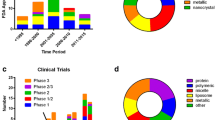
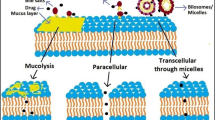
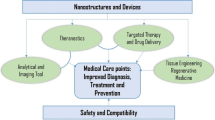
Abstract
Many natural substances are efficient in vitro and in vivo for the treatment of various disorders. However, treatment is often limited by their low bioavailability, water solubility and permeation. As a consequence, drugs are administered frequently and in large doses. There is therefore a need for techniques to enhance the solubility, permeability and the stability. Here, we review methods to improve solubility using particle engineering, complexation, solid dispersion, solubilization, chemical modifications and use of nanocarriers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- US FDA:
-
United State Food and Drug Administration
- CD:
-
Cyclodextrin
- HP-β-CD:
-
Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
- PDI:
-
Polydispersity index
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- SLN:
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles
- NLC:
-
Nanostructured lipid carrier
References
Ahire E, Thakkar S, Darshanwad M, Misra M (2018) Parenteral nanosuspensions: a brief review from solubility enhancement to more novel and specific applications. Acta Pharm Sin B 8(5):733–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2018.07.011
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, Samiei M, Kouhi M, Nejati-Koshki K (2013) Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 8(1):102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276x-8-102
Anwer MK, Al-Mansoor MA, Jamil S, Al-Shdefat R, Ansari MN, Shakeel F (2016) Development and evaluation of PLGA polymer based nanoparticles of quercetin. Int J Biol Macromol 92:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.002
Atanacković M, Poša M, Heinle H, Gojković-Bukarica L, Cvejić J (2009) Solubilization of resveratrol in micellar solutions of different bile acids. Colloids Surf B 72(1):148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.03.029
Barras A, Mezzetti A, Richard A, Lazzaroni S, Roux S, Melnyk P, Betbeder D, Monfilliette-Dupont N (2009) Formulation and characterization of polyphenol-loaded lipid nanocapsules. Int J Pharm 379(2):270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.05.054
Behera A, Sahoo S, Patil S (2010) Enhancement of solubility: a pharmaceutical overview. Der Pharmacia Lettre 2(2):310–318
Bhadoriya SS, Mangal A, Madoriya N, Dixit P (2011) Bioavailability and bioactivity enhancement of herbal drugs by “Nanotechnology”: a review. J Curr Pharm Res 8:1–7
Bhardwaj A, Dwivedi H, Kymonil KM, Pareek A, Upadhyay SC, Tripathi CB, Saraf SA (2016) Solubility enhancement of Boswellia serrata Roxb ex Colebr extract through a self dispersible lipidic formulation approach. Ind J Nat Prod Resour (IJNPR) Formerly Natural Product Radiance (NPR) 7(1):9–18
Boy HIA, Rutilla AJH, Santos KA, Ty AMT, Yu AI, Mahboob T, Tangpoong J, Nissapatorn V (2018) Recommended medicinal plants as source of natural products: a review. Digital Chinese Medicine 1(2):131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-3777(19)30018-7
Cao R, Zhao Y, Zhou Z, Zhao X (2018) Enhancement of the water solubility and antioxidant activity of hesperidin by chitooligosaccharide. J Sci Food Agric 98(6):2422–2427. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8734
Cao R, Li X, Zhou Z, Zhao Z (2019) Synthesis and biophysical analysis of Naringin-Chitooligosaccharide complex. Natl Pro Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1628752
Challa R, Ahuja A, Ali J, Khar R (2005) Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 6(2):E329–E357. https://doi.org/10.1208/pt060243
Chella N, Shastri NR (2017) Lipid carriers: role and applications in nano drug delivery. In: Jana S, Jana S (eds) Particulate technology for delivery of therapeutics. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 253–289
Cho E, Jung S (2015) Supramolecular complexation of carbohydrates for the bioavailability enhancement of poorly soluble drugs. Molecules 20(10):19620–19646. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201019620
Coimbra M, Isacchi B, van Bloois L, Torano JS, Ket A, Wu X, Broere F, Metselaar JM, Rijcken CJ, Storm G (2011) Improving solubility and chemical stability of natural compounds for medicinal use by incorporation into liposomes. Int J Pharm 416(2):433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.01.056
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2005) Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol 100(1):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.011
