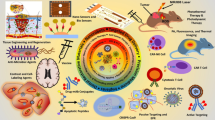
Abstract
Herein, we have presented a broad overview of microbial exopolysaccharide (EPS)-based nano-structures that are continuously being explored for their potential biomedical applications, e.g., cell and/or drug encapsulation, gene delivery, tissue engineering, diagnostics, and related therapeutics. The sustainable exploitation of naturally occurring EPS-based polymeric nano-carriers using state-of-the-art nanotech engineering approaches has provided an excellent alternative to conventional bioimaging and drug delivery technologies. EPS-based drug transport covers a specific niche “intelligent therapeutics” which is still being established and has not been well described in the literature. Thus, herein, an effort has been made to cover this literature gap to present unique multi-functional potentialities of microbial EPS with suitable examples. EPS-based nano-pharmaceutics exhibit certain advantages over conventional counterparts, such as ease in preparation, in vivo biocompatibility, biodegradability, and sustainability. EPS and their derivatives are successfully applied for several biomedical applications, e.g., wound dressing scaffolds, arthritis treatment, dental impressions, and tissue engineering purposes. The progress in targeted delivery systems using micro and nanosystems has opened a new dimension in biopolymer-based biomedicines and smart surgical procedures. This huge area of biomedical engineering is described by the availability of a diverse range of EPS-derivatives, whose multi-functional characteristics can be controlled. Through bioconjugation, i.e., functionalized composite production, different systems have been designed, such as controlled drug release and target accumulation of therapeutic substances. Potential EPS applications are not just limited to targeted transport but also covers several emerging diagnostic technologies. Several bioactive EPS have also been studied for their properties like anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-tumor and immunomodulatory activities. Based on currently available data on EPS-based nano-structures for biomedical domains, it can be undoubtedly stated that they present a broad future ahead.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- AIDS:
-
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- EPS:
-
Exopolysaccharide
- FMT:
-
Fluorescent molecular tomography
- IPN:
-
Interpenetrating polymer networks
- IPS:
-
Intracellular polysaccharides
- PCL:
-
Polycaprolactone
- PDT:
-
Photodynamic therapy
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PLA:
-
Polylactic acid
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Agnello S, Gasperini L, Mano JF, Pitarresi G, Palumbo FS, Reis RL, Giammona G (2017) Synthesis, mechanical and thermal rheological properties of new gellan gum derivatives. Int J Biol Macromol 98:646–653.
Ali AAA, Hsu FT, Hsieh CL, Shiau CY, Chiang CH, Wei ZH, Huang HS (2016) Erlotinib-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles as a smart cancer-targeted theranostic probe for MRI. Sci Rep 6:36650. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36650
Alves da Cunha MA, Turmina JA, Ivanov RC, Barroso RR, Marques PT, Fonseca EA (2012) Lasiodiplodan, an exocellular (1-→6)-D-glucan from Lasiodiplodia theobromae MMPI: production on glucose, fermentation kinetics, rheology and anti-proliferative activity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1179–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1112-2
Arad SM, Levy-Ontman O (2010) Red microalgal cell-wall polysaccharides: biotechnological aspects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2010.02.008
Asgher M, Urooj Y, Qamar SA, Khalid N (2020a) Improved exopolysaccharide production from Bacillus licheniformis MS3: optimization and structural/functional characterization. Int J biol Macromol 151:984–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.094
Asgher M, Arshad S, Qamar SA, Khalid N (2020b) Improved biosurfactant production from Aspergillus Niger through chemical mutagenesis: characterization and RSM optimization. SN Applied Sciences 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2783-3
Augimeri RV, Varley AJ, Strap JL (2015) Establishing a role for bacterial cellulose in environmental interactions: lessons learned from diverse biofilm-producing Proteobacteria. Front Microbiol 6:1282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01282
Bhatia S (2016) Marine polysaccharides based nano-materials and its applications. In natural polymer drug delivery systems. Springer, Cham. pp 185-225. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41129-3_5
Billingham RE, Reynolds J (1952) Transplantation studies on sheets of pureepidermal epithelium and on epidermal cell suspensions. Br J Plast Surg 5:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1226(52)80004-9
