Abstract
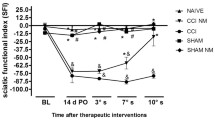
Neuromodulatory techniques have been studied to treat drug addiction or compulsive eating as well as different chronic pain conditions, such as neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the clinical and preclinical settings. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on the association of alcohol withdrawal with neuropathic pain based on nociceptive and neurochemical parameters in rats. Thirty-six adult male Wistar rats were randomized into five groups: control, neuropathic pain, neuropathic pain + tDCS, neuropathic pain + alcohol, and neuropathic pain + alcohol + tDCS. The neuropathic pain model was induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) to the sciatic nerve. Rats were then exposed to alcohol (20%) by oral gavage administration for 15 days (beginning 24 h after CCI). tDCS was started on the 17th day after surgery and lasted for 8 consecutive days. The nociceptive test (hot plate) was performed at baseline, 16 days after CCI, and immediately and 24 h after the last session of tDCS. Rats were killed by decapitation, and structures were removed and frozen for biochemical analysis (nerve growth factor and interleukin (IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-10 measurements). Neuropathy-induced thermal hyperalgesia was reversed by tDCS, an effect that was delayed by alcohol abstinence. In addition, tDCS treatment induced modulation of central levels of IL-1α, IL-1ß, and IL-10 and neurotrophic growth factor. We cannot rule out that the antinociceptive effect of tDCS could be related to increased central levels of IL-1α and IL-10. Therefore, tDCS may be a promising non-pharmacological therapeutic approach for chronic pain treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen SP, Mao J (2014) Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and their clinical implications. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f7656
Chang SL, Huang W, Han H, Sariyer IK (2019) Binge-like exposure to ethanol enhances morphine’s anti-nociception in B6 mice. Front Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00756
Shield KD, Parry C, Rehm J (2013) Chronic diseases and conditions related to alcohol use. Alcohol Res 35:155
Yamada A, Koga K, Kume K, Ohsawa M, Furue H (2018) Ethanol-induced enhancement of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the rat spinal substantia gelatinosa. Mol Pain. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806918817969
Thompson T, Oram C, Correll CU, Tsermentseli S, Stubbs B (2017) Analgesic effects of alcohol: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled experimental studies in healthy participants. J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2016.11.009
Wilens TE (2004) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the substance use disorders: the nature of the relationship, subtypes at risk, and treatment issues. Psychiatr Clin North Am. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0193-953X(03)00113-8
Natraviola E, Xie JY, Okun A, Qu C, Eyde N, Ci S, Ossipov MH, King T, Fields HL, Porreca F (2012) Pain relief produces negative reinforcement through activation of mesolimbic reward–valuation circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1214605109
Yu W, Hwa LS, Makhijani VH, Besheer J, Kash TL (2019) Chronic inflammatory pain drives alcohol drinking in a sex-dependent manner for C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.10.002
Kerns RT, Ravindranathan A, Hassan S, Cage MP, York T, Sikela JM, Williams RW, Miles MF (2005) Ethanol-responsive brain region expression networks: implications for behavioral responses to acute ethanol in DBA/2J versus C57BL/6J mice. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4372-04.2005
Gatch MB (2009) Ethanol withdrawal and hyperalgesia. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874473710902010041
Jochum T, Boettger MK, Burkhardt C, Juckel G, Bär K (2012) Increased pain sensitivity in alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Eur J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2009.11.008
Riley JL, King C (2009) Self-report of alcohol use for pain in a multi-ethnic community sample. J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2009.03.005
Brennan PL, Schutte KK, Moos RH (2005) Pain and use of alcohol to manage pain: prevalence and 3-year outcomes among older problem and non‐problem drinkers. Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2005.01074.x
Mellion M, Gilchrist JM, De La Monte S (2011) Alcohol-related peripheral neuropathy: nutritional, toxic, or both? Muscle Nerve. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21946
Schunck RVA, Torres ILS, Laste G, De Souza A, Macedo IC, Valle MTC, Leal MB (2015) Protracted alcohol abstinence induces analgesia in rats: possible relationships with BDNF and interleukin-10. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.05.011
Egli M, Koob GF, Edwards S (2012) Alcohol dependence as a chronic pain disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.010
Li J, Fu C, Liu H, Fu R, Zuo W, Kang S, Chen P, Gregor D, Paulose R, Bekker A, Ye J (2017) Electroacupuncture attenuates hyperalgesia in rats withdrawn from chronic alcohol drinking via habenular mu opioid receptors. Alcoholism. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13332