Craig DQM (2002) The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int J Pharm 231(2):131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00891-2
Dai L, Wang L, Deng L, Liu J, Lei J, Li D, He J (2014) Novel multiarm polyethylene glycol-dihydroartemisinin conjugates enhancing therapeutic efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 4:5871. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05871
Del Valle EM (2004) Cyclodextrins and their uses: a review. Process Biochem 39(9):1033–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00258-9
Dian L, Yu E, Chen X, Wen X, Zhang Z, Qin L, Wang Q, Li G, Wu C (2014) Enhancing oral bioavailability of quercetin using novel soluplus polymeric micelles. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):684. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-684
Esmaili M, Ghaffari SM, Moosavi-Movahedi Z, Atri MS, Sharifizadeh A, Farhadi M, Yousefi R, Chobert J-M, Haertlé T, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2011) Beta casein-micelle as a nano vehicle for solubility enhancement of curcumin; food industry application. LWT Food Sci Technol 44(10):2166–2172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2011.05.023
Etuk E (2006) A review of medicinal plants with hypotensive or antihypertensive effects. J Med Sci 6:894–900. https://doi.org/10.3923/jms.2006.894.900
Fang Y-P, Lin Y-K, Su Y-H, Fang J-Y (2011) Tryptanthrin-loaded nanoparticles for delivery into cultured human breast cancer cells, MCF7: the effects of solid lipid/liquid lipid ratios in the inner core. Chem Pharm Bull 59(2):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.59.266
Gnananath K, Nataraj KS, Rao BG (2017) Phospholipid complex technique for superior bioavailability of phytoconstituents. Adv Pharm Bull 7(1):35
Greenwald RB, Gilbert CW, Pendri A, Conover CD, Xia J, Martinez A (1996) Drug delivery systems: water soluble taxol 2‘-poly(ethylene glycol) ester prodrugs design and in vivo effectiveness. J Med Chem 39(2):424–431. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm950475e
Gunasekaran T, Haile T, Nigusse T, Dhanaraju MD (2014) Nanotechnology: an effective tool for enhancing bioavailability and bioactivity of phytomedicine. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4:S1–S7. https://doi.org/10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C980
Guo Z (2017) The modification of natural products for medical use. Acta Pharm Sinica B 7(2):119–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.06.003
Hani U, Shivakumar H (2014) Solubility enhancement and delivery systems of curcumin a herbal medicine: a review. Curr Drug Deli 11(6):792–804. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201811666140825130003
Hermanson GT (2013) Bioconjugate techniques. Academic Press, Cambridge
Hernandez-Patlan D, Solis-Cruz B, Cano-Vega MA, Beyssac E, Garrait G, Hernandez-Velasco X, Lopez-Arellano R, Tellez G, Rivera-Rodriguez GR (2019) Development of chitosan and alginate nanocapsules to increase the solubility, permeability and stability of curcumin. J Pharm Innov 14(2):132–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-018-9341-1
Ibrahim AH, Rosqvist E, Smått J-H, Ibrahim HM, Ismael HR, Afouna MI, Samy AM, Rosenholm JM (2019) Formulation and optimization of lyophilized nanosuspension tablets to improve the physicochemical properties and provide immediate release of silymarin. Int J Pharm 563:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.03.064
Jachak SM, Saklani A (2007) Challenges and opportunities in drug discovery from plants. Curr Sci pp 1251–1257
Jain H, Chella N (2020) Solubility enhancement techniques for natural product delivery. In: Saneja A, Panda A, Lichtfouse E (eds) Sustainable agriculture reviews: sustainable agriculture reviews, vol 43. Springer, Cham, pp 33–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41838-0_2
Jeengar MK, Rompicharla SVK, Shrivastava S, Chella N, Shastri NR, Naidu VGM, Sistla R (2016) Emu oil based nano-emulgel for topical delivery of curcumin. Int J Pharm 506(1):222–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.04.052
Jeong D, Choi JM, Choi Y, Jeong K, Cho E, Jung S (2013) Complexation of fisetin with novel cyclosophoroase dimer to improve solubility and bioavailability. Carbohyd Polym 97(1):196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.066
Kanaze F, Kokkalou E, Niopas I, Barmpalexis P, Georgarakis E, Bikiaris D (2010) Dissolution rate and stability study of flavanone aglycones, naringenin and hesperetin, by drug delivery systems based on polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) nanodispersions. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 36(3):292–301. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639040903140589
