Abstract
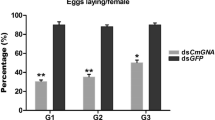
The cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, is a highly polyphagous pest, causing enormous losses to various economically important crops. The identification and in vitro functional validation of target genes of a pest is a prerequisite to combat pest via host-mediated RNA interference (RNAi). In the present study, six hormonal biosynthesis genes of H. armigera were chosen and evaluated by feeding insect larvae with dsRNAs corresponding to each target gene, viz., juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase (HaJHAMT), prothoracicotropic hormone (HaPTTH), pheromone biosynthesis-activating peptide (HaPBAP), molt regulating transcription factor (HaHR3), activated protein 4 (HaAP-4) and eclosion hormone precursor (HaEHP). The loss of function phenotypes for these hormonal genes were observed by releasing second instar larvae on to artificial diet containing target gene-specific dsRNAs. Ingestion of dsRNAs resulted in mortality ranging from 60% to 90%, reduced larval weight, phenotypic deformities and delayed pupation. The quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis showed that the target gene transcript levels were decreased drastically (31% to 77%) as compared to control or unrelated control (GFP-dsRNA), and correlated well with the mortality and developmental defects of larvae. Also, a comparison of the silencing efficacy of un-diced long HaPTTH-dsRNA with RNase III diced HaPTTH-dsRNA (siRNAs) revealed that long dsRNAs were more efficient in silencing the target gene. These results indicated that the hormonal biosynthesis genes have varied sensitivity towards RNAi and could be the vital targets for insect resistance in crop plants like cotton which are infested by H. armigera.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asokan R, Chandra GS, Manamohan M and Kumar NK 2013 Effect of diet delivered various concentrations of double-stranded RNA in silencing a midgut and a non-midgut gene of Helicoverpa armigera. Bull. Entomol. Res. 103 555–563
Asokan R, Chandra GS, Manamohan M, Kumar NK and Sita T 2014 Response of various target genes to diet-delivered dsRNA mediated RNA interference in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Pest Sci. 87 163–172
Belles X 2010 Beyond Drosophila: RNAi in vivo and functional genomics in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 55 111–128
Baum JA, Bogaert T, Clinton W, Heck GR, Feldmann P, Ilagan O, Johnson S, Plaetinck G, Munyikwa T, Pleau M and Vaughn T 2007 Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 25 1322–1326
Chaitanya BN, Asokan R, Sita T, Rebijith KB, Kumar PR and Kumar NK 2017 Silencing of JHEH and EcR genes of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) through double stranded RNA oral delivery. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 20 637–643
Chikate YR, Dawkar VV, Barbole RS, Tilak PV, Gupta VS and Giri AP 2016 RNAi of selected candidate genes interrupts growth and development of Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 133 44–51
Choudhary M and Sahi S 2011 In silico designing of insecticidal small interfering RNA (siRNA) for Helicoverpa armigera control. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 49 469–474
El-Wakeil NE 2007 Evaluation of efficiency of Trichogramma evanescens reared on different factitious hosts to control Helicoverpa armigera. J. Pest Sci. 80 29–34
Gordon KH and Waterhouse PM 2007 RNAi for insect-proof plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 25 1231–1232
Griebler M, Westerlund SA, Hoffmann KH and Meyering-Vos M 2008 RNA interference with the allatoregulating neuropeptide genes from the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and its effects on the JH titer in the hemolymph. J. Insect Physiol. 54 997–1007
Guan R, Li H and Miao X 2016 RNAi pest control and enhanced BT insecticidal efficiency achieved by dsRNA of chymotrypsin-like genes in Ostrinia furnacalis. J. Pest Sci. 90 745–757
Gupta GP, Birah A and Rani S 2004 Development of artificial diet for mass rearing of American bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Indian J. Agr. Sci. 74 548–551
He B, Chu Y, Yin M, Müllen K, An C and Shen J 2013 Fluorescent nanoparticle delivered dsRNA toward genetic control of insect pests. Adv. Mater. 25 4580-4584