Castillo RC, MacKenzie EJ, Wegener ST, Bosse MJ, Group LS (2006) Prevalence of chronic pain seven years following limb threatening lower extremity trauma. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2006.04.020
Holmes A, Williamson O, Hogg M, Arnold C, Prosser A, Clements J, O’Donnell M (2010) Predictors of pain severity 3 months after serious injury. Pain Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2010.00890.x
Gilpin NW, Koob GF (2008) Neurobiology of alcohol dependence: focus on motivational mechanisms. Alcohol Res 31:185
Koob GF (2003) Alcoholism: allostasis and beyond. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.alc.0000057122.36127.c2
Stewart S, Finn PR, Pihl RO (1995) A dose–response study of the effects of alcohol on the perception of pain and discomfort due to electric shock in men at high familial-genetic risk for alcoholism. Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02246289
Katon W, Egan K, Miler D (1985) Chronic pain: lifetime psychiatric diagnoses and family history. Am J Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.142.10.1156
Filho PRM, Vercelino R, Cioato SG, Medeiros LF, de Oliveira C, Scarabelot VL, Torres ILS (2016) Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) reverts behavioral alterations and brainstem BDNF level increase induced by neuropathic pain model: long-lasting effect. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.06.016
Lopes BC, Medeiros LF, de Souza VS, Cioato SG, Medeiros HR, Regner GG, de Oliveira CL, Frengi F, Caumo W, Torres ILS (2020) Transcranial direct current stimulation combined with exercise modulates the inflammatory profile and hyperalgesic response in rats subjected to a neuropathic pain model: long-term effects. Brain Stimulation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2020.02.025
Laste G, Caumo W, Adachi LNS, Rozisky JR, De Macedo IC, Filho PRM, Torres ILS (2012) After-effects of consecutive sessions of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in a rat model of chronic inflammation. Exp Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3149-x
Lehnert M, Kovacs EJ, Molina PE, Relja B (2014) Modulation of inflammation by alcohol exposure. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/283756
Molina PE, Happel KI, Zhang P, Kolls JK, Nelson S (2010) Focus on: alcohol and the immune system. Alcohol Res Health. 33, 97
Brietzke AP, Zortea M, Carvalho F, Sanches PRS, Silva JDP, da Torres IL, Caumo W (2019) Large treatment effect with extended home-based transcranial direct current stimulation over dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in fibromyalgia: a proof of concept sham-randomized clinical study. J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2019.06.013
Da Silva Moreira SF, Medeiros LF, De Souza A, De Oliveira C, Scarabelot VL, Fregni F, Torres ILS (2016) Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) neuromodulatory effects on mechanical hyperalgesia and cortical BDNF levels in ovariectomized rats. Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.10.011
Nakamura-Palacios EM, Lopes IBC, Souza RA, Klauss J, Batista EK, Conti CL, de Souza RSM (2016) Ventral medial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) as a target of the dorsolateral prefrontal modulation by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in drug addiction. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-016-1559-9
de Oliveira C, de Freitas JS, Macedo IC, Scarabelot VL, Ströher R, Santos DS, Torres ILS (2019) Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) modulates biometric and inflammatory parameters and anxiety-like behavior in obese rats. Neuropeptides. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2018.09.006
Song S, Zilverstand A, Gui W, Li H, Jie, Zhou X (2019) Effects of single-session versus multi-session non-invasive brain stimulation on craving and consumption in individuals with drug addiction, eating disorders or obesity: a meta-analysis. Brain Stimulation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2018.12.975
Lefaucheur JP, Antal A, Ayache SS, Benninger DH, Brunelin J, Cogiamanian F, Paulus W (2017) Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Clin Neurophysiol 128:56–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.10.087
Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, Priori A, Lang N, Antal A, Pascual-Leone A (2008) Transcranial direct current stimulation: state of the art 2008. Brain Stimulation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2008.06.004
da Graca-Tarragó M, Lech M, Angoleri LDM, Santos DS, Deitos A, Brietzke AP, Caumo W (2019) Intramuscular electrical stimulus potentiates motor cortex modulation effects on pain and descending inhibitory systems in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, factorial, sham-controlled study. J Pain Res. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S181019
Cioato SG, Medeiros LF, Filho PRM, Vercelino R, De Souza A, Scarabelot VL, Torres ILS (2016) Long-lasting effect of transcranial direct current stimulation in the reversal of hyperalgesia and cytokine alterations induced by the neuropathic pain model. Brain Stimulation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.12.001
