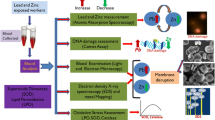
Abstract
Occupational exposure to heavy metals like lead and cadmium causes a wide range of biological effects and may elevate the risk of genetic damage. Heavy metal toxicity is now becoming a significant public health problem. There are many discrepancies in the results of the studies on the genotoxicity of heavy metals. Therefore, the study aimed to estimate lead, cadmium, and 8-OHdG levels (8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine) and expression of DNA repair gene OGG1 (8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1) in occupationally heavy metal exposed workers. The study comprised 100 workers, occupationally exposed to lead and cadmium from different factories and 100 controls without history of metal exposure. The lead and cadmium mean ± SD were 5.69 ± 12.07 µg/dL and 3.44 ± 1.33 µg/L in the cases and 1.27 ± 1.10 µg/dL and 1.07 ± 0.67 µg/L in the controls. The 8-OHdG concentration was significantly higher in the cases than the controls. Cadmium showed a significant positive correlation with 8-OHdG in the cases. The expression of OGG1 was significantly down-regulated in the cases compared to the controls. Lead levels did not show any significant correlation with OGG1, whereas cadmium level had a significant positive correlation with OGG1 in the cases. To conclude, the exposure to heavy metals is associated with increased oxidative DNA damage and impaired expression of the DNA repair gene, OGG1.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. V., & Newcomb, P. A. (2013). Cadmium blood and urine concentrations as measures of exposure: NHANES 1999–2010. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 24(2), 163–170.
Akram, Z., Riaz, S., Kayani, M. A., Jahan, S., Ahmad, M. W., Ullah, M. A., et al. (2018). Lead induces DNA damage and alteration of ALAD and antioxidant genes mRNA expression in construction site workers. Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health, 74(4), 171–178.
Al Bakheet, S. A., Attafi, I. M., Maayah, Z. H., Abd-Allah, A. R., Asiri, Y. A., & Korashy, H. M. (2013). Effect of long-term human exposure to environmental heavy metals on the expression of detoxification and DNA repair genes. Environmental Pollution, 181, 226–232.
Alarcon, W. A., Roscoe, R. J., Calvert, G. M., & Graydon, J. R. (2009). Adult blood lead epidemiology and surveillance-United States, 2005–2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 58(14), 365–369.
Alli, L. A. (2015). Blood level of cadmium and lead in occupationally exposed persons in Gwagwalada, Abuja, Nigeria. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 8(3), 146–150.
Alnajjar, K. S., & Sweasy, J. B. (2019). A new perspective on oxidation of DNA repair proteins and cancer. DNA Repair, 76, 60–69.
ATSDR, U. (2005). Toxicological profile for lead. US Department of Health and Human Services. Public Health Service, Atlanta, USA, 582.
Ba, X., & Boldogh, I. (2018). 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1: Beyond repair of the oxidatively modified base lesions. Redox Biology, 14, 669–678.
Ba, X., Aguilera-Aguirre, L., Rashid, Q. T. A. N., Bacsi, A., Radak, Z., Sur, S., et al. (2014). The role of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 in inflammation. International journal of molecular sciences, 15(9), 16975–16997.
Bravard, A., Vacher, M., Gouget, B., Coutant, A., de Boisferon, F. H., Marsin, S., et al. (2006). Redox regulation of human OGG1 activity in response to cellular oxidative stress. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 26(20), 7430–7436.
Cavalcante, D. N. D. C., Sposito, J. C. V., Crispim, B. D. A., Nascimento, A. V. D., & Grisolia, A. B. (2017). Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of passive smoking and urban air pollutants in buccal mucosa cells of children enrolled in public school. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods, 27(5), 346–351.
Dobrakowski, M., Pawlas, N., Kasperczyk, A., Kozłowska, A., Olewińska, E., Machoń-Grecka, A., et al. (2017). Oxidative DNA damage and oxidative stress in lead-exposed workers. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 36(7), 744–754.
Duggal, V., Rani, A., Mehra, R., & Balaram, V. (2017). Risk assessment of metals from groundwater in northeast Rajasthan. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 90(1), 77–84.
Goyal, T., Mitra, P., Singh, P., Sharma, S., & Sharma, P. (2020). Assessment of blood lead and cadmium levels in occupationally exposed workers of Jodhpur, Rajasthan. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 1–8.
Himani, H., Kumar, R., Ansari, J., Mahdi, A., Sharma, D., Karunanand, B., et al. (2018). Blood lead levels in occupationally exposed workers involved in battery factories of Delhi-NCR region: effect on vitamin D and calcium metabolism. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 35(1), 80–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-018-0797-z.
Jomova, K., & Valko, M. (2011). Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology, 283(2–3), 65–87.
Joseph, P. (2009). Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 238, 272–279.
