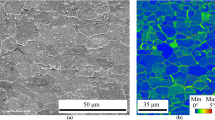
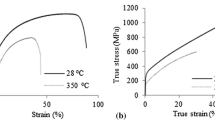
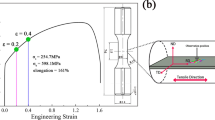
Abstract
Under asymmetrical stress-controlled cyclic loading accompanied by ratcheting, the evolution of microscopic substructures of stainless steel 304 (SS304), a face-centered cubic metal, was detected using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). This observation demonstrates that dislocation slip is the main mechanism of uniaxial ratcheting in the non-steady stage (stage I). Dislocation proliferate rapidly duo to the high stress level of the cyclic tests, and dislocation density increases continuously with the the number of cycles. The ratcheting rate decreases continuously due to the interaction of moveable dislocations, and the planar dislocation substructures (dislocation pileups and tangles) are the dominant patterns in this stage. In the later stage I, distinct lath \(\alpha \)-martensite was observed in the material due to the nucleation of martensite and the phase transformation zones increase gradually with the growth of axial ratcheting strain in the stage II of uniaxial ratcheting. The multiply and cross-slip were activated gradually in increasing numbers of grains, and the prevailing dislocation configurations evolve into more complicated and stable ones (dislocation walls and cells). In addition the dislocation configurations after various prescribed tensile strain of the monotonic tension and creep deformation with three different holding times were also observed by TEM. Comparing the evolution of microscopic substructures in various loading modes, the physical mechanism of uniaxial ratcheting of SS304 can be revealed as combination of the evolution of dislocation configurations and martensite transformation in the stage II of uniaxial ratcheting.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohno, N.: Recent topics in constitutive modeling of cyclic plasticity and viscoplasticity. Appl. Mech. Rev. 43, 283–295 (1990)
Chaboche, J.L.: A review of some plasticity and viscoplasticity constitutive theories. Int. J. Plast. 24, 1642–1693 (2008)
Liew, K.M., Pan, Z., Zhang, L.W.: The recent progress of functionally graded CNT reinforced composites and structures. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63(3), 234601 (2020)
Khutia, N., Dey, P.P., Hassan, T.: An improved nonproportional cyclic plasticity model for multiaxial low-cycle fatigue and ratcheting responses of 304 stainless steel. Mech. Mater. 91, 12–25 (2015)
Kang, G.Z., Bruhns, O.T., Saï, K.: Cyclic polycrystalline visco-plastic model for ratchetting of 316l stainless steel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 50, 1399–1405 (2011)
Yu, C., Kang, G.Z., Kan, Q.H.: Crystal plasticity based constitutive model of niti shape memory alloy considering different mechanisms of inelastic deformation. Int. J. Plast. 54, 132–162 (2014)
Dong, Y.W., Kang, G.Z., Yu, C.: A dislocation-based cyclic polycrystalline visco-plastic constitutive model for ratchetting of metals with face-centered cubic crystal structure. Comput. Mater Sci. 91, 75–82 (2014)
Zhang, L.W., Ji, W.M., Hu, Y., Liew, K.M.: Atomistic insights into the tunable transition from cavitation to crazing in diamond nanothread-reinforced polymer composites. Research 2020, 7815462 (2020)
Dong, Y.W., Xie, D.Y., Zhang, Y., Xiao, X.: On the study of cyclic crystal plasticity ratchetting constitutive model for polycrystalline pure copper. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 11, 1950041 (2019)
Wang, W., Liu, J.X., Soh, A.K.: Crystal plasticity modeling of strain rate and temperature sensitivities in magnesium. Acta Mech. 230, 2071–2086 (2019)
Taleb, L., Cailletaud, G., Blaj, L.: Numerical simulation of complex ratcheting tests with a multi-mechanism model type. Int. J. Plast. 22, 724–753 (2006)
Velay, V., Bernhart, G., Penazzi, L.: Cyclic behavior modeling of a tempered martensitic hot work tool steel. Int. J. Plast. 22, 459–496 (2006)
Saï, K.: Multi-mechanism models: present state and future trends. Int. J. Plast. 27, 250–281 (2011)
Wang, B., Kang, G.Z., Wu, W.P., Zhou, K., Kan, Q.H., Yu, C.: Molecular dynamics simulations on nanocrystalline super-elastic NiTi shape memory alloy by addressing transforamtion ratchetting and its atomic mechanism. Int. J. Plast. 125, 374–394 (2020)
Kundu, A., Field, D.P., Chandra Chakraborti, P.: Influence of strain amplitude on the development of dislocation structure during cyclic plastic deformation of 304 ln austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 762, 138090 (2019)
Sauzay, M., Kubin, L.P.: Scaling laws for dislocation microstructures in monotonic and cyclic deformation of fcc metals. Prog. Mater Sci. 56, 725–784 (2011)
