Abstract
Key Message
First study of mepiquat chloride as a growth regulator in Eucalyptus. Application of mepiquat chloride in Eucalyptus clones at planting may promote drought resistance.
Abstract
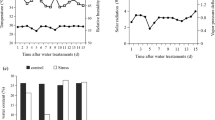
The reduction of available areas has pushed Eucalyptus away to marginal areas with low water availability. Management practices such as the application of growth retardants may have potential to modify plant morphological and physiological features, increasing their drought tolerance. Trying to understand the drought tolerance mechanisms of Eucalyptus clones, the objective of this work was to evaluate the effects of different mepiquat chloride (MC) concentrations to Eucalyptus clones on morphological and physiological changes. Commercial clones of E. grandis × E. urophylla hybrid were planted in 20 L pots in a complete randomized block design with eight replications and four treatments. The treatments consisted of three concentrations of MC: 250, 500 and 1000 mg L−1 of MC. The control treatment consisted of a non-MC application (0 mg L−1 of MC). Evaluations of morphological and physiological parameters were carried out for 35 days after the MC application. Results indicated morphophysiological changes after the MC application. Eucalyptus clones increased root dry mass (RDM), total dry mass (TDM), number of leaves and secondary branches, and decreased height. MC application modified the physiological plant system improving intrinsic water use efficiency (WUEi) and SPAD index, and decreasing transpiration rates (E) and stomatal conductance (gs). RDM, TDM, E, WUEi and SPAD index improved when 250 and 500 mg L−1 MC concentration were applied. Our results suggest that MC application may promote drought resistance to Eucalyptus clones.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard P, Renou JP, Berthomé R, Harberd NP, Genschik P (2008) Plant DELLAs restrain growth and promote survival of adversity by reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species. Curr Biol 18:656–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.04.034
Alvares CA, Stape JL, Sentelhas PC, de Moraes G, Leonardo J, Sparovek G (2013) Köppen's climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol Z 22(6):711–728. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0507
Armstrong EL, Nicol HI (1991) Reducing height and lodging in rapeseed with growth-regulators. Aust J Exp Agric 31(2):245–250. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA9910245
Awati MG, D'Souza GF, Renukaswamy NS, Venkataramanan D, Anand CG (2007) Influence of foliar application of mepiquat chloride and ethephon on flowering and crop yield in arabica coffee. J Coffee Res 35:1–9
Berova M, Zlatev Z (2003) Physiological response of paclobutrazol-treated triticale plants to water stress. Biol Plant 46:133–136. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022360809008
Bongers FJ, Olmo M, Lopez-Iglesias B, Anten NPR, Villar R (2017) Drought responses, phenotypic plasticity and survival of Mediterranean species in two different microclimatic sites. Plant Biol 19:386–395. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.12544
Chorbadjian RA, Bonello P, Herms DA (2011) Effect of the growth regulator paclobutrazol and fertilization on defensive chemistry and herbivore resistance of austrian pine (Pinus nigra) and paper birch (Betula papyrifera). Aust J Forensic Sci 37(6):278–287
Colebrook EH, Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (2014) The role of gibberellin signalling in plant responses to abiotic stress. J Exp Biol 217:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.089938
Debaeke P, Rouet P, Justes E (2006) Relationship between the normalized SPAD index and the nitrogen nutrition index: application to durum wheat. J Plant Nutr 29:75–92. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582009000200022
Driessche RVD (1996) Drought resistance and water use efficiency of conifer seedlings treated with paclobutrazol. New Forest 11:65–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034893
Echer FR, Rosolem CA (2012) Plant growth regulator losses in cotton as affected by adjuvants and rain. Ciência Rural 42(12):2138–2144. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782012005000120
Eliasson MK, Beyl CA, Barker PA (1994) In vitro responses and acclimatization of Prunus serotina with paclobutrazol. J Plant Growth Regul 13:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF001963
Espindula MC, Rocha VS, Grossi JAS, Souza MA, Souza LT, Favarato LF (2009) Use of growth retardants in wheat. Planta Daninha 27:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582009000200022
Fernández JA, Balenzategui L, Banon S, Franco JA (2006) Induction of drought tolerance by paclobutrazol and irrigation deficit in Phillyrea angustifolia during the nursery period. Sci Hortic 107(3):277–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2005.07.008
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations – FAO (2015) The state of food insecurity in the world 2015. In: Meeting the 2015 international hunger targets: taking stock of uneven progress. Rome: FAO; 2015
Gao J, Hofstra G, Fletcher RA (1988) Anatomical changes induced by triazoles in wheat seedlings. Can J Bot 66:1178–1185. https://doi.org/10.1139/b88-168
Gao Y, Zeng Q, Guo J, Cheng J, Ellis BE, Chen JG (2007) Genetic characterization reveals no role for the reported ABA receptor, GCR2, in ABA control of seed germination and early seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03291.x
Gausman HW, Walter H, Stein E, Rittig, FR, Leamer RW, Escobar DE, Rodriguez RR (1979) Leaf CO2 uptake and chlorophyll ratios of PIX-treated cotton. In: Proceedings-Plant Growth Regulator Working Group.
