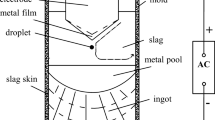
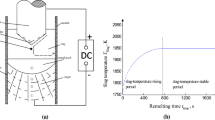
Abstract
Slag–metal reaction experiments in MoSi2 resistance furnace combined with electroslag remelting (ESR) experiments in ESR furnace are used to study the effect of slag on zirconium distribution in ESR ingot by establishing a new mass transfer model of slag–metal reaction. The mass transfer model consists of Al + Al2O3, Si + SiO2, Zr + ZrO2, and Fe + FeO systems based on the penetration and film theories. Both experimental and simulated results show that the returned slag (CaF2:CaO:Al2O3:MgO:ZrO2 = 57:20:16:3:3) combined with extra 4% Al2O3 added into molten slag in the first slag-temperature-rising period can control the zirconium in ESR ingot ranging from 0.35 to 0.40% and improve the homogeneous distribution of zirconium in ESR ingot. The returned slag of Exp.A containing low silica being used in Exp.C can not only contribute to the recycling of returned slag, but also improve the homogeneous distribution of Zr along the height of ESR ingot.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(J_{{\text{M}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Mass transfer flux of element M (mol cm−2 s−1)
- \(T_{{{\text{Slag}}}}\) :
-
The slag temperature in ESR furnace (K)
- \(D_{{\text{M}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient of M in metal (cm2 s−1)
- \(D_{{{\text{MO}}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient of MOn in slag (cm2 s−1)
- \(k_{{{\text{MO}}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Mass transfer coefficients of MOn in slag (cm2 s−1)
- \(k_{{\text{M}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Mass transfer coefficient of M in metal (cm2 s−1)
- \(k_{{\text{M}}}^{\Theta }\) :
-
Comprehensive mass transfer coefficient (cm2 s−1)
- \(\tau\) :
-
Reaction time of fluid particle (s)
- \(\rho_{{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Density of molten steel (g cm−3)
- \(\rho_{{\text{s}}}\) :
-
Density of molten slag (g cm−3)
- \(w_{{\text{[M]}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Average mass fraction of element M in metal (wt%)
- \(w_{{\text{[M]}}}^{*}\) :
-
Mass fraction of element M at interface (wt%)
- \(w_{{{\text{(MO}}_{n} )}}^{{\text{o}}}\) :
-
Initial mass fraction of MOn in slag (wt%)
- \(w_{{\text{[M]}}}^{{\text{o}}}\) :
-
Initial mass fraction of element M in metal (wt%)
- \(w_{{{\text{(MO}}_{n} )}}^{{}}\) :
-
Average mass fraction of MOn in slag (wt%)
- \(w_{{{\text{(MO}}_{n} )}}^{*}\) :
-
Mass fraction of MOn at interface (wt%)
- \(\Delta w_{{\text{[M]}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Mass fraction difference of M during reaction, (wt%)
- \(\Delta w_{{{\text{(MO}}_{{\text{n}}} )}}^{{}}\) :
-
Mass fraction difference of MOn in slag (wt%)
- \({\text{M}}_{{\text{M}}}\) :
-
Molar weight of element M (g mol−1)
- \({\text{M}}_{{{\text{MO}}_{n} }}\) :
-
Molar weight of component MOn (g mol−1)
- \(K_{{\text{M}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Thermodynamic equilibrium constant
- \(\Omega_{{\text{M}}}\) :
-
Apparent equilibrium constant
- \(L_{{\text{S}}}\) :
-
Distribution ratio of sulfur
- \(C\) :
-
Total molar number of 100 g slag (mol)
- \(a_{{\text{[M]}}}^{*}\) :
-
Activity of element M at slag–metal interface
- \(a_{{\text{[O]}}}^{*}\) :
-
Activity of [O] at slag–metal interface
- \(a_{{{\text{(MO}}_{n} )}}^{*}\) :
-
Activity of MOn at slag–metal interface
- \(e_{i}^{j}\) :
-
First interaction coefficient in metal
- \(f_{{\text{[M]}}}^{{}}\) :
-
Activity coefficient of M in metal
- \(\gamma_{{{\text{MO}}_{n} }}^{{}}\) :
-
Activity coefficient of MOn in slag
- \(X_{{{\text{MO}}_{n} }}^{{}}\) :
-
Mole fraction of MOn in slag
- \(t_{{{\text{time}}}}\) :
-
ESR remelting time (s)
- \(A\) :
-
Area of slag–metal interface (cm2)
- \(W_{{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Volume remelting velocity during ESR process (cm3 s−1)
- \(V_{{\text{S}}}\) :
-
Volume of slag in ESR furnace (cm3)
- \(V_{{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Volume of reaction molten metal (cm3)
- \(I_{{{\text{FeO}}}}\) :
-
The increment of iron oxide in ESR furnace (g s−1)
References
Jiang ZH, Hou D, Dong YW, Cao YL, Cao HB, Gong W (2016) Effect of slag on titanium, silicon and aluminum content in superalloy during electroslag remelting. Metall Mater Trans B 47:1465–1474
Baker TN (2015) Role of zirconium in microalloyed steels: a review. Mater Sci Technol 31:265–294
Hou D, Jiang ZH, Dong YW, Gong W, Cao YL, Cao HB (2017) Effect of slag composition on the oxidation kinetics of alloying elements during electroslag remelting of stainless steel: Part-1 mass-transfer model. ISIJ Int 57:1400–1409
Wei JH, Mitchell A (1984) Changes in composition during A.C. ESR Acta Metallurgica Sinica 20:261–279