Karadag A, Ozcelik B, Huang Q (2014) Quercetin nanosuspensions produced by high-pressure homogenization. J Agric Food Chem 62(8):1852–1859
Kawabata Y, Wada K, Nakatani M, Yamada S, Onoue S (2011) Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: basic approaches and practical applications. Int J Pharm 420(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.032
Keck CM, Müller RH (2006) Drug nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs produced by high pressure homogenisation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 62(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2005.05.009
Khadka P, Ro J, Kim H, Kim I, Kim JT, Kim H, Cho JM, Yun G, Lee J (2014) Pharmaceutical particle technologies: an approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J Pharm Sci 9(6):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.05.005
Khan AW, Kotta S, Ansari SH, Sharma RK, Ali J (2015) Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of grapefruit flavonoid Naringenin by solid dispersion utilizing fourth generation carrier. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 41(5):772–779. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2014.902466
Kim Y, Shinde VV, Jeong D, Choi Y, Jung S (2019) Solubility enhancement of atrazine by complexation with cyclosophoraose isolated from rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1. Polymers 11(3):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030474
Klayman DL (1985) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science 228(4703):1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3887571
Koroleva M, Yurtov E (2012) Nanoemulsions: the properties, methods of preparation and promising applications. Russ Chem Rev 81:21. https://doi.org/10.1070/RC2012v081n01ABEH004219
Kuche K, Bhargavi N, Dora CP, Jain S (2019) Drug-phospholipid complex—a go through strategy for enhanced oral bioavailability. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 20(2):43. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1252-4
Kwon SH, Kim SY, Ha KW, Kang MJ, Huh JS, Kim YM, Park YM, Kang KH, Lee S, Chang JY (2007) Pharmaceutical evaluation of genistein-loaded pluronic micelles for oral delivery. Arch Pharmacal Res 30(9):1138–1143. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980249
Lee S, Seo D-h, Park H-l, Choi Y, Jung S (2003) Solubility enhancement of a hydrophobic flavonoid, luteolin by the complexation with cyclosophoraoses isolated from Rhizobium meliloti. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 84(3):201. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026075215921
Lee J-S, Kim ES, Lee HG (2017) Improving the water solubility and antimicrobial activity of silymarin by nanoencapsulation. Colloids Surf B 154:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.03.004
Li B, Harich K, Wegiel L, Taylor LS, Edgar KJ (2013) Stability and solubility enhancement of ellagic acid in cellulose ester solid dispersions. Carbohyd Polym 92(2):1443–1450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.051
Li L, Liu Y, Xue Y, Zhu J, Wang X, Dong Y (2017) Preparation of a ferulic acid–phospholipid complex to improve solubility, dissolution, and B16F10 cellular melanogenesis inhibition activity. Chem Cent J 11(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-017-0254-8
Liu K, Dai L, Li C, Liu J, Wang L, Lei J (2016) Self-assembled targeted nanoparticles based on transferrin-modified eight-arm-polyethylene glycol–dihydroartemisinin conjugate. Sci Rep 6(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29461
Lodhi G, Kim Y-S, Hwang J-W, Kim S-K, Jeon Y-J, Je J-Y, Ahn C-B, Moon S-H, Jeon B-T, Park P-J (2014) Chitooligosaccharide and its derivatives: preparation and biological applications. BioMed Res Int 2014
Loftsson T, Duchêne D (2007) Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int J Pharm 329(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.10.044
Loh ZH, Samanta AK, Heng PWS (2015) Overview of milling techniques for improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Asian J Pharm Sci 10(4):255–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.12.006
Manju S, Sreenivasan K (2011) Conjugation of curcumin onto hyaluronic acid enhances its aqueous solubility and stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 359(1):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.03.071
Martinez MN, Amidon GL (2002) A mechanistic approach to understanding the factors affecting drug absorption: a review of fundamentals. J Clin Pharmacol 42(6):620–643. https://doi.org/10.1177/00970002042006005
