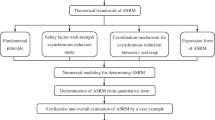
Abstract
Slope stability has been the research focus in the field of geotechnical engineering. Both the asynchronous decay speeds and distinct stability contributions of cohesion c and friction φ during slope instability have been evidenced. In this study, based on linear softening model and weighted average hypothesis, a modified double-reduction method is established. The research includes: 1) the asynchronism between decay speeds of c and φ are described by adopting different slopes in linear softening model for c and tanφ, in which case the respective reduction factors in strength reduction method Fc and Fφ are solved. 2) The distinct slope stability contributions of c and φ is readily linked with the different influences to safety factor, and therefore, introducing the equivalent influence angle θe (defined as the slope angle at which c and φ share identical contributions to stability), as well as its determination method. 3) According to weighted average hypothesis that the overall safety factor Fs is the weighted average of Fc and Fφ, the contribution scaling factor μ (defined as the weighted ratio of Fc and Fφ is proposed, which promotes the solution of respective weighted coefficients wc and wφ of two reduction factors by combining θe, achieving a new double-reduction method. 4) The validity of this method is verified via comprehensive comparison with existing double-reduction methods of practical slope examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Cohesion
- c cr :
-
Critical cohesion of slope
- c ini :
-
Initial cohesion of slope
- F c :
-
The reduction factor of cohesion
- F s :
-
The overall safety factor of slope
- F φ :
-
The reduction factor of friction
- w c :
-
Weighted coefficients of the reduction factor of cohesion
- w φ :
-
Weighted coefficients of the reduction factor of internal friction angle
- Δx :
-
Translation distance in x-direction
- Δy :
-
Translation distance in y-direction
- η :
-
Scaling coefficient
- θ e :
-
Equivalent influence angle of slope
- ϑ :
-
Rotation angle
- μ :
-
Contribution scaling factor
- φ :
-
Friction
- φ cr :
-
Critical internal friction angle of slope
- φ ini :
-
Initial internal friction angle of slope
References
Arvin M, Zakeri A, Bahmani S (2019) Using finite element strength reduction method for stability analysis of geocell-reinforced slopes. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 37(3):1453–146, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0699-0
Bai B, Yuan W, Li X (2014) A new double-reduction method for slope stability analysis. Journal of Central South University 21(3):1158–1164, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2049-6
Bai B, Yuan W, Shi L, Li J, Li X (2015) Comparing a new double-reduction method to classic strength reduction method for slope stability analysis. Rock and Soil Mechanics 36(5):1275–1281, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2015.05.005 (in Chinese)
Chen R, Kang E, Wu L, Yang J, Ji X, Zhang Z (2005) Discussion on the distribution of cold regions in China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology (4):469-475 (in Chinese)
Cheng YM, Lansivaara T, Wei WB (2007) Two-dimensional slope stability analysis by limit equilibrium and strength reduction methods. Computers and Geotechnics 34(3):137–150, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2006.10.011
Conte E, Silvestri F, Troncone A (2010) Stability analysis of slopes in soils with strain-softening behaviour. Computers and Geotechnics 37(5):710–722, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2010.04.010
Dawson E, Roth W, Drescher A (1999) Slope stability by strength reduction. Geotechnique 49(6):835–840, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1999.49.6.835
Fu W, Liao Y (2010) Non-linear shear strength reduction technique in slope stability calculation. Computers and Geotechnics 37(3):288–298, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.11.002
Griffiths D (1989) Computation of collapse loads in geomechanics by finite elements. Ingenieur-Archiv 59(3):237–244
Griffiths D, Lane P (1999) Slope stability analysis by finite elements. Geotechnique 49(3):387–403, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1999.49.3.387
Hammouri N, Malkawi A, Yamin M (2008) Stability analysis of slopes using the finite element method and limiting equilibrium approach. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 67(4):471–478, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-008-0156-z
Isakov A, Moryachkov Y (2014) Estimation of slope stability using two-parameter criterion of stability. International Journal of Geomechanics 14(3):613–624, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000326
Jiang X, Wang Z, Liu L, Zhou Z (2013) The determination of reduction ratio factor in homogeneous soil-slope with finite element double strength reduction method. Open Civil Engineering Journal 7(1):205–209, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1874149501307010205