Pham, M.S., Solenthaler, C., Janssens, K.G.F., Holdsworth, S.R.: Dislocation structure evolution and its effects on cyclic deformation response of aisi 316l stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 528, 3261–3269 (2011)
Roa, J.J., Fargas, G., Jiménez-Piqué, E., Mateo, A.: Deformation mechanisms induced under high cycle fatigue tests in a metastable austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 597, 232–236 (2014)
Wang, H., Jing, H.Y., Zhao, L., Han, Y.D., Lv, X.Q., Xu, L.Y.: Dislocation structure evolution in 304l stainless steel and weld joint during cyclic plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 690, 16–31 (2017)
Liu, X., Sun, W.K., Liew, K.M.: Multiscale modeling of crystal plastic deformation of polycrystalline titanium at high temperatures. Comput. Method Appl. Mech. Eng. 340, 932–955 (2018)
Carneiro, L., Wang, X.G., Jiang, Y.Y.: Cyclic deformation and fatigue behavior of 316l stainless steel processed by surface mechanical rolling treatment. Int. J. Fatigue 134, 105469 (2020)
Bocher, L., Delobelle, P., Robinet, P., Feaugas, X.: Mechanical and microstructural investigations of an austenitic stainless steel under non-proportional loadings in tension-torsion-internal and external pressure. Int. J. Plast. 17, 1491–1530 (2001)
Feaugas, X., Gaudin, C.: Ratchetting process in the stainless steel aisi 316l at 300 k: an experimental investigation. Int. J. Plast. 20, 643–662 (2004)
Gaudin, C., Feaugas, X.: Cyclic creep process in aisi 316l stainless steel in terms of dislocation patterns and internal stresses. Acta Mater. 52, 3097–3110 (2004)
Taleb, L., Hauet, A.: Multiscale experimental investigations about the cyclic behavior of the 304l ss. Int. J. Plast. 25, 1359–1385 (2009)
Kang, G.Z., Dong, Y.W., Wang, H., Liu, Y.J., Cheng, X.J.: Dislocation evolution in 316l stainless steel subjected to uniaxial ratchetting deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 527, 5952–5961 (2010)
Dong, Y.W., Kang, G.Z., Liu, Y.J., Wang, H., Cheng, X.J.: Dislocation evolution in 316l stainless steel during multiaxial ratchetting deformation. Mater. Charact. 65, 62–72 (2012)
Dong, Y.W., Kang, G.Z., Liu, Y.J., Jiang, H.: Multiaxial ratcheting of 20 carbon steel: macroscopic experiments and microscopic observations. Mater. Charact. 83, 1–12 (2013)
Kang, G.Z., Dong, Y.W., Liu, Y.J., Wang, H., Cheng, X.J.: Uniaxial ratchetting of 20 carbon steel: macroscopic and microscopic experimental observations. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 528, 5610–5620 (2011)
Kang, G.Z., Dong, Y.W., Liu, Y.J., Jiang, H.: Macroscopic and microscopic investigations on uniaxial ratchetting of two-phase Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Charact. 92, 26–35 (2014)
Hamidinejad, S.M., Varvani-Farahani, A.: Ratcheting of 304 stainless steel under multiaxial step-loading conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 80–89 (2015)
Taleb, L., Keller, C.: Experimental contribution for better understanding of ratchetting in 304L SS. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 146–167, 527–535 (2018)
Sarkar, A., De, P.S., Mahato, J.K., Kundu, A., Chakraborti, P.C.: Effect of mean stress and solution annealing temperature on ratcheting behaviour of aisi 304 stainless steel. Procedia Eng. 74, 376–383 (2014)
Xu, B.B., Xu, W., Guo, F.L.: Creep behavior due to interface diffusion in unidirectional fiber-reinforced metal matrix composites under general loading conditions: A micromechanics analysis. Acta Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-019-02592-8
Pontini, A.E., Hermida, J.D.: X-ray diffraction measurement of the stacking fault energy reduction induced by hydrogen in an aisi 304 steel. Scr. Mater. 37, 1831–1837 (1997)
Cheng, X.J., Wang, H., Kang, G.Z., Dong, Y.W., Liu, Y.J.: Study on strain-induced martensite transformation of 304 stainless steel during ratcheting deformationtion. Acta. Metall. Sin. 45, 830–834 (2009)
Jackson, P.J.: The role of cross-slip in the plastic deformation of crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 57, 39–47 (1983)
Püschl, W.: Models for dislocation cross-slip in close-packed crystal structures: a critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 47, 415–461 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to gratefully acknowledge the financial supports by the National Science Foundation of China (grant no. 11502115), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant nos. BK20150777 and BK20190437), as well as the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. 30920021147)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Zhang, Z. & He, X. Microscopic substructures of stainless steel 304 undergoing a uniaxial ratcheting deformation. Acta Mech 231, 4919–4931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02804-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-020-02804-6