Heath G, Childs D, Docker MF, McCauley DW and Whyard S 2014 RNA interference technology to control pest sea lampreys-a proof-of-concept. PLoS ONE 9 e88387
Hong B, Zhang ZF, Tang SM, Yi YZ, Zhang TY and Xu WH 2006 Protein-DNA interactions in the promoter region of the gene encoding diapause hormone and pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. BBA-Gene Struct. Expr. 1759 177–185
Hu CH, Hong B and Xu WH 2010 Identification of an E‐box DNA binding protein, activated protein 4, and its function in regulating the expression of the gene encoding diapause hormone and pheromone biosynthesis‐activating neuropeptide in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol. Biol.19 243–52
Hunter W, Ellis J, Hayes J, Westervelt D, Glick E, Williams M, Sela I, Maori E, Pettis J, Cox-Foster D and Paldi N 2010 Large-scale field application of RNAi technology reducing Israeli acute paralysis virus disease in honey bees (Apis mellifera, Hymenoptera: Apidae). PLoS Pathog. 6 e1001160
Huvenne H and Smagghe G 2010 Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: a review. J. Insect Physiol. 56 227–235
Israni B and Rajam MV 2016 Silencing of ecdysone receptor, insect intestinal mucin and sericotropin genes by bacterially produced double‐stranded RNA affects larval growth and development in Plutella xylostella and Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol. Biol. 26 164–80
Kalleda N, Naorem A and Rajam MV 2013 Targeting fungal genes by diced siRNAs: a rapid tool to decipher gene function in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 8 e75443
Kataoka H, Nagasawa H, Isogai A, Tamura S, Mizoguchi A, Fujiwara Y, Suzuki C, Ishizaki H and Suzuki A 1987 Isolation and partial characterization of a prothoracicotropic hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Agric. Biol. Chem. 51 1067–1076
Kumar M, Gupta GP and Rajam MV 2009 Silencing of acetylcholinesterase gene of Helicoverpa armigera by siRNA affects larval growth and its life cycle. J. Insect Physiol. 55 273–278
Li X, Zhang M and Zhang H 2011 RNA interference of four genes in adult Bactrocera dorsalis by feeding their dsRNAs. PLoS ONE 6 e17788
Lim ZX, Robinson KE, Jain RG, Chandra GS, Asokan R, Asgari S and Mitter N 2016 Diet-delivered RNAi in Helicoverpa armigera–progresses and challenges. J. Insect Physiol. 85 86–93
Liu F, Wang XD, Zhao YY, Li YJ, Liu YC and Sun J 2015 Silencing the HaAK gene by transgenic plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval growth of Helicoverpa armigera. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 11 67–74
Liu J, Smagghe G and Swevers L 2013 Transcriptional response of BmToll9–1 and RNAi machinery genes to exogenous dsRNA in the midgut of Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 59 646–654
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25 402–408
Mamta, Reddy KRK and Rajam MV 2016 Targeting chitinase gene of Helicoverpa armigera by host-induced RNA interference confers insect resistance in tobacco and tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 90 281-292
Mao YB, Cai WJ, Wang JW, Hong GJ, Tao XY, Wang LJ, Huang YP and Chen XY 2007 Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 25 1307–1313
Mao YB, Tao XY, Xue XY, Wang LJ and Chen XY 2011 Cotton plants expressing CYP6AE14 double-stranded RNA show enhanced resistance to bollworms. Transgenic Res. 20: 665–673
Minakuchi C, Namiki T, Yoshiyama M and Shinoda T 2008 RNAi-mediated knockdown of juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase gene causes precocious metamorphosis in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. FEBS J. 275 2919–2931
Mizoguchi A, Ohsumi S, Kobayashi K, Okamoto N, Yamada N, Tateishi K, Fujimoto Y and Kataoka H 2013 Prothoracicotropic hormone acts as a neuroendocrine switch between pupal diapause and adult development. PLoS ONE 8 e60824
Nimbalkar RK, Shinde SS, Tawar DS and Muley SP 2009 Response of cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to different insecticides in Maharashtra, India. World J. Agr. Sci. 5 250–255
Price DR and Gatehouse JA 2008 RNAi-mediated crop protection against insects. Trends Biotechnol. 26 393–400
Rajagopal R, Sivakumar S, Agrawal N, Malhotra P and Bhatnagar RK 2002 Silencing of Midgut Aminopeptidase N of Spodoptera litura by Double-stranded RNA Establishes Its Role as Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 277 46849–46851
