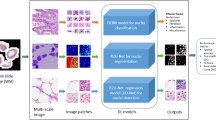
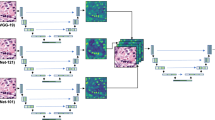
Abstract
Automatic identification of abnormal and normal cells is a critical step in computer-assisted pathology, owing to certain heterogeneous characteristics of cancer cells. However, automated nuclei detection is problematic in unevenly shaped, overlapping and touching nuclei. It is, consequently, essential to detect single and overlapping nuclei and distinguish them from single ones for a reasonable quantitative analysis. Diagnosis is improved by introducing a computer-aided diagnosis system to automatically detect breast cancer tissue nuclei from whole slide images of hematoxylin and eosin stains. We propose a method for the automatic cell nuclei detection, segmentation, and classification of breast cancer using a deep convolutional neural network (Deep-CNN) approach. The main contribution of this work is the detection of nuclei using anisotropic diffusion in a filter and applying a novel multilevel saliency nuclei detection model in ductal carcinoma of breast cancer tissue. The detected nuclei are classified into benign and malignant cells by applying the new Deep-CNN model. Finally, the novel multilevel saliency nuclei detection technique is integrated with the Deep-CNN to produce an nMSDeep-CNN model that turns out to be the most accurate results with very less computation time. The accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of the proposed system are 98.62%, 0.947 and 0.964, respectively. The classification for benign and malignant cells is evaluated by applying 10 fold cross-validation. Thus, the system can be clinically used for an objective, accurate, and rapid diagnosis of abnormal tissue. The effectiveness of the suggested framework is demonstrated through experiments on several datasets.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alom, M.Z., Hasan, M., Yakopcic, C., Taha, T.M., Asari, V.K.: Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06955 (2018)
Araújo, T., Aresta, G., Castro, E., Rouco, J., Aguiar, P., Eloy, C., Polónia, A., Campilho, A.: Classification of breast cancer histology images using convolutional neural networks. PLoS ONE 12(6), e0177544 (2017)
Bajger, M., Ma, F., Williams, S., Bottema, M.: Mammographic mass detection with statistical region merging. In: 2010 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, pp. 27–32. IEEE (2010)
Bandhyopadhyay, S.K., Paul, T.U.: Automatic segmentation of brain tumour from multiple images of brain MRI. Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag. IJAIEM 2(1), 240–8 (2013)
Bargalló, X., Velasco, M., Santamaría, G., Del Amo, M., Arguis, P., Gómez, S.S.: Role of computer-aided detection in very small screening detected invasive breast cancers. J. Digit. Imaging 26(3), 572–577 (2013)
Bartels, D., Hanke, C., Schneider, K., Michel, D., Salamini, F.: A desiccation-related elip-like gene from the resurrection plant craterostigma plantagineum is regulated by light and ABA. EMBO J. 11(8), 2771–2778 (1992)
Bayramoglu, N., Kannala, J., Heikkilä, J.: Deep learning for magnification independent breast cancer histopathology image classification. In: 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 2440–2445. IEEE (2016)
Beevi, K.S., Nair, M.S., Bindu, G.: A multi-classifier system for automatic mitosis detection in breast histopathology images using deep belief networks. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 5, 1–11 (2017)
Breast Cancer Histopathological Database. https://web.inf.ufpr.br/vri/databases/breast-cancer-histopathological-database-breakhis/ (2017)
Cancer Imaging Archive: The cancer imaging archive (TCIA). https://www.cancerimagingarchive.net/histopathology-imaging-on-tcia (2019)
Chen, J.M., Qu, A.P., Wang, L.W., Yuan, J.P., Yang, F., Xiang, Q.M., Maskey, N., Yang, G.F., Liu, J., Li, Y.: New breast cancer prognostic factors identified by computer-aided image analysis of he stained histopathology images. Sci. Rep. 5, 10690 (2015)
Chen, H., Qi, X., Yu, L., Dou, Q., Qin, J., Heng, P.A.: DCAN: deep contour-aware networks for object instance segmentation from histology images. Med. Image Anal. 36, 135–146 (2017)
Chen, J.M., Li, Y., Xu, J., Gong, L., Wang, L.W., Liu, W.L., Liu, J.: Computer-aided prognosis on breast cancer with hematoxylin and eosin histopathology images: a review. Tumor Biol. 39(3), 1010428317694550 (2017)
Deniz, E., Şengür, A., Kadiroğlu, Z., Guo, Y., Bajaj, V., Budak, Ü.: Transfer learning based histopathologic image classification for breast cancer detection. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 6(1), 18 (2018)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep learning. http://www.deeplearningbook.org (2016)
