Abstract
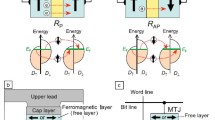
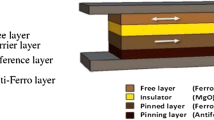
The paper presents theoretical model of a straintronics magnetoelectric random-access memory (MeRAM) storage cell with configurational anisotropy. The MeRAM cell consists of ferromagnetic layers with different orientations of the quasi-uniform magnetization, which is divided into identical magnetic tunnel junction’s ferromagnet|insulator|ferromagnet, in the form of a sandwich of planar layers. The modified theory for magnetic tunnel junction is used to calculate the spin-dependent current and tunnel magnetoresistance like functions of orientations magnetizations of layers.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Bukharaev, A. K. Zvezdin, A. P. Pyatakov, and Yu. K. Fetisov, Phys. Usp. 61, 1175 (2018).
J. Atulasimha and S. Bandyopadhyay, Nanomagnetic and Spintronic Devices for Energy-Efficient Memory and Computing (Wiley, Chichester, 2016).
M. Barangi and P. Mazumder, IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 9, 15 (2015).
C.-Y. Liang, A. Sepulveda, S. Keller, and G. P. Carman, J. Appl. Phys. 119, 113903 (2016).
G. Varvaro and F. Casoli, Ultra-High-Density Magnetic Recording. Storage Materials and Media Designs (CRC, New York, 2016).
K. L. Wang, J. G. Alzate, and P. Khalili Amiri, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 74003 (2013).
S. Salahuddin and S. Datta, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 093503 (2007).
C. Tannous and J. Gieraltowski, Eur. J. Phys. 29, 475 (2008).
J. Atulasimha and S. Bandyopadhyay, Nanomagnetic and Spintronic Devices for Energy-Efficient Memory and Computing (Wiley, New York, 2016).
N. D’Souza, M. Salehi-Fashami, S. Bandyopadhyay, and J. Atulasimha, Nano Lett. 16, 1069 (2016).
D. A. Bizyaev, A. A. Bukharaev, A. P. Chuklanov, and N. I. Nurgazizov, Phys. Solid State 60, 2194 (2018).
A. Bukharaev, D. A. Bizyaev, N. I. Nurgazizov, A. P. Chuklanov, and N. Kh. Useinov, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500, 166315 (2020).
M. Yamamoto and S. Taniguchi, Phys. Chem. Metall. 7, 35 (1955).
P. Talagala, P. S. Fodor, D. Haddad, R. Naik, L. E. Wenger, P. P. Vaishnava, and V. M. Naik, Phys. Rev. B 66, 144426 (2002).
M. J. Donahue and D. G. Porter, OOMMF User’s Guide, Version 1.0 (Natl. Inst. Standards Technol., Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1999). http://math.nist.gov/oommf.
J. de la Venta, S. Wang, J. G. Ramirez, and I. K. Schuller, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 122404 (2013).
A. N. Useinov, R. G. Deminov, N. Kh. Useinov, and L. R. Tagirov, Phys. Status Solidi B 247, 1797 (2010).
A. N. Useinov, C.-H. Lai, N. Kh. Useinov, and L. R. Tagirov, in Novel Magnetic Nanostructures, 1st ed. (Unique Properties Appl., Elsevier, 2018), Chap. 1, p. 373.
J. C. Slonczewski, Phys. Rev. B 39, 6995 (1989).
R. P. Erickson, B. Hathaway, and J. R. Cullen, Phys. Rev. B 47, 2626 (1993).
M. B. Stearns, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 5, 167 (1977).
A. Manchon, N. Ryzhanova, N. Strelkov, A. Vedyayev, and B. Dieny, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19, 165212 (2007).
D. A. Lifatova, A. V. Vedyaev, N. V. Ryzhanova, O. A. Kotel’nikova, M. G. Chshiev, and N. V. Strelkov, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 129, 283 (2019).
E. Camblong, P. M. Levy, and S. Zhang, Phys. Rev. B 51, 16052 (1995).
M. Sharma, S. X. Wang, and J. H. Nickel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 616 (1999).
Funding
The computer simulation was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-02-00204). The elaboration of the theoretical model was partially funded by the Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Useinov, N.K., Chuklanov, A.P., Bizyaev, D.A. et al. Spin-Dependent Electron Transport in MeRAM. Phys. Solid State 62, 1706–1712 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420090310
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783420090310