Shinoda T and Itoyama K 2003. Juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase: A key regulatory enzyme for insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 11986–11991
Tabashnik BE, Brévault T and Carrière Y 2013 Insect resistance to Bt crops: lessons from the first billion acres. Nat. Biotechnol. 31 510–521
Terenius O, Papanicolaou A, Garbutt JS, etc. 2011 RNA interference in Lepidoptera: an overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 57 231–245
Turner CT, Davy MW, MacDiarmid RM, Plummer KM, Birch NP and Newcomb RD 2006 RNA interference in the light brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Walker) induced by double-stranded RNA feeding. Insect Mol. Biol. 15 383–391
Verma KK 2007 Polyphenism in insects and the juvenile hormone. J. Biosci. 32 415-420
Wang J, Wu M, Wang B and Han Z 2013 Comparison of the RNA interference effects triggered by dsRNA and siRNA in Tribolium castaneum. Pest Manag. Sci. 69 781–786
Wei ZJ, Zhang QR, Kang L, Xu WH and Denlinger DL 2005 Molecular characterization and expression of prothoracicotropic hormone during development and pupal diapause in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Insect Physiol. 51 691–700
Whyard S, Singh AD and Wong S 2009 Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39: 824–832
Xiong Y, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Xu D and Qiu D 2013 Silencing the HaHR3 gene by transgenic plant-mediated RNAi to disrupt Helicoverpa armigera development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 9 370–381
Younis A, Siddique MI, Kim CK and Lim KB 2014 RNA interference (RNAi) induced gene silencing: a promising approach of hi-tech plant breeding. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 10 1150–1158
Yu N, Christiaens O, Liu J, Niu J, Cappelle K, Caccia S, Huvenne H and Smagghe G 2013 Delivery of dsRNA for RNAi in insects: an overview and future directions. Insect Sci. 20 4–14
Yu XD, Liu ZC, Huang SL, Chen ZQ, Sun YW, Duan PF, Ma YZ and Xia LQ 2016 RNAi‐mediated plant protection against aphids. Pest Manag. Science 72 1090–8
Zhang M and Xu WH 2006 Isolation of an eclosion hormone gene from the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera: temporal and spatial distribution of transcripts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 143 351–359
Zhang Q, Nachman RJ and Denlinger DL 2015 Diapause hormone in the Helicoverpa/Heliothis complex: A review of gene expression, peptide structure and activity, analog and antagonist development, and the receptor. Peptides 72 196–201
Zhang X, Mysore K, Flannery E, Michel K, Severson DW, Zhu KY and Duman-Scheel M 2015 Chitosan/Interfering RNA nanoparticle mediated gene silencing in disease vector mosquito larvae. J. Vis. Exp. 97 e52523
Zhao XF, Wang JX, Xu XL, Li ZM and Kang CJ 2004 Molecular cloning and expression patterns of the molt‐regulating transcription factor HHR3 from Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol. Biol. 13 407–412
Zhao J, Zhou Y, Li X, Cai W and Hua H 2017 Silencing of juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase gene (Nljheh) enhances short wing formation in a macropterous strain of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Insect Physiol. 102 18–26
Zhu KY and Palli SR 2020 Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 65 293–311
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Department of Biotechnology (Grant No. BT/AGR/TF/2006), New Delhi, for financial assistance (to MVR). AJ is thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, for the award of Junior and Senior DST-INSPIRE fellowship. We also thank the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for special assistance programme (DRS-III), DST for FIST (Level 2) programme and DU-DST PURSE (Phase II) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Genetic Intervention in Plants: Mechanisms and Benefits.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaiwal, A., Natarajaswamy, K. & Rajam, M.V. RNA silencing of hormonal biosynthetic genes impairs larval growth and development in cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J Biosci 45, 109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00079-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00079-6