Lin H (2009) Study on the strength reduction method for slope described by linear and non-linear failure criteria. PhD Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China (in Chinese)
Lin H, Xiong W, Cao P (2013) Stability of soil nailed slope using strength reduction method. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering 17(9):872–885, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2013.828658
Lin H, Zhong W, Cao P (2016) Three-dimensional rock slope stability analysis considering the surface load distribution. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering 20(8):877–898, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2015.1084382
Matsui T, San K (1992) Finite element slope stability analysis by shear strength reduction technique. Soils and Foundations 32(1):59–70, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.32.59
Shen J, Karakus M (2014) Three-dimensional numerical analysis for rock slope stability using shear strength reduction method. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 51(2):164–172, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2013-0191
Sun C, Chai J, Xu Z, Qin Y, Chen X (2016) Stability charts for rock mass slopes based on the Hoek-Brown strength reduction technique. Engineering Geology 214:94–106, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.09.017
Tang F, Zheng Y (2008) Mechanism analysis on dual reduction factors about the progressive failure of slope. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 4(3):436–441 (in Chinese)
Tang F, Zheng Y, Zhao S (2007) Discussion on two safety factors for progressive failure of soil slope. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 26(7):1402–1407, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(07)60007-9
Xue H, Dang F, Yin X, Ding W, Yang C (2016) Nonproportional correlative reduction finite element method for slope strength parameters. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 11(15):1–10, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2725354
Xue H, Dang F, Yin X, Yang C, Yan F (2015) Research on method of slope strength parameters non-proportional associated reduction. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 34(2):4005–4012, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.1216 (in Chinese)
Yang G, Zhang Y, Zhang Y (2009) Variable modulus elastoplastic strength reduction method and its application to slope stability analysis. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 28(7):1506–1512 (in Chinese)
Yuan W, Bai B, Li X, Wang H (2013) A strength reduction method based on double-reduction parameters and its application. Journal of Central South University 20(9):2555–2562, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1768-4
Yuan W, Hao X, Li X, Bai B, Wang W, Chen X, Ji X (2016a) A strength reduction method considering reduction of strength parameters coordinating with deformation parameters. Rock and Soil Mechanics 37(7):2096–2100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.07.034 (in Chinese)
Yuan W, Li J, Li Z, Wang W, Sun X (2020) A strength reduction method based on the Generalized Hoek-Brown (GHB) criterion for rock slope stability analysis. Computers and Geotechnics 117, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103240
Yuan W, Li X, Wang W, Bai B, Wang Q, Chen X (2016b) Study on strength reduction method based on double-reduction parameters. Rock and Soil Mechanics 37(8):2222–2230, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.08.013 (in Chinese)
Zhang K, Tan P, Ma G, Cao P (2015) Modeling of the progressive failure of an overhang slope subject to differential weathering in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 13(5):1–11, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0672-4
Zheng H, Tham L, Liu D (2006) On two definitions of the factor of safety commonly used in the finite element slope stability analysis. Computers and Geotechnics 33(3):188–195, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2006.03.007
Zhu Y, Yang X, Ma X, Yang X, Ye S (2018) Several questions of double-reduction method for slope stability analysis. Rock and Soil Mechanics 39(1):331–338, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.0141 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This paper gets its funding from project (51774107, 51774322, 51774131) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2018JJ2500) supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China; Scientific research innovation project for graduate students of Central South University (2019zzts303). The authors wish to acknowledge these supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Lin, H., Wang, Y. et al. Modified Double-Reduction Method considering Strain Softening and Equivalent Influence Angle. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 3257–3266 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0547-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0547-7