Boridy S, Takahashi H, Akiyoshi K, Maysinger D (2009) The binding of pullulan modified cholesteryl nanogels to Aβ oligomers and their suppression of cytotoxicity. Biomaterials 30:5583–5591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.06.010
Bowen WH, Koo H (2011) Biology of Streptococcus mutants-derived glucosyltransferases: role in extracellular matrix formation of cariogenic biofilms Caries Res 45:69-86. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324598
Cervino G, Fiorillo L, Herford A, Laino L, Troiano G, Amoroso G, Cicciu M (2019) Alginate materials and dental impression technique: a current state of the art and application to dental practice. Mar Drugs 17:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010018
Chase WR, Zhaxybayeva O, Rocha J, Cosgrove DJ, Shapiro LR (2019) From morphogenesis to pathogenesis: a cellulose loosening protein is one of the most widely distributed tools in nature. bioRxiv, 2019:637728. https://doi.org/10.1101/637728
Chen X, Song L, Wang H, Liu S, Yu H, Wang X, Li P (2019) Partial characterization, the immune modulation and anticancer activities of sulfated polysaccharides from filamentous microalgae Tribonema sp. Molecules 24:322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020322
Choromanska A, Kulbacka J, Rembialkowska N, Pilat J, Oledzki R, Harasym J, Saczko J (2015) Anticancer properties of low molecular weight oat beta-glucan–an in vitro study. Int J biol Macromol 80:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.05.035
Chou CH, Sung TJ, Hu YN, Lu HY, Yang LC, Cheng KC, Hsieh CW (2019) Chemical analysis, moisture-preserving, and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Pholiota nameko by fractional precipitation. Int J Biol Macromol 131:1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.154
Chunshom N, Chuysinuan P, Techasakul S, Ummartyotin S (2018) Dried-state bacterial cellulose (Acetobacter xylinum) and polyvinyl-alcohol-based hydrogel: an approach to a personal care material. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 3:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.06.004
Coutinho DF, Sant SV, Shin H, Oliveira JT, Gomes ME, Neves NM, Reis RL (2010). Modified Gellan Gum hydrogels with tunable physical and mechanical properties. Biomaterials 31(29):7494–7502.
Curcio M, Diaz-Gomez L, Cirillo G, Concheiro A, Iemma F, Alvarez-Lorenzo C (2017) pH/redox dual-sensitive dextran nanogels for enhanced intracellular drug delivery Eur J Pharm Biopharm 117:324-332. /https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.05.002
Deepak V, Ramachandran S, Balahmar RM, Pandian SRK, Sivasubramaniam SD, Nellaiah H, Sundar K (2016) In vitro evaluation of anti-cancer properties of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus acidophilus in colon cancer cell lines. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Animal 52:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9970-3
Deniaud-Bouët E, Hardouin K, Potin P, Kloareg B, Hervé C (2017) A review about brown algal cell walls and fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides: cell wall context, biomedical properties and key research challenges. Carbohydr Polym 175:395–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.082
Dilna SV, Surya H, Aswathy RG, Varsha KK, Sakthikumar DN, Pandey A, Nampoothiri KM (2015) Characterization of an exopolysaccharide with potential health-benefit properties from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum RJF4. LWT Food Sci Technol 64:1179–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.040
Ding Z, Liu P, Hu D, Sheng Z, Yi H, Gao G, Cai L (2017) Redox-responsive dextran based theranostic nanoparticles for near-infrared/magnetic resonance imaging and magnetically targeted photodynamic therapy. Biomater Sci 5:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6BM00846A
Duquesnoy RJ (2002) HLA matchmaker: a molecularly based algorithm for histocompatibility determination. I. Description of the algorithm. Hum Immunol 63:339–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0198-8859(02)00382-8
Esawy MA, Abdel-Fattah AM, Ali MM, Helmy WA, Salama BM, Taie HA, Awad GE (2013) Levansucrase optimization using solid state fermentation and Levan biological activities studies. Carbohydr Polym 96:332–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.089
Frei E, Preston RD (1964) Non-cellulosic structural polysaccharides in algal cell walls I. Xylan in siphoneous green algae. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 160:293–313. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1964.0041
Gao F, Li L, Zhang H, Yang W, Chen H, Zhou J, Liu L (2010) Deoxycholic acid modified-carboxymethyl curdlan conjugate as a novel carrier of epirubicin: in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Pharm 392:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.03.044
Gao ZM, Yang XQ, Wu NN, Wang LJ, Wang JM, Guo J, Yin SW (2014) Protein-based pickering emulsion and oil gel prepared by complexes of zein colloidal particles and stearate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(12):2672–2678.
