Abstract
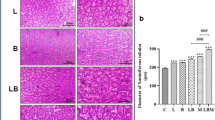
The current study evaluated the effects of nano delivery of Spirulina platensis on growth performance, digestive enzymes, and biochemical, immunological, and antioxidative status, as well as resistance to Aeromonas veronii and some physical stressor challenges in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Three experimental fish groups (n = 270) with mean weights of 26 ± 0.30 g and mean lengths of 10 ± 0.5 cm were used; the first additive-free basal diet served as the control group, whereas the following two groups were supplemented with spirulina nanoparticles (SPNP) at 0 (control), 0.25, and 0.5%/kg diet for 4 weeks. Following the feeding trial, fish were challenged with hypoxia, cold stresses, and pathogenic bacteria (A. veronii) infection (9 × 108 CFU/ml). SPNP supplementation, especially 0.5%, (p < 0.05) significantly increased growth performance (specific growth rate % day−1, feed conversion ratio, and length gain rate %), immunological (plasma lysozyme and liver nitrous oxide) antioxidants (superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase in liver), biochemical (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine transaminase, glucose, and cortisol concentrations in plasma) assays, and digestive enzymes (lipase and amylase in plasma). The expression of liver’s heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and interleukin 1, beta (IL-1β) genes showed a significant upregulation outline of 0.5% SPNP > 0.25% SPNP > 0% SPNP compared with the control. Protection in the incorporated fish groups exposed to A. veronii was 100% compared with the control group, which showed 50% cumulative mortalities. In conclusion, dietary SPNP supplementation improved growth performance, antioxidant activity, immune response, digestive enzymes, related gene expression, and resistance of Nile Tilapia to hypoxia, cold, and A. veronii infection. Thus, SPNP could be used as a natural therapy for controlling those stressors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkhalek NKM, Eissa IAM, Ahmed E et al (2017) Protective role of dietary Spirulina platensis against diazinon-induced oxidative damage in Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 54:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.07.002
Abdel-Tawwab M, Samir F, Abd El-Naby AS, Monier MN (2018) Antioxidative and immunostimulatory effect of dietary cinnamon nanoparticles on the performance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) and its susceptibility to hypoxia stress and Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.033
Adel M, Yeganeh S, Dadar M, Sakai M, Dawood MAO (2016) Effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on growth performance, humoral and mucosal immune responses and disease resistance in juvenile great sturgeon (Huso huso Linnaeus, 1754). Fish Shellfish Immun 56:436–444
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro, in: Methods in Enzymology, Oxygen Radicals in Biological Systems. Academic Press, pp. 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Aly SM, Al Zohairy MA, Rahmani AH, FathiM, Atti NM (2016) Trials to improve the response of Orechromis niloticus to Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine using immunostimulants (garlic, Echinacea) and probiotics (Organic GreenTM and Vet-YeastTM). Afr J Biotechnol 15(21):989–994. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2015.15155
Amer S (2016) Effect of Spirulina platensis as feed supplement on growth performance, immune response and antioxidant status of mono-sex Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Benha Vet Med J 30(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.21608/bvmj.2016.31332
Anderson DP, Dixon OW, Simon RC (1980) Fish biologics: vaccine standards for sport fisheries and commercial aquaculture. Dev Biol Stand 45:157–162
Barton BA, Iwama GK (1991) Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Annu Rev Fish Dis 1:3–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-8030(91)90019-G
Bermejo P, Piñero E, Villar ÁM (2008) Iron-chelating ability and antioxidant properties of phycocyanin isolated from a protean extract of Spirulina platensis. Food Chem 110:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.021
Cao S, Zhang P, Zou T, Fei S, Han D, Jin J, Liu H, Yang Y, Zhu X, Xie S (2018) Replacement of fishmeal by spirulina Arthrospira platensis affects growth, immune related-gene expression in Gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio var. CAS III), and its challenge against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 79:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.05.022
Castro R, Zou J, Secombes CJ, Martin SAM (2011) Cortisol modulates the induction of inflammatory gene expression in a rainbow trout macrophage cell line. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.10.010