Guo, Y., Dong, H., Song, F., Zhu, C., Liu, J.: Breast cancer histology image classification based on deep neural networks. In: International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, pp. 827–836. Springer (2018)
Hamouda, S.K.M., Wahed, M.E., Alez, R.H.A., Riad, K.: Robust breast cancer prediction system based on rough set theory at national cancer institute of Egypt. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 153, 259–268 (2018)
Hrebień, M., Steć, P., Nieczkowski, T., Obuchowicz, A.: Segmentation of breast cancer fine needle biopsy cytological images. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 18(2), 159–170 (2008)
Hu, K., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Cao, C., Xiao, F., Huang, W., Gao, X.: Automatic segmentation of dermoscopy images using saliency combined with adaptive thresholding based on wavelet transform. Multimedia Tools Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7160-0
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: Multiresunet: rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 121, 74–87 (2020)
Indiana University Health Pathology Lab. https://iuhealth.org/pathology-lab-services (2017)
Irshad, H., Veillard, A., Roux, L., Racoceanu, D.: Methods for nuclei detection, segmentation, and classification in digital histopathology: a review current status and future potential. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 97–114 (2014)
Jiao, Z., Gao, X., Wang, Y., Li, J.: A deep feature based framework for breast masses classification. Neurocomputing 197, 221–231 (2016)
Kapoor, A., Biswas, K., Hanmandlu, M.: An evolutionary learning based fuzzy theoretic approach for salient object detection. Vis. Comput. 33(5), 665–685 (2017)
Kaur, T., Gandhi, T.K.: Deep convolutional neural networks with transfer learning for automated brain image classification. Mach. Vis. Appl. 31, 1–16 (2020)
Keatmanee, C., Chaumrattanakul, U., Kotani, K., Makhanov, S.S.: Initialization of active contours for segmentation of breast cancer via fusion of ultrasound, doppler, and elasticity images. Ultrasonics 94, 438–453 (2017)
Kratz, A., Kettlitz, N., Hotz, I.: Particle-based anisotropic sampling for two-dimensional tensor field visualization. Vis. Model. Vis. (2011). https://doi.org/10.2312/PE/VMV/VMV11/145-152
Li, G., Liu, T., Nie, J., Guo, L., Chen, J., Zhu, J., Xia, W., Mara, A., Holley, S., Wong, S.: Segmentation of touching cell nuclei using gradient flow tracking. J. Microsc. 231(1), 47–58 (2008)
Lim, X., Sugimoto, K., Kamata, S.I.: Nuclei detection based on secant normal voting with skipping ranges in stained histopathological images. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 101(2), 523–530 (2018)
Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Cai, G., Chen, Y., Yun, Z., Feng, Q., Yang, W.: Automatic delineation of ribs and clavicles in chest radiographs using fully convolutional densenets. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 180, 105014 (2019)
Luo, E., Chan, S.H., Nguyen, T.Q.: Image denoising by targeted external databases. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2450–2454. IEEE (2014)
Mahbod, A., Schaefer, G., Ellinger, I., Ecker, R., Smedby, Ö., Wang, C.: A two-stage u-net algorithm for segmentation of nuclei in H&E-stained tissues. In: European Congress on Digital Pathology, pp. 75–82. Springer (2019)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp. 565–571. IEEE (2016)
Murakami, R., Kumita, S., Tani, H., Yoshida, T., Sugizaki, K., Kuwako, T., Kiriyama, T., Hakozaki, K., Okazaki, E., Yanagihara, K., et al.: Detection of breast cancer with a computer-aided detection applied to full-field digital mammography. J. Digit. Imaging 26(4), 768–773 (2013)
Nock, R., Nielsen, F.: Statistical region merging. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(11), 1452–1458 (2004)
Oquab, M., Bottou, L., Laptev, I., Sivic, J.: Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1717–1724 (2014)
Pan, H., Wang, B., Jiang, H.: Deep learning for object saliency detection and image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.01173 (2015)
Pan, X., Li, L., Yang, H., Liu, Z., Yang, J., Zhao, L., Fan, Y.: Accurate segmentation of nuclei in pathological images via sparse reconstruction and deep convolutional networks. Neurocomputing 229, 88–99 (2017)
Paramanandam, M., O Byrne, M., Ghosh, B., Mammen, J.J., Manipadam, M.T., Thamburaj, R., Pakrashi, V.: Automated segmentation of nuclei in breast cancer histopathology images. PLoS ONE 11(9), e0162053 (2016)
Peikari, M., Salama, S., Nofech-Mozes, S., Martel, A.L.: A cluster-then-label semi-supervised learning approach for pathology image classification. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–13 (2018)
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(7), 629–639 (1990)