Schwerdtfeger K, Wepner W, Pateisky G (1978) Modelling of chemical reactions occurring during electroslag remelting: oxidation of titanium in stainless steel. Ironmaking Steelmaking 5:143–135
Hou D, Jiang ZH, Dong YW, Li Y, Gong W, Liu FB (2017) Mass transfer model of desulfurization in the electroslag remelting Process. Metall Mater Trans B 48:1885–1897
Fraser ME, Mitchell A (1976) Mass transfer in the electroslag process: Part 1 mass-transfer model. Ironmaking Steelmaking 3:279–287
Duan SC, Shi X, Mao MT, Yang WS, Han SW, Guo HJ, Guo J (2018) Investigation of the oxidation behaviour of Ti and Al in Inconel 718 superalloy during electroslag remelting. Sci Rep 8:1–14
Wang Q, He Z, Li GQ, Li BK, Zhu CY, Chen PJ (2017) Numerical investigation of desulfurization behavior in electroslag remelting process. Int J Heat Mass Transf 104:943–951
Hou D, Jiang ZH, Dong YW, Gong W, Cao YL, Cao HB (2017) Effect of slag composition on the oxidation kinetics of alloying elements during electroslag remelting of stainless steel: Part-2 control of titanium and aluminum content. ISIJ Int 57:1410–1419
Li HB, Zhou EZ, Ren YB, Zhang DW, Xu DK, Yang CG, Feng H, Jiang ZH, Li XG, Gu TY, Yang K (2016) Investigation of microbiologically influenced corrosion of the high nitrogen nickel-free stainless steel by pseudomonas aeruginosa. Corros Sci 111:811–821
Verein Deutscher Eisenhuttenleute (1995) Slag atlas. Germany Publishers, Germany, p 234
Hou D, Jiang ZH, Dong YW, Cao YL, Cao HB, Gong W (2016) Thermodynamic design of electroslag remelting slag for high titanium and low aluminum stainless steel based on IMCT. Ironmaking Steelmaking 43:517–525
Deng ZY, Zhu MY (2013) Evolution mechanism of non-metallic inclusions in Al-killed alloyed steel during secondary refining process. ISIJ Int 53:450–458
Inoue R, Ariyama T, Suito H (2008) Thermodynamics of zirconium deoxidation equilibrium in liquid iron by EMF measurements. ISIJ Int 48:1175–1181
Okuyama G, Yamaguchi K, Takeuchi S, Sorimachi K (2000) Effect of slag composition on the kinetics of formation of Al2O3–MgO inclusions in aluminum killed ferritic stainless steel. ISIJ Int 40:121–128
Yang XM, Shi CB, Zhang M, Chai GM (2011) A thermodynamic model of sulfur distribution ratio between CaO–SiO2–MgO–FeO-MnO-Al2O3 slags and molten steel during LF refining process based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory. Metall Mater Trans B 42:1150–1180
Yang XM, Shi CB, Zhang M, Duan JP, Zhang J (2011) A thermodynamic model of phosphate capacity for CaO-SiO2-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-MnO-Al2O3-P2O5 slags equilibrated with molten steel during a top-bottom combined blown converter steelmaking process based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory. Metall Mater Trans B 42:951–2011
Yang XM, Duan JP, Shi CB, Zhang M, Zhang YL, Wang JC (2011) A thermodynamic model of phosphorus distribution ratio between CaO-SiO2-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-MnO-Al2O3-P2O5 slags and molten steel during a top-bottom combined blown converter steelmaking process based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory. Metall Mater Trans B 42:738–770
The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (1988) The 19th Committee on Steelmaking: Steelmaking Data Sourcebook. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York
Karasev A, Suito H (1999) Quantitative evaluation of inclusion in deoxidation of Fe-10 mass pct Ni alloy with Si, Ti, Al, Zr, and Ce. Metall Mater Trans B 30:249–257
Park JH, Lee SB, Kim DS, Pak JJ (2009) Thermodynamic of titanium oxide in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-CaF2 slag equilibrated with Fe-11mass%Cr melt. ISIJ Int 49:337–342
Xiang CJ (1984) Chart data manual for steelmaking. Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing
Morales RD, Rodriguez HH, Garnica GP, Romero JA (1997) Mathematical model for the reduction kinetics of iron oxide in electric furnace slags by graphite injection. ISIJ Int 37:1072–1080
Shi CB, Chen XC, Guo HJ, Zhu ZJ, Ren H (2012) Assessment of oxygen control and its effect on inclusion characteristics during electroslag remelting of die steel. Steel Res Int 83:472–486
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51804205, U1860205 and 51874203) and Open Foundation of The State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy (Grant No. G201607).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Kazuki Morita.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, D., Wang, D., Jiang, Z. et al. The Design of Slag and Electroslag Remelting Production Technology of Steel Containing Zirconium. J. Sustain. Metall. 6, 463–477 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00287-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00287-2