Corripio-Miyar Y, Bird S, Tsamopoulos K, Secombes CJ (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1 beta and IL-8, in haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Mol Immunol 44:1361–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2006.05.010
Dawood MAO, Koshio S (2016) Recent advances in the role of probiotics and prebiotics in carp aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 454:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.12.033
Dong HT, Techatanakitarnan C, Jindakittikul P, Thaiprayoon A, Taengphu S, Charoensapsri W, Khunrae P, Rattanarojpong T, Senapin S (2017) Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J Fish Dis 40:1395–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12617
El Latif AMA, Elabd H, Amin A et al (2019) High mortalities caused by Aeromonas veronii: identification, pathogenicity, and histopathological studies in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac Int 27:1725–1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00429-8
Elabd H, Wang H-P, Shaheen A, Yao H, Abbass A (2016) Feeding Glycyrrhiza glabra (liquorice) and Astragalus membranaceus (AM) alters innate immune and physiological responses in yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Fish Shellfish Immunol 54:374–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.024
Elabd H, Wang H-P, Shaheen A et al (2017) Anti-oxidative effects of some dietary supplements on Yellow perch (Perca flavescens) exposed to different physical stressors. Aquac Rep 8:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2017.09.002
FAO (2016) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016. Contributing to food security and nutrition for all, Rome, p 200
Fitzsimmons K (2016) Supply and demand in global tilapia markets, 2015. Aquaculture 2016, Las Vegas, pp 23–26. https://doi.org/10.13140/rg.2.1.2848.9448
Gröner F, Ziková A, Kloas W (2015) Effects of the pharmaceuticals diclofenac and metoprolol on gene expression levels of enzymes of biotransformation, excretion pathways and estrogenicity in primary hepatocytes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol CBP 167:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2014.09.003
Güroy B, Şahin İ, Mantoğlu S, Kayalı S (2012) Spirulina as a natural carotenoid source on growth, pigmentation and reproductive performance of yellow tail cichlid Pseudotropheus acei. Aquac Int 20:869–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-012-9512-x
Hill EK, Li J (2017) Current and future prospects for nanotechnology in animal production. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 8:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-017-0157-5
Hu C-C, Lin J-T, Lu F-J, Chou FP, Yang DJ (2008) Determination of carotenoids in Dunaliella salina cultivated in Taiwan and antioxidant capacity of the algal carotenoid extract. Food Chem 109:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.043
Huang X-J, Choi Y-K, Im H-S, Yarimaga O, Yoon E, Kim H-S (2006) Aspartate aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) detection techniques. Sensors 6:756–782
Ibrahem M, Mohamed M, Ibrahim M (2013) The role of Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira platensis) in growth and immunity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and its resistance to bacterial infection. J Agric Sci 5:p109. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v5n6p109
Jensen C, Birk E, Jokumsen A, Skibsted LH, Bertelsen G (1998) Effect of dietary levels of fat, α-tocopherol and astaxanthin on colour and lipid oxidation during storage of frozen rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and during chill storage of smoked trout. Z Für Leb -Forsch A 207:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170050317
Khalil SR, Reda RM, Awad A (2017) Efficacy of Spirulina platensis diet supplements on disease resistance and immune-related gene expression in Cyprinus carpio L. exposed to herbicide atrazine. Fish Shellfish Immunol 67:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.065
Klemm DJ, Stober QJ, Lazorchak JM (1993) Fish field and laboratory methods for evaluating the biological integrity of surface waters. Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory-Cincinnati, Office of Modeling, Monitoring Systems, and Quality Assurance, Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati
Liu Z, Que S, Xu J, Peng T (2014) Alanine aminotransferase-old biomarker and new concept: a review. Int J Med Sci 11:925–935. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.8951
Madeira D, Narciso L, Cabral HN, Vinagre C, Diniz MS (2013) Influence of temperature in thermal and oxidative stress responses in estuarine fish. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 166:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.06.008
Magnadóttir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.006