Md S, Kit B, Jagdish S, David DJ, Pandey M, Chatterjee LA (2018) Development and in vitro evaluation of a zerumbone loaded nanosuspension drug delivery system. Crystals 8(7):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8070286
Mehnert W, Mäder K (2001) Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv Drug Del Rev 47(2):165–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00105-3
Mishra PR, Al Shaal L, Müller RH, Keck CM (2009) Production and characterization of Hesperetin nanosuspensions for dermal delivery. Int J Pharm 371(1–2):182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.12.030
Müller RH, Mäder K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50(1):161–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(00)00087-4
Murdande SB, Pikal MJ, Shanker RM, Bogner RH (2011) Aqueous solubility of crystalline and amorphous drugs: challenges in measurement. Pharm Dev Technol 16(3):187–200. https://doi.org/10.3109/10837451003774377
Nacsa Á, Ambrus R, Berkesi O, Szabó-Révész P, Aigner Z (2008) Water-soluble loratadine inclusion complex: analytical control of the preparation by microwave irradiation. J Pharm Biomed Anal 48(3):1020–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.07.001
Narayana L, Chella N, Kumar D, Shastri NR (2015) Design of a novel type IV lipid-based delivery system for improved delivery of drugs with low partition coefficient. J Liposome Res 25(4):325–333. https://doi.org/10.3109/08982104.2015.1010544
Omari-Siaw E, Wang Q, Sun C, Gu Z, Zhu Y, Cao X, Firempong CK, Agyare R, Xu X, Yu J (2016) Tissue distribution and enhanced in vivo anti-hyperlipidemic-antioxidant effects of perillaldehyde-loaded liposomal nanoformulation against Poloxamer 407 induced hyper lipidemia. Int J Pharm 513(1–2):68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.08.042
Pandita D, Kumar S, Poonia N, Lather V (2014) Solid lipid nanoparticles enhance oral bioavailability of resveratrol, a natural polyphenol. Food Res Int 62:1165–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.05.059
Patel VR, Agrawal Y (2011) Nanosuspension: an approach to enhance solubility of drugs. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2(2):81. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.82950
Qin J, Chen D, Lu W, Xu H, Yan C, Hu H, Chen B, Qiao M, Zhao X (2008) Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of liposomal ferulic acid in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34(6):602–608
Rabinow BE (2004) Nanosuspensions in drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(9):785–796. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1494
Rangel-Yagui CO, Pessoa A Jr, Tavares LC (2005) Micellar solubilization of drugs. J Pharm Pharm Sci 8(2):147–163
Ren T, Hu M, Cheng Y, Shek TL, Xiao M, Ho NJ, Zhang C, Leung SSY, Zuo Z (2019) Piperine-loaded nanoparticles with enhanced dissolution and oral bioavailability for epilepsy control. Eur J Pharm Sci 137:104988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2019.104988
Rishton GM (2008) Natural products as a robust source of new drugs and drug leads: past successes and present day issues. Am J Cardiol 101(10):S43–S49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.02.007
Saoji SD, Raut NA, Dhore PW, Borkar CD, Popielarczyk M, Dave VS (2016) Preparation and evaluation of phospholipid-based complex of standardized centella extract (SCE) for the enhanced delivery of phytoconstituents. AAPS J 18(1):102–114. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9837-2
Savjani KT, Gajjar AK, Savjani JK (2012) Drug solubility: importance and enhancement techniques. ISRN Pharm. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/195727
Serajuddin AT (2007) Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59(7):603–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.010
Shao B, Cui C, Ji H, Tang J, Wang Z, Liu H, Qin M, Li X, Wu L (2015) Enhanced oral bioavailability of piperine by self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: in vitro, in vivo and in situ intestinal permeability studies. Drug Deliv 22(6):740–747. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2014.898109
Sharma D (2016) Solubility enhancement strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs in solid dispersions: a review. Asian J Pharm 1(1)
Shen B, Chen H, Shen C, Xu P, Li J, Shen G, Yuan H, Han J (2015) Hepatoprotective effects of lignans extract from Herpetospermum caudigerum against CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 164:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.044
