Abstract
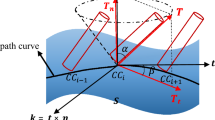
Tool path generation is a fundamental problem in 5-axis CNC machining, which consists of tool orientation planning and cutter-contact (CC) point planning. The planning strategy highly depends on the type of tool cutters. For ball-end cutters, the tool orientation and CC point location can be planned separately; while for flat end cutters, the two are highly dependent on each other. This paper generates a smooth tool path of workpiece surfaces for flat end mills from two stages: Computing smooth tool orientations on the surface without gouging and collisions and then designing the CC point path. By solving the tool posture optimization problem the authors achieve both the path smoothness and the machining efficiency. Experimental results are provided to show the effectiveness of the method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loney G C and Ozsoy T M, NC machining of free form surfaces, Computer-Aided Design, 1987, 19(2): 85–90.
Elber G and Cohen E, Toolpath generation for freeform surface models, Computer-Aided Design, 1994, 26(6): 490–496.
Han Z L and Yang D C H, Iso-phote based tool-path generation for machining free-form surfaces, Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, ASME Transactions, 1999, 121(4): 656–664.
Ding S, Mannan M A, Poo A N, et al., Adaptive iso-planar tool path generation for machining of free-form surfaces, Computer-Aided Design, 2003, 35(2): 141–153.
Suresh K and Yang D C H, Constant scallop height machining of free form surfaces, Journal of Engineering for Industry, ASME Transactions, 1994, 116(2): 253–259.
Lin R S and Koren Y, Efficient tool-path planning for machining free-form surfaces, Journal of Engineering for Industry, ASME Transactions, 1996, 118(1): 20–28.
Zou Q and Zhao J B, Iso-parametric tool-path planning for point clouds, Computer-Aided Design, 2013, 45(11): 1459–1468.
Lee Y S, Non-isoparametric tool path planning by machining strip evaluation for 5-axis sculptured surface machining, Computer-Aided Design, 1998, 30(7): 559–570.
Hu P C, Chen L F, and Tang K, Efficiency-optimal iso-planar tool path generation for five-axis finishing machining of freeform surfaces, Computer-Aided Design, 2017, 83: 33–50.
Cheng M, A new iso-scallop height tool path planning method in threedimensional space, Computer Aided Drafting, Design and Manufacturing, 2012, 22(3): 35–42.
Guo J X, Zhang Q, Gao X S, et al., Time optimal feedrate generation with confined tracking error based on linear programming, Journal of Systems Science & Complexity, 2013, 28(1): 80–95.
Zou Q, Zhang J Y, Deng B L, et al., Iso-level tool path planning for free-form surfaces, Computer-Aided Design, 2014, 53: 117–125
Zhang K and Tang K, Optimal five-axis tool path generation algorithm based on double scalar fields for freeform surfaces, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 83: 1503–1514.
Liu X, Li Y G, Ma S B, et al., A tool path generation method for freeform surface machining by introducing the tensor property of machining strip width, Computer-Aided Design, 2015, 66: 1–13.
Kumazawa G H, Feng H Y, and Fard M J B, Preferred feed direction field: A new tool path generation method for efficient sculptured surface machining, Computer-Aided Design, 2015, 67–68: 1–12.
Wang Y, Yan C Y, Yang J Z, et al., Tool path generation algorithm based on covariant field theory and cost functional optimization and its applications in blade machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 90(1–4): 927–943.
Chiou C J and Lee Y S, A machining potential field approach to tool path generation for multi-axis sculptured surface machining, Computer-Aided Design, 2002, 34: 357–371.
Lozano-Perez T and Wesley M A, An algorithm for planning collision-free paths among polyhedral obstacles, Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(10): 560–570.
Lozano-Perez T, Spatial planning: A configuration space approach, IEEE Transactions on Computers, 1983, 100(2): 108–120.
Bajaj C and Kim M S, Generation of configuration space obstacles: The case of moving algebraic curves, Algorithmica, 4 (2): 157–172.
Morishige K, Kase Y, and Takeuchi Y, Collision-free tool path generation using 2-dimensional C-space for 5-axis control machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 1997, 13: 393–400.
Chen L, Xu K, and Tang K, Collision-free tool orientation optimization in five-axis machining of bladed disk, Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2015, 2: 197–205.
Lacharnay V, Lavernhe S, Tournier C, et al., A physically-based model for global collision avoidance in 5-axis point milling, Computer-Aided Design, 2015, 64: 1–8.
Mi Z P, Yuan C M, Ma X H, et al., Tool orientation optimization for 5-axis machining with C-space method, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, 88(5–8): 1243–1255.
Jun C S, Cha K, and Lee Y S, Optimizing tool orientations for 5-axis machining by configuration-space search method, Computer-Aided Design, 2003, 35(6): 549–566.
Lu J, Cheatham R, Jensen C G, et al., A three-dimensional configuration-space method for 5-axis tessellated surface machining, Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf., 2008, 21(5): 550–568.
Lin Z W, Fu J Z, Shen H Y, et al., Non-singular tool path planning by translating tool orientations in C-space, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2004, 71(9–12): 1835–1848.
Wang N and Tang K, Automatic generation of gouge-free and angular-velocity-compliant five-axis toolpath, Computer-Aided Design, 2007, 39(10): 841–852.
Castagnetti C, Duc E, and Ray P, The domain of admissible orientation concept: A new method for five-axis tool path optimisation, Computer-Aided Design, 2008, 40: 938–950.
Kim Y J, Elber G, Bartoň M, et al., Precise gouging-free tool orientations for 5-axis CNC machining, Computer-Aided Design, 2015, 58: 220–229.
Li X Y, Lee C H, Hu P C, et al., Cutter partition-based tool orientation optimization for gouge avoidance in five-axis machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 95(5–8): 1–17.
Piegl L and Tiller W, The NURBS Book, 2nd Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1997.
Radzevich S P, Kinematic Geometry of Surface Machining, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2008.
Giri V, Bezbaruah D, Bubna P, et al., Selection of master cutter paths in sculptured surface machining by employing curvature principle, International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2005, 45(10): 1202–1209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11688101, 61872332, Beijing National Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. Z190004, National Center for Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Sciences, and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor-in-Chief GAO Xiao-Shan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, C., Mi, Z., Jia, X. et al. Tool Orientation Optimization and Path Planning for 5-Axis Machining. J Syst Sci Complex 34, 83–106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9270-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-020-9270-1