Gilley A, Fletcher RA (1998) Gibberellin antagonizes paclobutrazol-induced stress protection in wheat seedlings. J Plant Physiol 153:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(98)80066-7
Gómez MB, Castro PA, Mignone C, Bertero HD (2011) Can yield potential be increased by manipulation of reproductive partitioning in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa)? Evidence from gibberellic acid synthesis inhibition using Paclobutrazol. Funct Plant Biol 38(5):420–430. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP10168
Gonçalves JLM, Alvares CA, Higa AR, Silva LD, Alfenas AC, Stahl J, Bouillet JPD et al (2013) Integrating genetic and silvicultural strategies to minimize abiotic and biotic constraints in Brazilian eucalypt plantations. Forest Ecol Manag 301:6–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.12.030
Halevy AH, Kessler B (1963) Increased tolerance of bean plants to soil drought by means of growth-retarding substances. Nature 197:310–311. https://doi.org/10.1038/197310a0
Higa RCV, Mora AL, Higa AR (2000) Plantio de Eucalipto na Pequena Propriedade Rural. Embrapa Florestas, Curitiba
IBA (2019) Indústria Brasileira de Árvores. Relatório 2019. Available online at https://iba.org/datafiles/publicacoes/relatorios/iba-relatorioanual2019.pdf . Accessed 21 May 2020
Jia QJ, Zhang XQ, Westcott S, Broughton S, Cakir YJM et al (2011) Expression level of a gibberellin 20-oxidase gene is associated with multiple agronomic and quality traits in barley. Theor Appl Genet 122:1451–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1544-5
Larcher W (2000) Ecofisiologia vegetal. Rima, São Carlos, p 531
Li J, Wei S, Bo O, Taotao W, Khurram Z, Zhidan L et al (2012) Tomato SlDREB gene restricts leaf expansion and internode methylation and chromatin patterning elongation by downregulating key genes for gibberellin biosynthesis. J Exp Bot 63:695–709. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers295
Luisi A, Lorenzi P, Sorce C (2011) Strigolactone may interact with gibberellin to control apical dominance in pea (Pisum sativum). Plant Growth Regul 65:415–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-011-9603-0
Magome H, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Kamiya Y, Oda K (2004) dwarf and delayed-flowering 1, a novel Arabidopsis mutant deficient in gibberellin biosynthesis because of overexpression of a putative AP2 transcription factor. Plant J 37:720–729. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2003.01998.x
Mao L, Zhang L, Zhao X, Liu S, Werf W, Zhang S, Spiertz H, Li Z (2014) Crop growth, light utilization and yield of relay intercropped cotton as affected by plant density and a plant growth regulator. Field Crops Res 155:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.09.021
Markesteijn L, Poorter L, Bongers F, Paz H, Sack L (2011) Hydraulics and life history of tropical dry forest tree species: coordination of species’ drought and shade tolerance. New Phytol 191:480–495. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03708.x
Matos FS, Oliveira PRC, Gil JLRA, Sousa PV, Gonçalves GA, Sousa MPBL, Silveira PS, Silva LM (2016) Eucalyptus urocan drought tolerance mechanisms. Afr J Agric Res 11(18):1617–1622. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2016.10918
Mauriat M, Sandberg LG, Moritz T (2011) Proper gibberellin localization in vascular tissue is required to control auxin-dependent leaf development and bud outgrowth in hybrid aspen. Plant J 67:805–816. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04635.x
Mohammadi MHS, Etemadi N, Arab MM, Aalifar M, Arab M, Pessarakli M (2017) Molecular and physiological responses of Iranian perennial ryegrass as affected by trinexapac ethyl, paclobutrazol and abscisic acid under drought stress. Plant Physiol Bioch 111:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.11.014
Moraes CB, Carignato A, Uesugi G, Abílio FM, Palomino EC, Mori ES (2014) Variabilidade genética e alterações morfológicas em progênies de polinização aberta de Eucalyptus grandis sob o efeito de paclobutrazol. Científica 42(4):396–403. https://doi.org/10.15361/1984-5529.2014v42n4p396-403
Nachabe MH (1998) Refining the definition of field capacity in the literature. J Irrig Drain Eng 124:230–232. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1998)124:4(230)
