Abstract
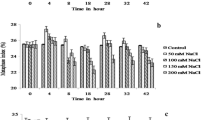
In this study, 10 mg L–1 L-tryptophan effects on the seedling growth (fresh weight, radicle length and radicle number), seed germination, chromosomal aberrations and mitotic activity in Allium cepa L. germinated in salinity (0.175 M NaCl) conditions were investigated. In only L-tryptophan medium, the radicle length and radicle number of the seedlings were partially reduced compared to the control seedlings grown in the pure water medium, the germination percentage and fresh weight indicate statistically the same values as the control. Moreover, the chromosomal aberrations and mitotic index in the root tip meristem cells of Allium cepa seeds germinated in alone L-tryptophan medium showed increase compared to the control seeds germinated in the pure water medium. On the other hand, salt stress significantly inhibited the germination rate, radicle length, radicle number and fresh weight of Allium cepa L. In addition, it important reduced the mitotic index (activity) and increased the chromosomal aberrations in root tip meristems of the seeds. Nevertheless, the inhibitory effects of salt stress on all the mentioned parameters were dramatically alleviated by L-tryptophan application. The germination percentage, radicle length, radicle number, fresh weight, mitotic index and chromosomal aberrations of the seedlings grown in 0.175 M salinity were 23%, 10.3 mm, 12.7, 7 g, 1.2 and 17% respectively, while these values became 77%, 15.3 mm, 16.7, 15.2 g, 11.6 and 14.6% in the seedlings treated with 10 mg L–1 L-tryptophan.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tanji, K.K., Nature and Extent of Agricultural Salinity, in Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management, Tanji, K.K., Ed., New York: Am. Soc. Civil Eng., 2th ed., 1990, pp. 1–13.
Jamil, A., Riaz, S., Ashraf, M., and Foolad, M.R., Gene expression profiling of plants under salt stress, Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 2011, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 435–458.
Dubouzet, J.G., Matsuda, F., Ishihara, A., Miyagawa, H., and Wakasa, K., Production of indole alkaloids by metabolic engineering of the tryptophan pathway in rice, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2013, vol. 11, pp. 1103–1111.
Leme, D.M. and Marin-Morales, M.A., Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its aplication, Mut. Res., 2009, vol. 682, pp. 71–81.
Çavuşoğlu, D., Tabur, S., and Çavuşoğlu, K., The effects of Aloe vera L. leaf extract on some physiological and cytogenetical parameters in Allium cepa L. seeds germinated under salt stress, Cytologia, 2016, vol. 81, no. 1, pp. 103–110.
Sharma, P.C. and Gupta, P.K., Karyotypes in some pulse crops, Nucleus, 1982, vol. 25, pp. 181–185.
Aslantürk, Ö.S. and Çelik, T.A., Preventive effect of lycopene on chromosome aberrations in Allium cepa,Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 2005, vol. 8, pp. 482–486.
Mohite, B., Isolation and characterization of indole acetic acid (IAA) producing bacteria from rhizospheric soil and its effect on plant growth, J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 2013, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 638–649.
Bakry, B.A., Ibrahim, F.M., Abdallah, M.M.S., and El-Bassiouny, H.M.S., Effect of banana peel extract or tryptophan on growth, yield and some biochemical aspects of quinoa plants under water deficit, Int. J. Pharm. Tech. Res., 2016, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 276–287.
Katonoguchi, H., Kosemura, S., Yamamura, S., Mizutani, J., and Hasegawa, K., Allelopathy of oats. 1. Assessment of allelopathic potential of extract of oat shoots and identification of an allelochemical, J. Chem. Ecol., 1994, vol. 20, pp. 309–314.
Akaneme, F.I. and Amaefule, C.C., Evaluation of the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of aqueous leaf extracts of Azardirachta indica A. Juss. using the Allium test, J. Med. Plants Res., 2012, vol. 6, pp. 3898–3907.
Turkoglu, S., Genotoxicity of five food preservatives tested on root tips of Allium cepa L., Mut. Res., 2007, vol. 626, pp. 4–14.
Roy, S.J., Negrão, S., and Tester, M., Salt resistant crop plants, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 26, pp. 115–124.
El-Awadi, M. and Hassan, E.A., Improving growth and productivity of fennel plant exposed to pendimethalin herbicide: Stress-recovery treatments, Nat. Sci., 2011, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 97–108.
Abbas, S.H., Sohail, M., Saleem, M., Tariq, M., Aziz, I., Qammar, M., Majeed, A., and Arif, M., Effects of L-tryptophan on plant weight and pod weight in chickpea under rain fed conditions, Sci. Tech. Dev., 2013, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 277–280.
Grisolia, C.K., Bilich, M.R., and Formigli, M.L., A comparative toxicologic and genotoxic study of the herbicide arsenal, its active ingredient imazapyr and the surfactant nonylphenol etoxylate, Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf., 2004, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 123–126.
Luzhna, L., Kathiria, P., and Kovalchuk, O., Micronuclei in genotoxicity assessment: From genetics to epigenetics and beyond, Front. Genet., 2013, vol. 4, p. 131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by the author.
About this article
Cite this article
Dilek Çavuşoğlu Cytogenetical and Physiological Effects of L-tryptophan in Onion (Allium cepa L.) Exposed to Salt Stress. Russ. Agricult. Sci. 46, 341–346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367420040059
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367420040059