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2013) Improving bioscience research reporting: the arrive guidelines for reporting animal research. Animals. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani4010035
Spezia Adachi LN, Caumo W, Laste G, Fernandes Medeiros L, Rozisky R, De Souza J, Torres A, I. L. S (2012) Reversal of chronic stress-induced pain by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in an animal model. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.009
Takano Y, Yokawa T, Masuda A, Niimi J, Tanaka S, Hironaka N (2011) A rat model for measuring the effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation using fMRI. Neurosci Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.01.004
Boggio PS, Sultani N, Fecteau S, Merabet L, Mecca T, Pascual-Leone A, Fregni F (2008) Prefrontal cortex modulation using transcranial DC stimulation reduces alcohol craving: a double-blind, sham-controlled study. Drug Alcohol Depend. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.06.011
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(88)90209-6
Guzman-silva MA, Pollastri CE, Augusto J, Pantaleão S, Carolina A, Carvalho B, De, Boaventura GT (2008) Tramadol minimizes potential pain during post-oophorectomy in Wistar rats. Aatex, (14), 91–92
Overstreet DH, Knapp DJ, Breese GR (2002) Accentuated decrease in social interaction in rats subjected to repeated ethanol withdrawals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ALC.0000023983.10615.D7
Caggiula AR, Perkins KA, Saylor S, Epstein LH (1995) Different methods of assessing nicotine-induced antinociception may engage different neural mechanisms. Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246552
Ossipov MH, Kovelowski CJ, Nichols ML, Hruby VJ, Porreca F (1995) Characterization of supraspinal antinociceptive actions of opiod delta agonists in the rat. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(94)00231-3
Rubinstein M, Mogil JS, Japon M, Chan EC, Allen RG, Low MJ (2002) Absence of opioid stress-induced analgesia in mice lacking beta-endorphin by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.9.3995
Spindola HM, Servat L, Denny C, Rodrigues RAF, Eberlin MN, Cabral E, Foglio MA (2010) Antinociceptive effect of geranylgeraniol and 6alpha,7beta-dihydroxyvouacapan-17beta-oate methyl ester isolated from Pterodon pubescens Benth. BMC Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2210-10-1
Woolfe G, Macdonald A (1944) The evaluation of the analgesic action of pethidine hydrochloride (Demerol). J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Emamuzo ED, Miniakiri SI, Tedwin EJO, Ufouma O, Lucky M (2010) Analgesic and anti—inflammatory activities of the ethanol extract of the leaves of Helianthus Annus in Wistar rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(10)60083-1
Gatch MB, Lal H (1999) Effects of ethanol and ethanol withdrawal on nociception in rats. Alcoholism. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.1999.tb04118.x
Souza A, Martins DF, Medeiros LF, Nucci-Martins C, Martins TC, Siteneski A, Torres ILS (2018) Neurobiological mechanisms of antiallodynic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in a mice model of neuropathic pain. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.12.005
Davies M (2003) The role of GABAA receptors in mediating the effects of alcohol in the central nervous system. J Psychiatry Neurosci 28:263
Rao PSS, Bell RL, Engleman EA, Sari Y (2015) Targeting glutamate uptake to treat alcohol use disorders. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00144
LeMarquand D, Pihl RO, Benkelfat C (1994) Serotonin and alcohol intake, abuse, and dependence: clinical evidence. Biol Psychiat. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(94)90630-0
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Yoshimoto K, Lumeng L, Li T (1993) Serotonin mechanisms in alcohol drinking behavior. Drug Dev Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.430300309
Font L, Luján M, Pastor R (2013) Involvement of the endogenous opioid system in the psychopharmacological actions of ethanol: the role of acetaldehyde. Front Behav Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00093
Gatch MB (1999) Effects of benzodiazepines on acute and chronic ethanol-induced nociception in rats. Alcoholism. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.1999.tb04068.x
Mogil JS, Marek P, Yirmiya R, Balian H, Sadowski B, Taylor AN, Liebeskind JC (1993) Antagonism of the non-opioid component of ethanol-induced analgesia by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(93)90251-h
Khanna JM, Mayer JM, Lê DA, Kalant H (1984) Differential response to ethanol, pentobarbital and morphine in mice selectively bred for ethanol sensitivity. Alcohol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0741-8329(84)90029-6
Newman LM, Curran MA, Becker GL (1986) Effects of chronic alcohol intake on anesthetic responses to diazepam and thiopental in rats. Anesthesiology. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-198608000-00012
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF (1989) Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2467382
Hoffman PL, Rabe CS, Moses F, Tabakoff B (1989) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and ethanol: inhibition of calcium flux and cyclic GMP production. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07280.x
