Abstract
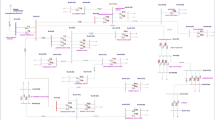
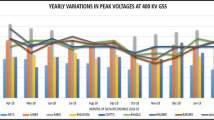
In this research work investigation of reactive power necessity at standard voltage level is practiced. The 39-bus test network modeled in mipower application is a part of Rajasthan power system, attached with North Regional National Grid synchronized at 765 kV voltage level. State power utilities are unable to obtain the profoundness in providing, static or dynamic compensation at multiple voltage available within the grid. Reactive power drawl from the network end is judged and analysed by placing imaginary generator at available voltage level. In Rajasthan power system voltage level arrays from 765 kV to 33 kV and the utilities are puzzled in managing var penetration due to poor estimation. As a result, higher loading levels and abrupt line tripping raises losses and reduces system reliability. The simulation case studies presented herby from the database of financial year 2018-19 will be envisaged by the utilities after evaluation is over. Presently State Load Dispatch Centers deliver instruction to substations to utilize any compensation device available without prior calculation. But this paper underlines a way to access the effects on voltage profile, losses etc. in power system structure after planned var support at optimum voltage level. Case studies over real time network is detailed, to check the observability for a load of 370 MW. The impact of practices followed is observed for the designed network.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kundur P, Balu N J, Lauby M G 1994 Power System Stability and Control. McGraw Hill publications, Professional, New York
Vyas B, Gupta M K and Sharma M P 2020 Distributed volt ampere reactive power compensation of modern power system to control high voltage. Journal of The Institution of Engineers, India Series-B 101, 93–100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-020-00422-3.
Solar Penetration Assessment calculations, Power Map updates, Peak load data obtained from Govt. Of India, Energy Portal, Website. https://energy.rajasthan.gov.in/content/raj/energydepartment/en/home.html. Accessed 20 Jan 2020.
Centre For Strategic & International Studies, “Developing Nations Power factor updates and New RE Integration projects” Website Last Accessed on: 21 Jan. 2020, https://indianstates.csis.org/states/rajasthan/
Singh S 2020 Editor Economic Times, Poor transmission network chokes power supply to Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh Punjab. Website Last Accessed on: 05 Jan. 2020. Online Avail - http://www.ecoti.in/INCKNb.
Dandotia H Kaushik, Sharma M P and Vyas B 2016 Loss reduction of 220 kV substation with optimum reactive power management at 33 kV voltage level a case study, In: IEEE 7th Power India International Conference (PIICON), Bikaner, 2016, pp. 1–6.
Kumar J and Majid C R 2020 Renewable energy for sustainable development in India: current status, future prospects, challenges, employment, and investment opportunities. Energy Sustain Society. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-019-0232-1.
Shabazi H and Karbalaei F 2018 Decentralized Voltage Control of Power Systems Using Multi-Agent Systems. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy. https://doi.org/10.35833/mpce.2018.000628.
Liu Z, Yi Y, Yang J, Tang W, Zhang Y, Xie X, Ji T 2020 Optimal planning and operation of dispatchable active power resources for islanded multi-microgrids under decentralised collaborative dispatch framework. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 14(3):408–422.
Panwar R, Sharma V, Sharma M P and Bhavesh Vyas, 2017 Circulating MVAR control in Rajasthan (India) transmission system. In: 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), 16 February 2017.
Vyas B, Gupta M, Sharma MP and Dandotia 2019 Sustainable Development of Agriculture Feeders by Solar-Var Incorporation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing in Science, Technology and Management (SUSCOM).
Roche R, Lauri F, Blunier B, Miraoui A and Koukam A 2013 Multi-Agent Technology for Power System Control. Chakraborty S, Simões M, Kramer W (eds) Power Electronics for Renewable and Distributed Energy Systems Green Energy and Technology. Springer.
Jing Xie and Chen-Ching Liu 2017 Multi-agent systems and their applications. Journal of International Council on Electrical Engineering 7:1, 188-197. https://doi.org/10.1080/22348972.2017.1348890.
Saini S, Sharma M P, Vyas B and Gupta M 2016 A case study for loss reduction in distribution networks using shunt capacitors. In: IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, 2016, pp. 1–6.
Sharma N, Sharma M P, Singh S and Vyas B 2019 Methodology for Valuation of Shunt Capacitor Bank in Power Grid. In: 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kanpur, India, 2019, pp. 1–7.
Perspective Transmission Plan for Twenty Years 2014–2034, Government of India. By Ministry of Power, Prepared in association with Central Electricity Authority, PGCIL and POSOCO on August 2014.
Manual on Transmission Planning Criteria by Central Electricity Authority, New Delhi, January 2013 [Online] https://cea.nic.in/reports/others/ps/pspa/tr_plg_criteria_manual_jan13.pdf.
Indian Electricity Grid Code by Central Electricity Regulatory Commission, New Delhi, 28 April, 2010 [Online]: https://powermin.nic.in/sites/default/files/uploads/Indian_Electricity_Grid_Code.pdf.
Bhavesh Vyas, Sharma M P and Smriti Jain 2015 Feeder Reconfiguration of distribution network using Minimum Power Flow methodology. In: 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), 17-20 Dec. 2015, E. ISSN: 2325-9418.
Corsi S, Marannino P, Losignore Nand Moreschini G 1994 Coordination Between The Reactive Power Scheduling Function And The hierarchical voltage control of the EHV EnelSystem. Power Engineering Society for Presentation at the IEEE sumer meeting, San Farancisco, July 24–28, 1994.
Bose S 2015 Analysis of Existing Framework for Renewables and RE policy in India, published by Deutshe Gesellschaft, Oct 2015, Indo-German Energy Program, GOI available at mnre.gov.in.
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to thank the research guide and family for the support, along with lab engineers working at Rajasthan Electricity Board for sharing the resources and providing me the opportunity perform research analytics. I gratefully acknowledge the support of SCADA Engineers (RVPN) for data analytics and Dr. Nagraja for Mipower Software support (PRDC), Bangalore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VYAS, B., GUPTA, M.K. & SHARMA, M.P. Assessment of voltage changeability with reactive power source allotment for real time network. Sādhanā 45, 233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01469-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01469-0