Gopi S, Amalraj A, Sukumaran NP, Haponiuk JT, Thomas S (2018) Biopolymers and their composites for drug delivery: a brief review. In Macromolecular Symposia 380:1800114. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201800114
Green H, Kehinde O, Thomas J (1979) Growth of cultured human epidermal cells into multiple epithelia suitable for grafting. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:5665–5668. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.11.5665
Gupta M, Gupta AK (2004) Hydrogel pullulan nanoparticles encapsulatingpBUDLacZ plasmid as an efficient gene delivery carrier. J Control Release 99:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.06.016
Han J, Cai J, Borjihan W, Ganbold T, Rana TM, Baigude H (2015) Preparation of novel curdlan nanoparticles for intracellular siRNA delivery. Carbohydr Polym 117:324–330
Hao L, Sheng Z, Lu J, Tao R, Jia S (2016) Characterization and antioxidant activities of extracellular and intracellular polysaccharides from Fomitopsis pinicola. Carbohydr Polym 141:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.048
Hasheminya SM, Mokarram RR, Ghanbarzadeh B, Hamishekar H, Kafil HS, Dehghannya J (2019) Development and characterization of biocomposite films made from kefiran, carboxymethyl cellulose and Satureja Khuzestanica essential oil. Food Chem 289:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.076
Huang M, Wang F, Zhou X, Yang H, Wang Y (2015) Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties of polysaccharides from Enterobacter cloacae Z0206 in KKAy mice. Carbohydr Polym 117:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.008
Ikada Y (2006) Challenges in tissue engineering. J Royal Soc Interface 3:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2006.0124
Julianti E, Rusmarilin H, Yusraini E (2017) Functional and rheological properties of composite flour from sweet potato, maize, soybean and xanthan gum. J Saudi Soc Agric 16:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2015.05.005
Kamoun EA, Kenawy ERS, Chen X (2017) A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. Int J Adv Res 8:217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.01.005
Kishimoto M, Nomoto R, Mizuno M, Osawa R (2017) An in vitro investigation of immunomodulatory properties of Lactobacillus plantarum and L. delbrueckii cells and their extracellular polysaccharides Biosci Microb Food H 17-001. https://doi.org/10.12938/bmfh.17-001
Klosterhoff RR, Bark JM, Glanzel NM, Iacomini M, Martinez GR, Winnischofer SM, Cordeiro LM (2018) Structure and intracellular antioxidant activity of pectic polysaccharide from acerola (Malpighia emarginata). Int J biol Macromol 106:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.032
Kong SH, Noh YW, Suh YS, Park HS, Lee HJ, Kang KW, Yang HK (2015) Evaluation of the novel near-infrared fluorescence tracers pullulan polymer nanogel and indocyanine green/γ-glutamic acid complex for sentinel lymph node navigation surgery in large animal models. Gastric Cancer 18:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-014-0345-3
Kumar D, Saini N, Pandit V, Ali S (2012) An insight to pullulan: a biopolymer in pharmaceutical approaches. Int J Basic Appl Sci 1:202–219. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijbas.v1i3.101
Kumar V, Sharma DK, Bansal V, Mehta D, Sangwan RS, Yadav SK (2019) Efficient and economic process for the production of bacterial cellulose from isolated strain of Acetobacter pasteurianus of RSV-4 bacterium. Bioresour Technol 275: 430-433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.042
Li W, Xia X, Tang W, Ji J, Rui X, Chen X, Dong M (2015) Structural characterization and anti-cancer activity of cell-bound exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1. J Agric Food Chem 63:3454–3463. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01086
Li T, Ding X, Tian L, Ramakrishna S (2017) Engineering BSA-dextran particles encapsulated bead-on-string nanofiber scaffold for tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci 52:10661–10672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1245-9
Liang Y, Zhao X, Ma PX, Guo B, Du Y, Han X (2019) pH-responsive injectable hydrogels with mucosal adhesiveness based on chitosan-grafted-dihydrocaffeic acid and oxidized pullulan for localized drug delivery. J Colloid Interface Sci 536:224–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.056
Lin B, Su H, Jin R, Li D, Wu C, Jiang X, Ai H (2015) Multi-functional dextran micelles as drug delivery carriers and magnetic resonance imaging probes. Sci Bull 60:1272–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0840-x
Liu Y, Chan-Park MB (2009) Hydrogel based on interpenetrating polymer networks of dextran and gelatin for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:196–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.041