Shikov AN, Pozharitskaya ON, Miroshnyk I, Mirza S, Urakova IN, Hirsjärvi S, Makarov VG, Heinämäki J, Yliruusi J, Hiltunen R (2009) Nanodispersions of taxifolin: impact of solid-state properties on dissolution behavior. Int J Pharm 377(1–2):148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.04.044
Shulman M, Cohen M, Soto-Gutierrez A, Yagi H, Wang H, Goldwasser J, Lee-Parsons CW, Benny-Ratsaby O, Yarmush ML, Nahmias Y (2011) Enhancement of naringenin bioavailability by complexation with hydroxypropoyl-β-cyclodextrin. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18033. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018033
Siddiqui A, Iram F, Siddiqui S, Sahu K (2014) Role of natural products in drug discovery process. Int J Drug Dev Res 6:172–204
Suvarna V, Gujar P, Murahari M (2017) Complexation of phytochemicals with cyclodextrin derivatives—an insight. Biomed Pharmacother 88:1122–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.157
Teixeira CCC, Mendonça LM, Bergamaschi MM, Queiroz RHC, Souza GEP, Antunes LMG, Freitas LAP (2016) Microparticles containing curcumin solid dispersion: stability, bioavailability and anti-inflammatory activity. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 17(2):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-015-0337-6
Tommasini S, Raneri D, Ficarra R, Calabrò ML, Stancanelli R, Ficarra P (2004) Improvement in solubility and dissolution rate of flavonoids by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. J Pharm Biomed Anal 35(2):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0731-7085(03)00647-2
Tønnesen HH, Másson M, Loftsson T (2002) Studies of curcumin and curcuminoids XXVII Cyclodextrin complexation: solubility, chemical and photochemical stability. Int J Pharm 244(1–2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00323-x
Tran TH, Guo Y, Song D, Bruno RS, Lu X (2014) Quercetin-containing self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for improving oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci 103(3):840–852. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23858
Upreti M, Strassburger K, Chen YL, Wu S, Prakash I (2011) Solubility enhancement of steviol glycosides and characterization of their inclusion complexes with gamma-cyclodextrin. Int J Mol Sci 12(11):7529–7553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12117529
Verma S, Gokhale R, Burgess DJ (2009) A comparative study of top-down and bottom-up approaches for the preparation of micro/nanosuspensions. Int J Pharm 380(1–2):216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.07.005
Yen C-C, Chen Y-C, Wu M-T, Wang C-C, Wu Y-T (2018) Nanoemulsion as a strategy for improving the oral bioavailability and anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide. Int J Nanomed 13:669. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S154824
Yu D, Peng P, Dharap SS, Wang Y, Mehlig M, Chandna P, Zhao H, Filpula D, Yang K, Borowski V (2005) Antitumor activity of poly (ethylene glycol)–camptothecin conjugate: the inhibition of tumor growth in vivo. J Contr Rel 110(1):90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.09.050
Zhang J, Huang Y, Liu D, Gao Y, Qian S (2013a) Preparation of apigenin nanocrystals using supercritical antisolvent process for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement. Euro J Pharma Sci 48(4–5):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2012.12.026
Zhang Q-F, Nie H-C, Shangguang X-C, Yin Z-P, Zheng G-D, Chen J-G (2013b) Aqueous solubility and stability enhancement of astilbin through complexation with cyclodextrins. J Agric Food Chem 61(1):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304398v
Zhang K, Zhang M, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Gu L, Hu G, Chen X, Jia J (2016a) Development of quercetin-phospholipid complex to improve the bioavailability and protection effects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. Fitoterapia 113:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2016.07.008
Zhang Y, Li Z, Zhang K, Yang G, Wang Z, Zhao J, Hu R, Feng N (2016b) Ethyl oleate-containing nanostructured lipid carriers improve oral bioavailability of trans-ferulic acid ascompared with conventional solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 511(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.06.131
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, H., Chella, N. Methods to improve the solubility of therapeutical natural products: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19, 111–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01082-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01082-x