Ni J, Gao C, Chen MS, Pan BZ, Ye K, Xu ZF (2015) Gibberellin promotes shoot branching in the perennial woody plant Jatropha curcas. Plant Cell Physiol 56(8):1655–1666. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv089
Nir I, Moshelion M, Weiss D (2014) The Arabidopsis gibberellin methyl transferase 1 suppresses gibberellin activity, reduces whole-plant transpiration and promotes drought tolerance in transgenic tomato. Plant Cell Environ 37:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12135
Nir I, Shohat H, Panizel I, Olszewski N, Aharoni A, Weiss D (2017) The tomato DELLA protein PROCERA acts in guard cells to promote stomatal closure. Plant Cell 29:3186–3197. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00542
O'Neill PM, Shanahan JF, Schepers JS (2006) Use of chlorophyll fluorescence assessments to differentiate corn hybrid response to variable water conditions. Crop Sci 46(2):681–687. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.06-0170
Plaza-Wüthrich S, Blosch R, Rindisbacher A, Cannarozzi G, Tadele Z (2016) Gibberellin deficiency confers both lodging and drought tolerance in small cereals. Front Plant Sci 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00643
Poole RT, Conover CA (1992) Water use and growth of eight foliage plants influence by paclobutrazol. Foliage Dig 15:1–3
Poorter H, Niinemets U, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Villar R (2009) Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): a meta-analysis. New Phytol 82:565–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02830.x
Rademacher W (2000) Growth retardants: effects on gibberellin biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 51:501–531. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.501
Rademacher W (2016) Chemical regulators of gibberellin status and their application in plant production. In: Hedden P, Thomas SG (eds) The gibberellins. Wiley, Chichester https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119210436.ch12
Ranney TG, Bassuk NL, Whitlow TH (1989) Effect of transplanting practices on growth and water relations of ‘Colt’ cherry trees during reestablishment. J Environ Hortic 7:41–45. https://doi.org/10.24266/0738-2898-7.1.41
Reddy AR, Reddy KR, Hodges HF (1996) Mepiquat chloride (PIX)-induced changes in photosynthesis and growth of cotton. Plant Growth Regul 20(3):179–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043305
Reich PB, Wright IJ, Cavender-Bares J, Craine JM, Oleksyn J, Westoby M, Walters MB (2003) The evolution of plant functional variation: traits, spectra, and strategies. Int J Plant Sci 164:143–164. https://doi.org/10.1086/374368
Reis GGD, Reis MDGF, Fontan IDCI, Monte MA, Gomes AN, Oliveira CHRD (2006) Crescimento de raízes e da parte aérea de clones de híbridos de Eucalyptus grandis x Eucalyptus urophylla e de Eucalyptus camaldulensis x Eucalyptus spp submetidos a dois regimes de irrigação no campo. Árvore 30(6):921–931. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622006000600007
Rezazadeh A, Harkess RL, Bi G (2016) Effects of paclobutrazol and flurprimidol on water stress amelioration in potted red firespike. HortTechnology 26(1):26–29. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH.26.1.26
Rieu I, Eriksson S, Powers SJ, Gong F, Griffiths J, Woolley L et al (2008) Genetic analysis reveals that C19-GA 2-oxidation is a major gibberellin inactivation pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:2420–2436. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058818
Rosolem CA, Oosterhuis DM, Souza FSD (2013) Cotton response to mepiquat chloride and temperature. Sci Agric 70(2):82–87. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162013000200004
Santos SMS, Matsumoto SN, Andrade e Silva R, Oliveira LS, Viana AES (2018) Modulation of the initial growth of Eucalyptus clones using paclobutrazol: when smaller is better. Aust J Crop Sci 12(04):610–616. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.18.12.04.pne894
SEPLANTEC/CEI – Secretaria do Planejamento Ciência e Tecnologia/Centro de Estatística e Informações (1994) Informações básicas dos municípios baianos: região Sudoeste. Salvador. 1994, 540 p.