Liu J, Luo J, Ye H, Zeng X (2012) Preparation, antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro of different derivatives of Levan from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Food Chem Toxicol 50:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.016
Llamas I, Del Moral A, Martínez-Checa F, Arco Y, Arias S, Quesada E (2006) Halomonas maura is a physiologically versatile bacterium of both ecological and biotechnological interest. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 89:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9043-9
Lu Y, Xu L, Cong Y, Song G, Han J, Wang G, Chen K (2019) Structural characteristics and anti-cancer/antioxidant activities of a novel polysaccharide from Trichoderma kanganensis. Carbohydr Polym 205:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.068
Mahapatra S, Banerjee D (2013) Fungal exopolysaccharide: production, composition and applications. Microbiol Insights 6:MBI-S10957. https://doi.org/10.4137/MBI.S10957
Makris EA, Gomoll AH, Malizos KN, Hu JC, Athanasiou KA (2015) Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol 11:21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2014.157
Mandawe J, Infanzon B, Eisele A, Zaun H, Kuballa J, Davari MD, Schwaneberg U (2018) Cover feature: directed evolution of hyaluronic acid synthase from Pasteurella multocida towards high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid. ChemBioChem 19:1350–1350. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201800093
Matricardi P, Di Meo C, Coviello T, Hennink WE, Alhaique F (2013) Interpenetrating polymer networks polysaccharide hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1172–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.04.002
Mbakidi JP, Brégier F, Ouk TS, Granet R, Alves S, Rivière E, Sol V (2015) Magnetic dextran nanoparticles that bear hydrophilic porphyrin derivatives: bimodal agents for potential application in photodynamic therapy. ChemPlusChem 80:1416-1426. /10.1002/cplu.201500087
Meng X, Liang H, Luo L (2016) Antitumor polysaccharides from mushrooms: a review on the structural characteristics, antitumor mechanisms and immunomodulating activities. Carbohydr Res 424:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2016.02.008
Miguel S, Ribeiro M, Coutinho P, Correia I (2017) Electrospun polycaprolactone/aloe vera_chitosan nanofibrous asymmetric membranes aimed for wound healing applications. Polymers 9:183. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9050183
Milas M, Shi X, Rinaudo M (1990) On the physicochemical properties of gellan gum. Biopolymers: Original Research on Biomolecules, 30(3–4), 451–464
Mirza Z, Soto ER, Dikengil F, Levitz SM, Ostroff GR (2017) Beta-glucan particles as vaccine adjuvant carriers. In vaccines for invasive fungal infections. Humana press, New York, NY, pp 143–157. /10.1007/978-1-4939-7104-6_11
Mocanu G, Souguir Z, Picton L, Le Cerf D (2012) Multi-responsive carboxymethyl polysaccharide crosslinked hydrogels containing Jeffamine side-chains. Carbohydr Polym 89:578–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.052
Moscovici M (2015) Present and future medical applications of microbial exopolysaccharides. Front Microbiol 6:1012. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01012
Murphy CA, Collins MN (2018) Microcrystalline cellulose reinforced polylactic acid biocomposite filaments for 3D printing. Polym Compos 39:1311-1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24069
Notararigo S, Corbi AL, Lopez P (2014) Immunomodulation of human macrophages and myeloid cells by 2-substituted (1-→3)- β-D-glucan from P. parvulus 2.6. Carbohydr Polym 112:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.073
Nwodo U, Green E, Okoh A (2012) Bacterial exopolysaccharides: functionality and prospects. Int J Mol Sci 13:14002–14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114002
Park GT, Go RE, Lee HM, Lee GA, Kim CW, Seo JW, Hwang KA (2017a) Potential anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory effects of marine microalgal exopolysaccharide on various human cancer cells and lymphocytes in vitro. Mar Biotechnol 19:136–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-017-9735-y
Park SB, Lih E, Park KS, Joung YK, Han DK (2017b) Biopolymer-based functional composites for medical applications. Prog Polym Sci 68:77–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2016.12.003
Patra D, Sengupta S, Duan W, Zhang H, Pavlick R, Sen A (2013) Intelligent, self-powered, drug delivery systems. Nanoscale 5:1273–1283. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2NR32600K
Prezotti FG, Cury BSF, Evangelista RC (2014) Mucoadhesive beads of gellan gum/pectin intended to controlled delivery of drugs. Carbohydr Polym 113:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.021
Qamar SA, Asgher M, Khalid N, Sadaf M (2019) Nanobiotechnology in health sciences: current applications and future perspectives. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 101388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101388