Le Bars D, Gozariu M, Cadden W (2001) Animal models of nociception. Pharmacol Rev 53:597
Shumilla JA, Liron T, Mochly-Rosen D, Kendig JJ, Sweitzer SM (2005) Ethanol withdrawal-associated allodynia and hyperalgesia: age-dependent regulation by protein kinase C epsilon and gamma isoenzymes. J Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2005.03.005
Fu R, Gregor D, Peng Z, Li J, Bekker A, Ye JH (2015) Chronic intermittent voluntary alcohol drinking induces hyperalgesia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 7:136
Li J, Chen P, Han X, Zuo W, Mei Q, Bian EY, Umeugo J, Ye J (2019) Differences between male and female rats in alcohol drinking, negative affects and neuronal activity after acute and prolonged abstinence. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 11:163
Duarte R, McNeill A, Drummond G, Tiplady B (2008) Comparison of the sedative, cognitive, and analgesic effects of nitrous oxide, sevoflurane, and ethanol. Br J Anaesth. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aem369
Perrino AC Jr, Ralevski E, Acampora G, Edgecombe J, Limoncelli D, Petrakis IL (2008) Ethanol and pain sensitivity: effects in healthy subjects using an acute pain paradigm. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00653.x
Saddler JM, James MF, Harington AP (1985) Naloxone does not reverse ethanol analgesia in man. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.1985.tb00883.x
Horn-Hofmann C, Buscher P, Lautenbacher S, Wolstein J (2015) The effect of nonrecurring alcohol administration on pain perception in humans: a systematic review. J Pain Res 8:175–187. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S79618
Chastain G (2006) Alcohol, neurotransmitter systems, and behavior. J Gen Psychol. https://doi.org/10.3200/GENP.133.4.329-335
Mika J, Korostynski M, Kaminska D, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Osikowicz M, Makuch W, Przewlocka B (2008) Interleukin-1alpha has antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activities in a rat neuropathic pain model. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.02.015
Dai W, Sun J, Li C, Mao W, Huang Y, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Lü N (2019) Involvement of interleukin-10 in analgesia of electroacupuncture on incision pain. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8413576
Stemkowski PL, Garcia-Caballero A, Gadotti VM, M’Dahoma S, Chen L, Souza IA, Zamponi GW (2017) Identification of interleukin-1 beta as a key mediator in the upregulation of Cav3.2–USP5 interactions in the pain pathway. Mol Pain. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806917724698
Ren K, Torres R (2009) Role of interleukin-1β during pain and inflammation. Brain Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.020
Souter AJ, Garry MG (2000) Spinal interleukin-1β reduces inflammatory pain. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3959(99)00315-2
Conner JM, Franks KM, Titterness AK, Russell K, Merrill DA, Christie BR, Tuszynski MH (2009) NGF is essential for hippocampal plasticity and learning. J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2594-09.2009
Miller MW, Mooney SM (2004) Chronic exposure to ethanol alters neurotrophin content in the basal forebrain-cortex system in the mature rat: effects on autocrine-paracrine mechanisms. J Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.20059
Gericke CA, Schulte-Herbrüggen O, Arendt T, Hellweg R (2006) Chronic alcohol intoxication in rats leads to a strong but transient increase in NGF levels in distinct brain regions. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0361-x
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Biomedical Engineering group from the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA) for the development of the tDCS equipment used in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the following Brazilian funding agencies: Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education—CAPES/MD-PhD (D.S. Santos, B.C. Lopes, L.S. Santos); National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPq (Dr. I.L.S. Torres, Dr. W. Caumo); Graduate Research Group of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre—GPPG (I.L.S. Torres, Grant No.: 15–0501) MCT/FINEP—COENG/2013; and the Support Program for Emerging Nuclei PRONEM (Paulo Roberto Sanches, Grant No. 16/2551-0000249-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DSS and ILST were responsible for the study concept and design. DSS, BCL, LSS, AS, and JA contributed to the acquisition of data. DSS, LFM, JA, and ILST were responsible for data analysis. DSS, LFM, FF, WC, and ILST drafted the manuscript. All authors revised and edited the manuscript as well as approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All experiments and procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre/HCPA (GPPG-HCPA protocol no. 15.0501). The experimental protocol complied with the ethical and methodological standards of the ARRIVE guidelines (Kilkenny et al. 2013).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, D.S., Lopes, B.C., Medeiros, L.F. et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Induces Analgesia in Rats with Neuropathic Pain and Alcohol Abstinence. Neurochem Res 45, 2653–2663 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03116-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03116-w