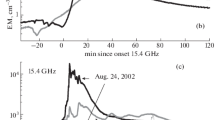
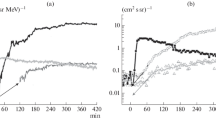
The hypothesis of two phases of charged particle acceleration in solar flares is well known, with subrelativistic electrons accelerated in the first phase and relativistic electrons and protons in the second. Both phases are distinguished in the solar proton events and their parent flares of December 26, 2001 (M7.1), November 2, 2003 (X8.3), and August 9, 2011 (X6.9), while in the interplanetary space only electrons were observed from the first phase and electrons and protons from the second. The temporal profiles of the electrons and protons from the second phase are similar; hence, it is concluded that the relativistic electrons and protons observed in the interplanetary space are predominantly accelerated in flares, rather than in the shock front of a coronal mass ejection. Most likely a stochastic acceleration mechanism is realized in flares where protons and electrons gain energy in many elementary events over the entire duration of the flare which lasts much longer than an elementary event. To ensure consistency of a stochastic acceleration process with the existence of two phases in solar flares it is necessary to consider gyrosynchronous radiative electron losses in the second phase which can be neglected in the first phase. The energy of the accelerated protons in the first phase is small for their detection in processes taking place on the sun, but in the second phase it may be sufficient to produce gamma lines, both nuclear and from pion decay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. B. Struminsky, Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Physics 83, 538 (2019).
I. Yu. Grigor’eva and A. B. Struminsky, Proc. XXII All-Russian Conf. on Solar Physics “Solar and Solar-earth Physics-2018,” A. V. Stepanov and Yu. A. Nagovitsyin, eds., GAO RAN, St. Petersburg 123 (2018).
I. Yu. Grigor’eva, A. B. Struminsky, Proc. XXII All-Russian Conf. on Solar Physics “Solar and Solar-earth Physics-2018,” A. V. Stepanov and Yu. A. Nagovitsyin, eds.GAO RAN, St. Petersburg 127 (2018).
J. P. Wild, S. F. Smerd, and A. A. Weiss, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1, 291 (1963).
R. Ramaty, S. A. Colgate, G. A. Dulk, et al., Proc. of the 2nd SKYLAB Workshop on Solar Flares. 117 (1978).
A. Y. Shih, R. P. Lin, and D. M. Smith, Astrophys. J. 698, 152 (2009).
A. B. Struminsky, I. Yu. Grigor’eva, Yu. I. Logachev, et al., Plasma Phys. Rep. 46, 174 (2020).
A. Benz, Solar Phys. 96, 357 (1985).
L. Vlahos, Solar Phys. 121, 431 (1989).
J. A. Miller, P. J. Cargill, A. Emslie, et al., J. Geophys. Res. 102, 14631 (1997).
Z. Svestka, Solar Phys. 13, 471 (1970).
V. V. Grechnev and A. A. Kochanov, Solar Phys. 291, 3705 (2016).
V. V. Grechnev, A. M. Uralov, V. I. Kiselev, et al., Solar Phys. 292, 3 (2017).
V. V. Grechnev, V. I. Kiselev, A. M. Uralov, et al., Solar Phys. 292, 102 (2017).
A. B. Struminsky, Geomagnetism Aeronomy 53, 843 (2013).
I. N. Sharykin, A. B. Struminsky, and I. V. Zimovets, Astron. Lett. 41, 53 (2015).
E. W. Cliver, S. W. Kahler, M. A. Shea, et al., Astrophys. J. 260, 362 (1982).
A. B. Struminsky and I. V. Zimovets, 21st ECRS, Kosice, Slovakia, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 237 (2009).
D. V. Reames, Astrophys. J. 706, 844 (2009).
E. I. Daibog, V. G. Stolpovskii, V. V. Mel’nikov, et al., Soviet Astron. Lett. 15, 432 (1989).
L. G. Kocharov, G. A. Kovaltsov, G. E. Kocharov, et al., Solar Phys. 150, 267 (1994).
V. V. Akimov, P. Ambro•, Belov A.V., et al., Solar Phys. 166, 107 (1996).
M. J. Aschwanden, Space Sci. Rev. 171, 3 (2012).
S. W. Kahler, Space Sci. Rev. 129, 359 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Astrofizika, Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 437-449 (August 2020)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struminsky, A.B., Grigorieva, I.Y., Logachev, Y.I. et al. Two Phases of Solar Flares and a Stochastic Mechanism for Acceleration of Electrons and Protons. Astrophysics 63, 388–398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-020-09643-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10511-020-09643-2