Qiao R, Yang C, Gao M (2009) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: from preparations to in vivo MRI applications. J Mater Chem 19:6274–6293. https://doi.org/10.1039/B902394A
Qin ZY, Jia XW, Liu Q, Kong BH, Wang H (2019) Fast dissolving oral films for drug delivery prepared from chitosan/pullulan electrospinning nanofibers. Int J Biol Macromol 137:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.224
Raemdonck K, Naeye B, Hogset A, Demeester J, De Smedt SC (2010) Prolonged gene silencing by combining siRNA nanogels and photochemical internalization. J Control Release 145: 281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.04.012
Ramamoorthy S, Gnanakan A, Lakshmana SS, Meivelu M, Jeganathan A (2018) Structural characterization and anti-cancer activity of extracellular polysaccharides from ascidian symbiotic bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. Carbohydr Polym 190:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.02.047
Raveendran R, Bhuvaneshwar GS, Sharma CP (2016) Hemocompatible curcumin–dextran micelles as pH sensitive pro-drugs for enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer cells. Carbohydr Polym 137:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.017
Ravichandran V, Kothandaraman GP, Bories C, Loiseau PM, Jayakrishnan A (2018) Synthetic polysaccharides as drug carriers: synthesis of polyglucose-amphotericin B conjugates and in vitro evaluation of their anti-fungal and anti-leishmanial activities. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18: 2405–2414. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14296
Rokstad AMA, Lacík I, de Vos P, Strand BL (2014) Advances in biocompatibility and physico-chemical characterization of microspheres for cell encapsulation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 67: 111–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.010
Saldias C, Velásquez L, Quezada C, Leiva A (2015) Physicochemical assessment of dextran-g-poly (ɛ-caprolactone) micellar nanoaggregates as drug nano-carriers. Carbohydr Polym 117: 458–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.035
Salvay DM, Shea LD (2006) Inductive tissue engineering with protein and DNA-releasing scaffolds. Mol Biosyst 2:36–48. https://doi.org/10.1039/B514174P
Sapper M, Talens P, Chiralt A (2019) Improving functional properties of cassava starch-based films by incorporating xanthan, gellan, or pullulan gums. International Journal of Polymer Science 2019
Sarika PR, James NR, Nishna N, Kumar PA, Raj DK (2015) Galactosylated pullulan–curcumin conjugate micelles for site specific anti-cancer activity to hepatocarcinoma cells. Colloid Surface B 133:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.06.020
Schulte S, Blank LM (2018) Metabolic engineering of microbial hosts for the biosynthesis of high molecular weight hyaluronan. Fachgruppe Biologie 2018:224575. https://doi.org/10.18154/RWTH-2018-224575
Senpuku H, Yonezawa H, Yoneda S, Suzuki I, Nagasawa R, Narisawa N (2018) SMU. 940 regulates dextran-dependent aggregation and biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutants. Mol Oral Microbiol 33: 47–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/omi.12196
Song X, Shen Q, Liu M, Zhang C, Zhang L, Ren Z, Jia L (2018) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of intracellular mycelium polysaccharides from Pleurotus geesteranus against alcoholic liver diseases. Int J Biol Macromol 114: 979–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.001
Sriprablom J, Luangpituksa P, Wongkongkatep J, Pongtharangkul T, Suphantharika M (2019) Influence of pH and ionic strength on the physical and rheological properties and stability of whey protein stabilized o/w emulsions containing xanthan gum. J Food Eng 242: 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.08.031
Sun G, Mao JJ (2012) Engineering dextran-based scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue repair. Nanomedicine 7:1771–1784. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.12.149
Sun G, Shen YI, Kusuma S, Fox-Talbot K, Steenbergen CJ, Gerecht S (2011) Functional neovascularization of biodegradable dextran hydrogels with multiple angiogenic growth factors. Biomaterials 32:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.091
Sutherland IW (1972) Bacterial exopolysaccharides. Adv Microb Physiol 8:143–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2911(08)60190-3
Swierczewska M, Han HS, Kim K, Park JH, Lee S (2016) Polysaccharide-based nanoparticles for theranostic nanomedicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 99:70–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.015
Takashima Y, Fujita K, Ardin AC, Nagayama K, Nomura R, Nakano K, Matsumoto-Nakano M (2015) Characterization of the dextran-binding domain in the glucan-binding protein C of Streptococcus mutants. J Appl Microbiol 119:1148–1157. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12895