Mahmoud HK, Al-Sagheer AA, Reda FM et al (2017) Dietary curcumin supplement influence on growth, immunity, antioxidant status, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 475:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.03.043
Mahmoud MMA, El-Lamie MMM, Kilany OE, Dessouki AA (2018) Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) supplementation improves growth performance, feed utilization, immune response, and relieves oxidative stress in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) challenged with Pseudomonas fluorescens. Fish Shellfish Immunol 72:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.11.006
Nair M, Jayant RD, Kaushik A, Sagar V (2016) Getting into the brain: potential of nanotechnology in the management of NeuroAIDS. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 103:202–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.02.008
Palmegiano GB, Gai F, Daprà F, Gasco L, Pazzaglia M, Peiretti PG (2008) Effects of Spirulina and plant oil on the growth and lipid traits of white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) fingerlings. Aquac Res 39:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.01914.x
Ponce-Canchihuamán JC, Pérez-Méndez O, Hernández-Muñoz R, Torres-Durán PV, Juárez-Oropeza MA (2010) Protective effects of Spirulina maxima on hyperlipidemia and oxidative-stress induced by lead acetate in the liver and kidney. Lipids Health Dis 9:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-9-35
Promya J, Chitmanat C (2011) The effects of Spirulina platensis and Cladophora algae on the growth performance, meat quality and immunity stimulating capacity of the African sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Int J Agric Biol 13:77–82
Reda RM, Selim KM, Mahmoud R, El-Araby IE (2018) Effect of dietary yeast nucleotide on antioxidant activity, non-specific immunity, intestinal cytokines, and disease resistance in Nile tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immunol 80:281–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.016
Shaheen AA (2013) An industry assessment of tilapia farming in Egypt. African Union – Inter-African Bureau for Animal Resources (AU-IBAR)
Shi G-C, Dong X-H, Chen G, Tan BP, Yang QH, Chi SY, Liu HY (2015) Physiological responses and HSP70 mRNA expression of GIFT strain of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under cold stress. Aquac Res 46:658–668. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12212
Somogyi A, Rosta K, Pusztai P, Tulassay Z, Nagy G (2007) Antioxidant measurements. Physiol Meas 28:R41–R55. https://doi.org/10.1088/0967-3334/28/4/R01
Song SK, Beck BR, Kim D, Park J, Kim J, Kim HD, Ringø E (2014) Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 40:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.06.016
Villamil L, Tafalla C, Figueras A, Novoa B (2002) Evaluation of immunomodulatory effects of lactic acid bacteria in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 9:1318–1323. https://doi.org/10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1318-1323.2002
Yilmaz S (2019) Effects of dietary blackberry syrup supplement on growth performance, antioxidant, and immunological responses, and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus to Plesiomonas shigelloides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:1125–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.012
Yu W, Wen G, Lin H, Yang Y, Huang X, Zhou C, Zhang Z, Duan Y, Huang Z, Li T (2018) Effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on growth performance, hematological and serum biochemical parameters, hepatic antioxidant status, immune responses and disease resistance of coral trout Plectropomus leopardus (Lacepede, 1802). Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:649–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.01.024
Yuan JS, Reed A, Chen F, Stewart CN (2006) Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinformatics 7:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-7-85
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Bradford Sherman at the Ohio State University for his editing work and comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The current study was performed in agreement with the approved guidelines for the Use of Laboratory Animals by the Experimental Animal Use Committee, Benha University, Qalyubia, Egypt.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elabd, H., Wang, HP., Shaheen, A. et al. Nano spirulina dietary supplementation augments growth, antioxidative and immunological reactions, digestion, and protection of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, against Aeromonas veronii and some physical stressors. Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 2143–2155 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00864-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00864-y