Petushi, S., Garcia, F.U., Haber, M.M., Katsinis, C., Tozeren, A.: Large-scale computations on histology images reveal grade-differentiating parameters for breast cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 6(1), 14 (2006)
Phung, S.L., Bouzerdoum, A.: Visual and Audio Signal Processing Lab. University of Wollongong, Dubai (2009)
Ragothaman, S., Narasimhan, S., Basavaraj, M.G., Dewar, R.: Unsupervised segmentation of cervical cell images using Gaussian mixture model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 70–75 (2016)
Rashwan, H.A., García, M.A., Puig, D.: Variational optical flow estimation based on stick tensor voting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(7), 2589–2599 (2013)
Rezaeilouyeh, H., Mollahosseini, A., Mahoor, M.H.: Microscopic medical image classification framework via deep learning and shearlet transform. J. Med. Imaging 3(4), 044501 (2016)
Sarkar, R., Acton, S.T.: SDL: saliency-based dictionary learning framework for image similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(2), 749–763 (2018)
Shaikh, T.A., Ali, R., Beg, M.S.: Transfer learning privileged information fuels cad diagnosis of breast cancer. Mach. Vis. Appl. 31(1), 9 (2020)
Shareef, S.R.: Breast cancer detection based on watershed transformation. IJCSI Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 11(1), 237–245 (2014)
Tata Medical Center: https://tmckolkata.com/tmc/ (2017)
Tokime, R.B., Elassady, H., Akhloufi, M.A.: Identifying the cells’ nuclei using deep learning. In: 2018 IEEE Life Sciences Conference (LSC), pp. 61–64. IEEE (2018)
Veta, M., van Diest, P.J., Kornegoor, R., Huisman, A., Viergever, M.A., Pluim, J.P.: Automatic nuclei segmentation in H&E stained breast cancer histopathology images. PLoS ONE 8(7), e70221 (2013)
Veta, M., Pluim, J.P., Van Diest, P.J., Viergever, M.A.: Corrections to “breast cancer histopathology image analysis: a review” [May 14 1400–1411]. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(11), 2819–2819 (2014)
Wan, T., Cao, J., Chen, J., Qin, Z.: Automated grading of breast cancer histopathology using cascaded ensemble with combination of multi-level image features. Neurocomputing 229, 34–44 (2017)
Wang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.H.: Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3183–3192 (2015)
Wang, C.W., Yu, C.P.: Automated morphological classification of lung cancer subtypes using H&E tissue images. Mach. Vis. Appl. 24(7), 1383–1391 (2013)
Wang, P., Hu, X., Li, Y., Liu, Q., Zhu, X.: Automatic cell nuclei segmentation and classification of breast cancer histopathology images. Signal Process. 122, 1–13 (2016)
Wienert, S., Heim, D., Saeger, K., Stenzinger, A., Beil, M., Hufnagl, P., Dietel, M., Denkert, C., Klauschen, F.: Detection and segmentation of cell nuclei in virtual microscopy images: a minimum-model approach. Sci. Rep. 2, 503 (2012)
Wulandari, C.D.R., Wibowo, S.A., Novamizanti, L.: Classification of diabetic retinopathy using statistical region merging and convolutional neural network. In: 2019 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Wireless and Mobile (APWiMob), pp. 94–98. IEEE (2019)
Xu, J., Janowczyk, A., Chandran, S., Madabhushi, A.: A high-throughput active contour scheme for segmentation of histopathological imagery. Med. Image Anal. 15(6), 851–862 (2011)
Yang, W., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Zhong, L., Qin, G., Lu, Z., Feng, Q., Chen, W.: Cascade of multi-scale convolutional neural networks for bone suppression of chest radiographs in gradient domain. Med. Image Anal. 35, 421–433 (2017)
You, Y.L., Xu, W., Tannenbaum, A., Kaveh, M.: Behavioral analysis of anisotropic diffusion in image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 5(11), 1539–1553 (1996)
Yu, C., Chen, H., Li, Y., Peng, Y., Li, J., Yang, F.: Breast cancer classification in pathological images based on hybrid features. Multimedia Tools Appl. 78(15), 21325–21345 (2019)
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1265–1274 (2015)
Zheng, B., Yoon, S.W., Lam, S.S.: Breast cancer diagnosis based on feature extraction using a hybrid of k-means and support vector machine algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(4), 1476–1482 (2014)
Zhou, Y., Chen, H., Xu, J., Dou, Q., Heng, P.A.: IRNET: instance relation network for overlapping cervical cell segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 640–648. Springer (2019)
Zhou, S.K., Greenspan, H., Shen, D.: Deep Learning for Medical Image Analysis. Academic Press, Cambridge (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krithiga, R., Geetha, P. Deep learning based breast cancer detection and classification using fuzzy merging techniques. Machine Vision and Applications 31, 63 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01122-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01122-0