Thu HE, Zulfakar MH, Ng SF (2012) Alginate based bilayer hydrocolloid films as potential slow-release modern wound dressing. Int J Pharm 434:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.05.044
Vasconcelos AFD, Dekker RFH, Barbosa AM, Carbonero ER, Silveira JLM, Glauser B (2013) Sulfonation and anti-coagulant activity of fungal exocellular β-(1-→6)-D-glucan (lasiodiplodan). Carbohydr Polym 92:1908–1914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.10.034
Vijayendra SVN, Shamala TR (2014) Film forming microbial biopolymers for commercial applications—a review. Crit rev Biotechnol 34:338–357. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2013.798254
Wang J, Cui S, Bao Y, Xing J, Hao W (2014a) Tocopheryl pullulan-based self assembling nanomicelles for anti-cancer drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 43:614-621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.07.066
Wang K, Li W, Rui X, Chen X, Jiang M, Dong M (2014b) Characterization of a novel exopolysaccharide with antitumor activity from Lactobacillus plantarum 70810. Int J Biol Macromol 63:133-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.10.036
Wang F, Li L, Liu B, Chen Z, Li C (2017) Hyaluronic acid decorated pluronic P85 solid lipid nanoparticles as a potential carrier to overcome multidrug resistance in cervical and breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 86:595–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.041
Wang J, Salem DR, Sani RK (2018) Extremophilic exopolysaccharides: a review and new perspectives on engineering strategies and applications. Carbohydr Polym 205:8-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.011
Wei X, Senanayake TH, Warren G, Vinogradov SV (2013) Hyaluronic acid-based nanogel–drug conjugates with enhanced anti-cancer activity designed for the targeting of CD44-positive and drug-resistant tumors. Bioconjug Chem 24:658-668. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc300632w
Xue M, Wen CQ, Liu L, Fang BZ, Salam N, Huang XM, Li WJ (2018) Halomonas litopenaei sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium isolated from a shrimp hatchery. Int J Syst Evol Micro 68:3914-3921. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003090
Yang WW, Wang LM, Gong LL, Lu YM, Pan WJ, Wang Y, Chen Y (2018) Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of a novel polysaccharide fraction from the fruiting bodies of Craterellus cornucopioides. Int J Biol Macromol 117:473-482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.212
Zhang Y, Kong H, Fang Y, Nishinari K, Phillips GO (2013a) Schizophyllan: a review of its structure, properties, bioactivity and recent developments. Bioactive Carbohydr Diet Fibre 1:53–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2013.01.002
Zhang Z, Chen X, Chen L, Yu S, Cao Y, He C, Chen X (2013b) Intracellular pH-sensitive PEG-block-acetalated-dextrans as efficient drug delivery platforms. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10760–10766. https://doi.org/10.1021/am402840f
Zhang C, Li S, Zhang J, Hu C, Che G, Zhou M, Jia L (2016) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of intracellular polysaccharide from Pleurotus eryngii SI-04. Int J Biol Macromol 91:568-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.05.104
Zhao H, Li S, Zhang J, Che G, Zhou M, Liu M, Jia L (2016) The antihyperlipidemic activities of enzymatic and acidic intracellular polysaccharides by Termitomyces albuminosus. Carbohydr Polym 151:1227–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.058
Zhou JL, Song F, Tian JF, Nie WC, Wang XL, Wang YZ (2017) Electrostatic wrapping of doxorubicin with curdlan to construct an efficient pH-responsive drug delivery system. Nanotechnology 28:295601. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa75b5
Zhou D, Li P, Dong Z, Wang T, Sun K, Zhao Y, Chen Y (2019) Structure and immunoregulatory activity of β-d-galactofuranose-containing polysaccharides from the medicinal fungus Shiraia bambusicola. Int J Biol Macromol 129:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.179
Acknowledgments
This study belongs to the project related to biodegradable biopolymers production for different biomedical and industrial biotechnological applications. The financial support for this project was received from the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan (grant number: NRPU 6417) is thankfully acknowledged. Figures were created at “BioRender.com” and exported under the terms of premium subscription.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asgher, M., Qamar, S.A. & Iqbal, H.M.N. Microbial exopolysaccharide-based nano-carriers with unique multi-functionalities for biomedical sectors. Biologia 76, 673–685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00588-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00588-7