Kasperczyk, S., Dobrakowski, M., Kasperczyk, J., Ostałowska, A., Zalejska-Fiolka, J., & Birkner, E. (2014). Beta-carotene reduces oxidative stress, improves glutathione metabolism and modifies antioxidant defense systems in lead-exposed workers. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 280(1), 36–41.
Kašuba, V., Rozgaj, R., Milić, M., Želježić, D., Kopjar, N., Pizent, A., et al. (2010). Evaluation of lead exposure in battery-manufacturing workers with focus on different biomarkers. Journal of Applied Toxicology: An International Journal, 30(4), 321–328.
Kayaaltı, Z., Yavuz, İ., Söylemez, E., Bacaksız, A., Tutkun, E., Sayal, A., et al. (2015). Evaluation of DNA damage using 3 comet assay parameters in workers occupationally exposed to lead. Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health, 70(3), 120–125.
Kippler, M., Hossain, M. B., Lindh, C., Moore, S. E., Kabir, I., Vahter, M., et al. (2012). Early life low-level cadmium exposure is positively associated with increased oxidative stress. Environmental Research, 112, 164–170.
Korashy, H. M., Attafi, I. M., Famulski, K. S., Bakheet, S. A., Hafez, M. M., Alsaad, A. M., et al. (2017). Gene expression profiling to identify the toxicities and potentially relevant human disease outcomes associated with environmental heavy metal exposure. Environmental Pollution, 221, 64–74.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2004). Heavy metal contamination of soil around Pali industrial area, Rajasthan, India. Environmental Geology, 47(1), 38–44.
Krokan, H. E., & Bjørås, M. (2013). Base excision repair. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 5(4), a012583.
Kumar, A., Pant, M. C., Singh, H. S., & Khandelwal, S. (2012). Reduced expression of DNA repair genes (XRCC1, XPD, and OGG1) in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck in North India. Tumor Biology, 33(1), 111–119.
Li, C., Xu, M., Wang, S., Yang, X., Zhou, S., Zhang, J., et al. (2011). Lead exposure suppressed ALAD transcription by increasing methylation level of the promoter CpG islands. Toxicology letters, 203(1), 48–53.
Mitra, P., Sharma, S., Purohit, P., & Sharma, P. (2017). Clinical and molecular aspects of lead toxicity: An update. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences, 54(7–8), 506–528.
Parmar, M., & Thakur, L. S. (2013). Heavy metal Cu, Ni and Zn: toxicity, health hazards and their removal techniques by low cost adsorbents: a short overview. International Journal of Plant, Animal and Environmental Sciences, 3(3), 143–157.
Parrish, M. C., Chaim, I. A., Nagel, Z. D., Tannenbaum, S. R., Samson, L. D., & Engelward, B. P. (2018). Nitric oxide induced S-nitrosation causes base excision repair imbalance. DNA Repair, 68, 25–33.
Pizzino, G., Bitto, A., Interdonato, M., Galfo, F., Irrera, N., Mecchio, A., et al. (2014). Oxidative stress and DNA repair and detoxification gene expression in adolescents exposed to heavy metals living in the Milazzo-Valle del Mela area (Sicily, Italy). Redox Biology, 2, 686–693.
Qiao, M., Cai, C., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Lin, A., & Zheng, Y. (2010). Characterization of soil heavy metal contamination and potential health risk in metropolitan region of northern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172(1–4), 353–365.
Singh, P., Mitra, P., Goyal, T., Sharma, S., & Sharma, P. (2020). Evaluation of DNA damage and expressions of DNA repair gene in occupationally lead exposed workers (Jodhpur, India). Biological Trace Element Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02298-2.
Skipper, A., Sims, J. N., Yedjou, C. G., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2016). Cadmium chloride induces DNA damage and apoptosis of human liver carcinoma cells via oxidative stress. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 13, 88.
Sughis, M., Penders, J., Haufroid, V., Nemery, B., & Nawrot, T. S. (2011). Bone resorption and environmental exposure to cadmium in children: A cross–sectional study. Environmental Health, 10, 104. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-10-104.
Tavakkoli, L., & Khanjani, N. (2016). Environmental and occupational exposure to cadmium in Iran: A systematic review. Reviews on Environmental Health, 31(4), 457–463.
Wise, J., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., & Shi, X. (2017). The 9th conference on metal toxicity and carcinogenesis: The conference overview. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 331, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.04.007.
World Health Organization. (2007). Health risks of heavy metals from long range trans-boundary air pollution. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/107872.
Wu, S., Peng, S., Zhang, X., Wu, D., Luo, W., Zhang, T., et al. (2015). Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148, 71–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Mitra, P., Goyal, T. et al. Blood lead and cadmium levels in occupationally exposed workers and their effect on markers of DNA damage and repair. Environ Geochem Health 43, 185–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00696-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00696-y