001982 promotes breast cancer cell carcinogenesis through decreasing miR-143. DNA Cell Biol 36:901–908. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.3862
Zhang J, Liu H, Hou L, Wang G, Zhang R, Huang Y, Chen X, Zhu J (2017) Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression. Mol Cancer 16:151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0719-3
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:178–196. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3758
Dongre A, Weinberg RA (2019) New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0080-4
Chen W, Wang J, Liu S, Wang S, Cheng Y, Zhou W, Duan C, Zhang C (2016) MicroRNA-361-3p suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting SH2B1 in NSCLC. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0357-4
Wang J, Li H, Liang Z (2019) circ-MYBL2 serves as a sponge for miR-361-3p promoting cervical cancer cells proliferation and invasion. Onco Targets Ther 12:9957–9964. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s218976
Zhang Q, Yu L, Qin D, Huang R, Jiang X, Zou C, Tang Q, Chen Y, Wang G, Wang X, Gao X (2015) Role of microRNA-30c targeting ADAM19 in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 10:e0120698. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120698
Wildeboer D, Naus S, Amy Sang QX, Bartsch JW, Pagenstecher A (2006) Metalloproteinase disintegrins ADAM8 and ADAM19 are highly regulated in human primary brain tumors and their expression levels and activities are associated with invasiveness. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:516–527. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.jnen.0000229240.51490.d3
Wang Y, Lian YM, Ge CY (2019) MiR-145 changes sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to gefitinib through targeting ADAM19. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:5831–5839. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201907_18323
Chan MW, Huang YW, Hartman-Frey C, Kuo CT, Deatherage D, Qin H, Cheng AS, Yan PS, Davuluri RV, Huang TH, Nephew KP, Lin HJ (2008) Aberrant transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and SMAD4 nuclear translocation confer epigenetic repression of ADAM19 in ovarian cancer. Neoplasia 10:908–919. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.08540
Wang X, Wang E, Cao J, Xiong F, Yang Y, Liu H (2017) MiR-145 inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via targeting ADAM19 in human glioblastoma. Oncotarget 8:92545–92554. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21442
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (TIF 275 kb)
Supplementary Fig.1 Influence of circ_0000034 inhibition on the predicted 10 miRNA levels in RB cells. (A and B) QRT-PCR revealed the levels of miR-1184, miR-1204, miR-1205, miR-361-3p, miR-450b-3p, miR-769-3p, miR-1270, miR-620, miR-638, and miR-873 in Y79 and Weri-Rb1 cells transfected with sh-circ#1 or sh-NC. *P < 0.05.
Supplementary file2 (TIF 281 kb)
Supplementary Fig.2 Influence of miR-361-3p overexpression on the predicted 10 mRNA levels in RB cells. (A and B) QRT-PCR revealed the levels of E2F2, JAK1, NOTCH2, ETV3, FZD4, CCND2, ADAM19, AKT2, MAPK4, ADAM10 mRNA in Y79 and Weri-Rb1 cells transfected with miR-361-3p or miR-NC. *P < 0.05.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Xiao, F., Wang, L. et al. Circular RNA has_circ_0000034 accelerates retinoblastoma advancement through the miR-361-3p/ADAM19 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 69–80 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03886-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03886-5