Sharma DK, Dubey AK, Srivastav M, Singh AK, Sairam RK, Pandey RN, Dahuja A, Kaur C (2011) Effect of putrescine and paclobutrazol on growth, physiochemical parameters, and nutrient acquisition of salt-sensitive citrus rootstock karna khatta (Citrus karna Raf.) under NaCl stress. J Plant Growth Regul 30:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-011-9192-1
Shen HJ, Zeng B (1993) Increased drought resistance of black locust seedlings via pretreatment of seeds with paclobutrazol. Can J For Res 23:2548–2551. https://doi.org/10.1139/x93-315
Siebert JD, Stewart AM (2006) Influence of plant density on cotton response to mepiquat chloride application. Agron J 98(6):1634–1639. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2006.0083
Silva W, Sediyama T, Silva AA, Ferreira FA (1998) Condutância estomática de Eucalyptus citriodora e E. grandis, em resposta a diferentes níveis de água no solo e de convivência com Brachiaria brizantha Stapf. Bragantia 57(2):339–347. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0006-87051998000200015
Silva MDA, Santos CMD, Vitorino HDS, Rhein L (2014) Pigmentos fotossintéticos e índice SPAD como descritores de intensidade do estresse por deficiência hídrica em cana-de-açúcar. Biosci J, pp 173–181
Silva JRJ, Cairo PAR, do Bomfim RAA, Barbosa MP, Souza MO, Leite TC (2020) Morphological and physiological changes during leaf ontogeny in genotypes of Eucalyptus young plants. Trees 34:759–769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-020-01955-2
Silverstone AL, Mak PYA, Martinez EC, Sun TP (1997) The new RGA locus encodes a negative regulator of gibberellin response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 146:1087–1099
Stape JL, Gonçalves JLM, Gonçalves AN (2001) Relationships between nursery practices and field performance for Eucalyptus plantations in Brazil: a historical overview and its increasing importance. New For 22:19–41. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012271616115
Stuart BL, Isbell VR, Wendt CW, Abernathy JR (1984) Modification of cotton water relations and growth with mepiquat chloride. Agron J 76(4):651–655. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1984.00021962007600040034x
Sumathi A, Prasad V, Vanangamudi M (2018) Plant Hormones enhance the yield by altering the physio-biological parameters in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). Legume Res Int J 41(4):543–550. https://doi.org/10.18805/LR-3761
Susiluoto S, Berninger F (2007) Interactions between morphological and physiological drought responses in Eucalyptus microtheca. Silva Fenn 41(2):221–233. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.292
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2010) Plant physiology, 5th edn. Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland
Tanis SR, McCullough DG, Cregg BM (2015) Effects of paclobutrazol and fertilizer on the physiology, growth and biomass allocation of three Fraxinus species. Urban For Urban Green 14:590–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2015.05.011
Varghese M, Ravi N, Kamalakannan R, Harwood CE (2008) Effect of silvicultural treatments on growth, fertility and capsule traits in seedling seed orchards of Eucalyptus camaldulensis and E. tereticornis. New Forest 37(1):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-008-9111-x
Vettakkorumakankav NN, Falk D, Saxena P, Fletcher RA (1999) A crucial role for gibberellins in stress protection of plants. Plant Cell Physiol 40:42–548. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029575
Wang KS, Lu CY, Chang SH (2011) Evaluation of acute toxicity and teratogenic effects of plant growth regulators by Daphnia magna embryo assay. J Hazard Mater 190:520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.068
Wang L, Mu C, Du M, Chen Y, Tian X, Zhang M, Li Z (2014) The effect of mepiquat chloride on elongation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) internode is associated with low concentration of gibberellic acid. Plant Sci 225:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.05.005
Wang WD, Chen GT, Hsu HJ, Wu CY (2015) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor 2 mediates the toxicity of Paclobutrazol on the digestive system of zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 159:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.11.018
Williams DR, Ross JJ, Reid JB, Potts BM (1999) Response of Eucalyptus nitens seedlings to gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitors. Plant Growth Regul 27:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006176928861
Xu X, Taylor HM (1992) Increase in drought resistance of cotton seedlings treated with mepiquat chloride. Agron J 84:569–574
Yamaguchi S (2008) Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:225–251. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092804
Zawaski C, Busov VB (2014) Roles of gibberellin catabolism and signaling in growth and physiological response to drought and short-day photoperiods in Populus trees. PLoS ONE 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086217
Zhao DL, Oosterhuis DM (2000) Pix plus and mepiquat chloride effects on physiology, growth, and yield of field-grown cotton. J Plant Growth Regul 19(4):415–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003440000018
Zunzunegui M, Dıaz Barradas MC, Ain-Lhout F, Alvarez-Cansino L, Esquivias MP, Garcıa Novo F (2010) Seasonal physiological plasticity and recovery capacity after summer stress in Mediterranean scrub communities. Plant Ecol 212:127–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-010-9809-7
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge support from UESB (Universidade Estadual Sudoeste da Bahia), FAPESB (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia) and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Beatriz Fernandez-Marin.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, J.A., Matsumoto, S.N., Trazzi, P.A. et al. Morphophysiological changes by mepiquat chloride application in Eucalyptus clones. Trees 35, 189–198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-020-02021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-020-02021-7